Korean J Orthod.
2020 Jan;50(1):33-41. 10.4041/kjod.2020.50.1.33.
Distribution and phenotypes of hemifacial microsomia and its association with other anomalies
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry and Dental Research Institute, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. drwhite@unitel.co.kr
- 2Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Myongji Hospital, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Private Practice, Pohang, Korea.
- 5Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea.
- 6Private Practice, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 9Private Practice, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2468639
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2020.50.1.33
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the distribution and phenotypes of hemifacial microsomia (HFM) and its association with other anomalies.
METHODS
This study included 249 Korean patients with HFM, whose charts, photographs, radiographs, and/or computed tomography scans acquired during 1998-2018 were available from Seoul National University Hospital and Dental Hospital. Prevalence according to sex, side involvement, degree of mandibular deformity, compensatory growth of the mandibular body, and Angle's classification, and its association with other anomalies were statistically analyzed.
RESULTS
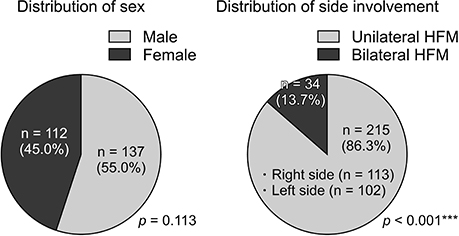
Prevalence was not different between male and female patients (55.0% vs. 45.0%, p > 0.05). Unilateral HFM (UHFM) was more prevalent than bilateral HFM (BHFM) (86.3% vs. 13.7%, p < 0.001). Although distribution of the Pruzansky-Kaban types differed significantly in patients with UHFM (I, 53.0%; IIa, 18.6%; IIb, 24.7%; III, 3.7%; p < 0.001), no difference was observed in occurrence between the right and left sides (52.6% vs. 47.4%, p > 0.05). Among patients with BHFM, prevalence of different Pruzansky-Kaban types on the right and left sides was greater than that of the same type on both sides (67.6% vs. 32.4%, p < 0.05). Despite hypoplasia of the condyle/ramus complex, compensatory growth of the mandibular body on the ipsilateral side occurred in 35 patients (14.1%). Class I and II molar relationships were more prevalent than Class III molar relationships (93.2% vs. 6.8%, p < 0.001). Forty-eight patients (19.3%) had other anomalies, with 50.0% and 14.4% in the BHFM and UHFM groups (p < 0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
Patients with HFM require individualized diagnosis and treatment planning because of diverse phenotypes and associations with other anomalies.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Treatment modalities for Korean patients with unilateral hemifacial microsomia according to Pruzansky–Kaban types and growth stages
Il-Hyung Yang, Jee Hyeok Chung, Sunjin Yim, Il-Sik Cho, Sukwha Kim, Jin-Young Choi, Jong-Ho Lee, Myung-Jin Kim, Seung-Hak Baek
Korean J Orthod. 2020;50(5):336-345. doi: 10.4041/kjod.2020.50.5.336.
Reference
-
1. Grabb WC. The first and second branchial arch syndrome. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1965; 36:485–508.
Article2. Longacre JJ. The surgical management of the first and second branchial arch syndrome. Br J Plast Surg. 1965; 18:243–253.
Article3. Converse JM, Coccaro PJ, Becker M, Wood-Smith D. On hemifacial microsomia. The first and second branchial arch syndrome. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1973; 51:268–279.4. Figueroa AA, Pruzansky S. The external ear, mandible and other components of hemifacial microsomia. J Maxillofac Surg. 1982; 10:200–211.
Article5. Cousley RR, Calvert ML. Current concepts in the understanding and management of hemifacial microsomia. Br J Plast Surg. 1997; 50:536–551.
Article6. Gougoutas AJ, Singh DJ, Low DW, Bartlett SP. Hemifacial microsomia: clinical features and pictographic representations of the OMENS classification system. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007; 120:112e–120e.
Article7. Poswillo D. Hemorrhage in development of the face. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975; 11:61–81.8. Rollnick BR, Kaye CI. Hemifacial microsomia and variants: pedigree data. Am J Med Genet. 1983; 15:233–253.
Article9. Hartsfield JK. Review of the etiologic heterogeneity of the oculo-auriculo-vertebral spectrum (Hemifacial Microsomia). Orthod Craniofac Res. 2007; 10:121–128.
Article10. Kaban LB, Moses MH, Mulliken JB. Correction of hemifacial microsomia in the growing child: a follow-up study. Cleft Palate J. 1986; 23 Suppl 1:50–52.11. Kaban LB, Moses MH, Mulliken JB. Surgical correction of hemifacial microsomia in the growing child. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1988; 82:9–19.
Article12. Choi JY, Hwang KG, Baek SH, Lee JH, Kim TW, Kim MJ, et al. Original sagittal split osteotomy revisited for mandibular distraction. J Maxillofac Surg. 2001; 29:165–173.
Article13. Kim S, Seo YJ, Choi TH, Baek SH. New approach for the surgico-orthodontic treatment of hemifacial microsomia. J Craniofac Surg. 2012; 23:957–963.
Article14. Suh J, Choi TH, Baek SH, Kim JC, Kim S. Mandibular distraction in unilateral craniofacial microsomia: longitudinal results until the completion of growth. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013; 132:1244–1252.15. Vento AR, LaBrie RA, Mulliken JB. The O.M.E.N.S. classification of hemifacial microsomia. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 1991; 28:68–76. discussion 77.
Article16. Horgan JE, Padwa BL, LaBrie RA, Mulliken JB. OMENS-Plus: analysis of craniofacial and extracraniofacial anomalies in hemifacial microsomia. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 1995; 32:405–412.
Article17. Tuin AJ, Tahiri Y, Paine KM, Paliga JT, Taylor JA, Bartlett SP. Clarifying the relationships among the different features of the OMENS+ classification in craniofacial microsomia. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015; 135:149e–156e.
Article18. Keogh IJ, Troulis MJ, Monroy AA, Eavey RD, Kaban LB. Isolated microtia as a marker for unsuspected hemifacial microsomia. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007; 133:997–1001.
Article19. Poon CC, Meara JG, Heggie AA. Hemifacial microsomia: use of the OMENS-Plus classification at the Royal Children's Hospital of Melbourne. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003; 111:1011–1018.
Article20. Pruzansky S. Not all dwarfed mandibles are alike. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1969; 5:120–129.21. Kaban LB, Padwa B, Mulliken JB. Mandibular deformity in hemifacial microsomia: a reassessment of the Pruzansky and Kaban classification. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014; 134:657e–658e.22. Mulliken JB, Kaban LB. Analysis and treatment of hemifacial microsomia in childhood. Clin Plast Surg. 1987; 14:91–100.
Article23. Baek SH, Kim S. The determinants of successful distraction osteogenesis of the mandible in hemifacial microsomia from longitudinal results. J Craniofac Surg. 2005; 16:549–558.
Article24. Park JU, Do TH, Kwon GY, Choi TH, Kim S. Statistical analysis using the OMENS classification in Oriental patients with hemifacial microsomia: a comparative analysis with Western centers. Ann Plast Surg. 2014; 72:50–55.
Article25. Xu S, Zhang Z, Tang X, Yin L, Liu W, Shi L. The influence of gender and laterality on the incidence of hemifacial microsomia. J Craniofac Surg. 2015; 26:384–387.
Article26. Heike CL, Wallace E, Speltz ML, Siebold B, Werler MM, Hing AV, et al. Characterizing facial features in individuals with craniofacial microsomia: a systematic approach for clinical research. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2016; 106:915–926.
Article27. Caron CJJM, Pluijmers BI, Wolvius EB, Looman CWN, Bulstrode N, Evans RD, et al. Craniofacial and extracraniofacial anomalies in craniofacial microsomia: a multicenter study of 755 patients. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2017; 45:1302–1310.
Article28. Fan WS, Mulliken JB, Padwa BL. An association between hemifacial microsomia and facial clefting. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005; 63:330–334.
Article29. Takahashi-Ichikawa N, Susami T, Nagahama K, Ohkubo K, Okayasu M, Uchino N, et al. Evaluation of mandibular hypoplasia in patients with hemifacial microsomia: a comparison between panoramic radiography and three-dimensional computed tomography. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2013; 50:381–387.
Article30. Tuin J, Tahiri Y, Paliga JT, Taylor JA, Bartlett SP. Distinguishing Goldenhar syndrome from craniofacial macrosomia. J Craniofac Surg. 2015; 26:1887–1892.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Distraction osteogenesis in patients with hemifacial microsomia
- Correction of Facial Asymmetry Using Costochondral Graft and Orthognathic Surgery in Hemifacial Microsomia Patient: Case Report
- A case report of hemifacial microsomia
- Three-dimensional functional unit analysis of hemifacial microsomia mandible-a preliminary report
- Clinical study of Simultaneous Correction of Bone and Soft Tissue Deformities in Hemifacial Microsmia