Yonsei Med J.
2020 Feb;61(2):198-200. 10.3349/ymj.2020.61.2.198.
Arthrodesis Using Bilateral Dual Iliac Screws with Autologous Iliac Bone Transfer for the Treatment of Pyogenic Sacroiliitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. BHLEE96@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2468496
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2020.61.2.198
Abstract
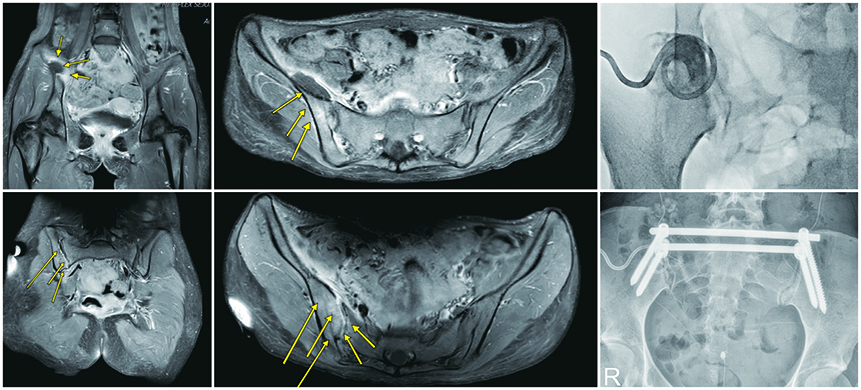
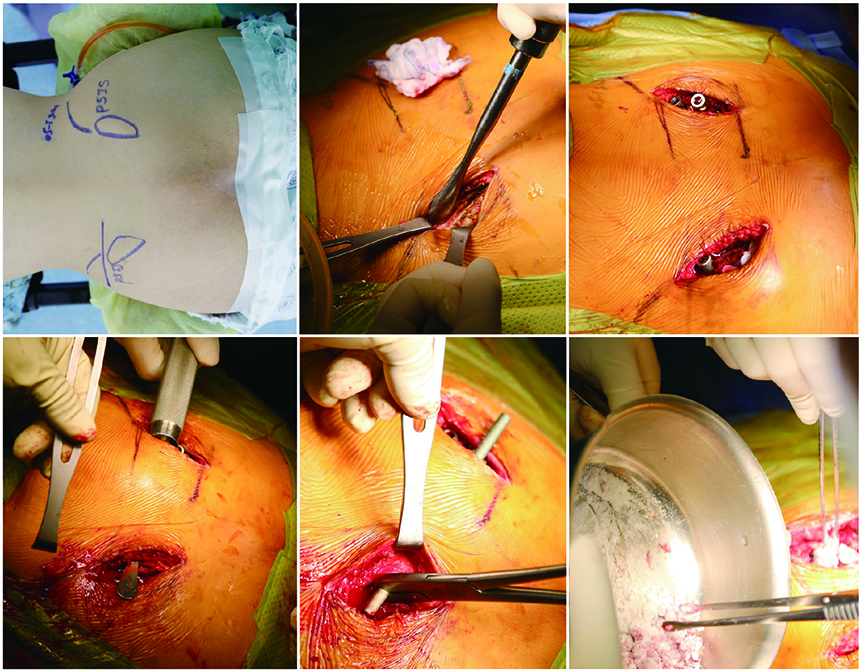
- Pyogenic sacroiliitis is a relatively rare condition that often leads to surgical treatment, including debridement and arthrodesis. Here we introduce a new surgical technique using bilateral dual iliac screws to secure early ambulation and maximal fusion success rate for the treatment of pyogenic sacroiliitis. We retrospectively reported a case and technical reports of pyogenic sacroiliitis treated by a new bilateral dual iliac screw fixation arthrodesis technique using radiologic outcomes, including plain X-rays and MRI scans, as well as outcomes based on the visual analogue scale for pain measurement. This technique improved uncontrolled pyogenic sacroiliitis with immediate stability that enabled ambulation and secured firm fixation for extensive evacuation of infected debris and subsequent autograft bone arthrodesis. In conclusion, we recommend bilateral dual iliac screw fixation for the treatment of pyogenic sacroiliitis, as this technique can improve uncontrolled pyogenic sacroiliitis with immediate stability.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mancarella L, De Santis M, Magarelli N, Ierardi AM, Bonomo L, Ferraccioli G. Septic sacroiliitis: an uncommon septic arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2009; 27:1004–1008.2. Hermet M, Minichiello E, Flipo RM, Dubost JJ, Allanore Y, Ziza JM, et al. Infectious sacroiliitis: a retrospective, multicentre study of 39 adults. BMC Infect Dis. 2012; 12:305.
Article3. Wu MS, Chang SS, Lee SH, Lee CC. Pyogenic sacroiliitis–a comparison between paediatric and adult patients. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007; 46:1684–1687.
Article4. Vleeming A, Schuenke MD, Masi AT, Carreiro JE, Danneels L, Willard FH. The sacroiliac joint: an overview of its anatomy, function and potential clinical implications. J Anat. 2012; 221:537–567.
Article5. Dmitriev AE, Shepilov GF, Kriukov BN, Trushin IuA. [Osteomyelitis of the sacrum]. Khirurgiia (Mosk). 1989; (8):3–7.6. Giannoudis PV, Tsiridis E. A minimally-invasive technique for the treatment of pyogenic sacroiliitis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007; 89:112–114.
Article7. Chan DS, Saklani A, Shah PR, Haray PN. Laparoscopic drainage of retroperitoneal abscess secondary to pyogenic sacroiliitis. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2010; 92:W32–W34.
Article8. Kanakaris NK, Psarakis S, Chalidis B, Kontakis G, Giannoudis PV. Management of pelvic instability secondary to chronic pyogenic sacroiliitis: case report. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2009; 10:353–358.
Article9. Bindal M, Krabak B. Acute bacterial sacroiliitis in an adult: a case report and review of the literature. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007; 88:1357–1359.
Article10. Doita M, Yoshiya S, Nabeshima Y, Tanase Y, Nishida K, Miyamoto H, et al. Acute pyogenic sacroiliitis without predisposing conditions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28:E384–E389.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cannulated Screw Fixation for Ankle and Hindfoot Arthrodesis
- One Level Lumbar Posterolateral Fusion with Autologous Local Bone Chips
- The Reharvesting of Iliac Crest Cancellous Bone for the Repair of the Alveolar Cleft
- Lumbo-sacro-pelvic Fixation Using Iliac Screws for the Complex Lumbo-sacral Fractures
- Endovascular repair of bilateral iliac artery aneurysm with branched iliac stents: case report and review of the current literature