Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2013 Sep;6(3):191-193.
Congenital Epidermoid Cyst of the Oral Cavity: Prenatal Diagnosis by Sonography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. imljj@naver.com
- 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
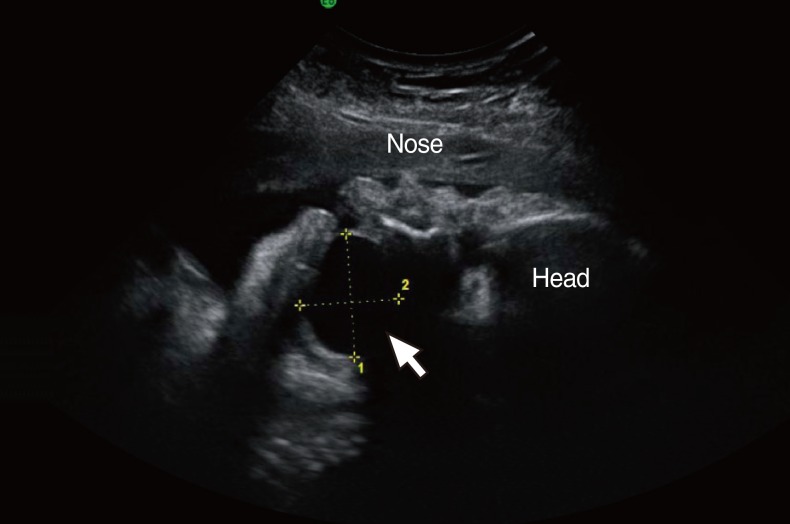
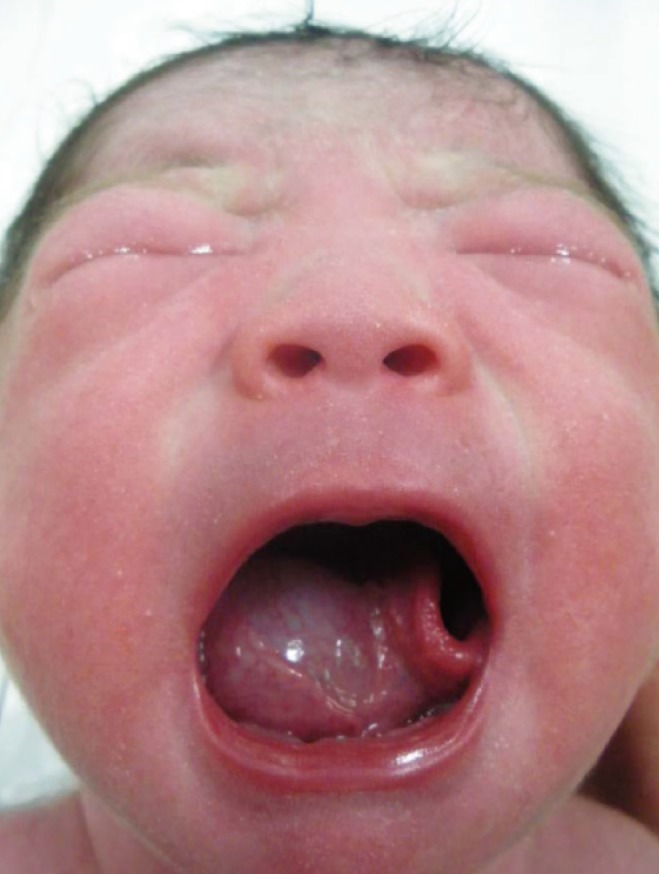
- Epidermoid cysts are benign developmental anomalies that are rarely observed in the oral cavity of neonate. If large in size, especially in the developing fetus or newborn infant, they can cause swallowing difficulty and occasionally respiratory difficulty. We report a case of epidermoid cyst in the oral cavity detected prenatal sonography. The sonographic finding was large cystic mass, measuring 30x25 mm. In this case, supplies and equipment for an emergency tracheostomy were made available prior to the delivery. However, the infant did not require intervention to secure the airway. The lesion was surgically excised, and histologic diagnosis was epidermoid cyst. After 6 months of follow up, the cyst had not recurred. This case illustrates the value of accurate prenatal diagnosis and planned perinatal management using a team approach.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mohta A, Sharma M. Congenital oral cysts in neonates: report of two cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006; 11. 102(5):e36–e38. PMID: 17052622.
Article2. Jham BC, Duraes GV, Jham AC, Santos CR. Epidermoid cyst of the floor of the mouth: a case report. J Can Dent Assoc. 2007; Jul-Aug. 73(6):525–528. PMID: 17672959.3. Ho MW, Crean SJ. Simultaneous occurrence of sublingual dermoid cyst and oral alimentary tract cyst in an infant: a case report and review of the literature. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2003; 11. 13(6):441–446. PMID: 14984051.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prenatal Diagnosis of Choledochal Cyst at 23 weeks by Sonography
- A Case of Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Neuroblastoma by Sonography
- A Case of Endoscopic Approach of Epidermoid Cyst Arising in the Inner Surface of Nasal Bone
- A Case of Epidermoid Cyst in the Fourth Ventricle
- Paraplegia due to Spinal Epidermoid Cyst Rupture at Asthma Attack