Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2013 Sep;6(3):135-139.
Agreement between the Facial Nerve Grading System 2.0 and the House-Brackmann Grading System in Patients with Bell Palsy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yeo2park@yahoo.co.kr
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
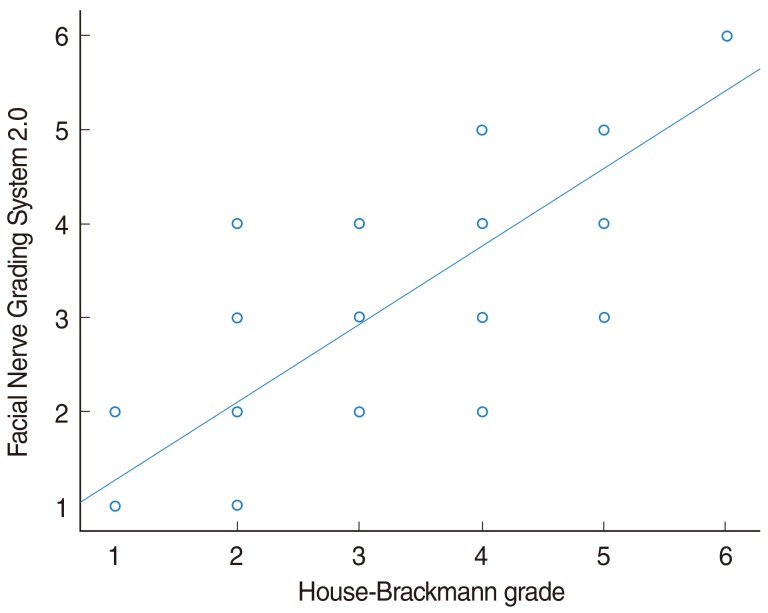
We have analyzed the correlation between the House-Brackmann (HB) scale and Facial Nerve Grading System 2.0 (FNGS 2.0) in patients with Bell palsy, and evaluated the usefulness of the new grading system.
METHODS
Sixty patients diagnosed with Bell palsy from May 2009 to December 2010 were evaluated using the HB scale and FNGS 2.0 scale during their initial visit, and after 3 and 6 weeks and 3 months.
RESULTS
The overall intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was 0.908 (P=0.000) and the Spearman correlation coefficient (SCC) was 0.912 (P<0.05). ICC and SCC displayed differences over time, being 0.604 and 0.626, respectively, at first visit; 0.834 and 0.843, respectively, after 3 weeks; 0.844 and 0.848, respectively, after 6 weeks; and 0.808 and 0.793, respectively, after 3 months. There was a significant difference in full recovery, depending on the scale used (HB, P=0.000; FNGS 2.0, P<0.05). The exact agreements between regional assessment and FNGS 2.0 for the mouth, eyes, and brow were 72%, 63%, and 52%, respectively.
CONCLUSION
FNGS 2.0 shows moderate agreement with HB grading. Regional assessment, rather than HB grading, yields stricter evaluation, resulting in better prognosis and determination of grade.
Figure
Reference
-
1. House JW, Brackmann DE. Facial nerve grading system. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1985; 4. 93(2):146–147. PMID: 3921901.
Article2. Ross BG, Fradet G, Nedzelski JM. Development of a sensitive clinical facial grading system. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1996; 3. 114(3):380–386. PMID: 8649870.
Article3. Yanagihara N. Grading of facial palsy. In : Fisch U, editor. Facial nerve surgery. Birmingham, AL: Aesculapius Publishing Co.;1977. p. 533–535.4. Vrabec JT, Backous DD, Djalilian HR, Gidley PW, Leonetti JP, Marzo SJ, et al. Facial Nerve Grading System 2.0. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009; 4. 140(4):445–450. PMID: 19328328.
Article5. Yen TL, Driscoll CL, Lalwani AK. Significance of House-Brackmann facial nerve grading global score in the setting of differential facial nerve function. Otol Neurotol. 2003; 1. 24(1):118–122. PMID: 12544040.
Article6. Berg T, Jonsson L, Engström M. Agreement between the Sunnybrook, House-Brackmann, and Yanagihara facial nerve grading systems in Bell's palsy. Otol Neurotol. 2004; 11. 25(6):1020–1026. PMID: 15547437.
Article7. Croxson G, May M, Mester SJ. Grading facial nerve function: House-Brackmann versus Burres-Fisch methods. Am J Otol. 1990; 7. 11(4):240–246. PMID: 2399941.8. Satoh Y, Kanzaki J, Yoshihara S. A comparison and conversion table of 'the House-Brackmann facial nerve grading system' and 'the Yanagihara grading system'. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2000; 7. 27(3):207–212. PMID: 10808106.
Article9. Hu WL, Ross B, Nedzelski J. Reliability of the Sunnybrook Facial Grading System by novice users. J Otolaryngol. 2001; 8. 30(4):208–211. PMID: 11771031.
Article10. Linder TE, Abdelkafy W, Cavero-Vanek S. The management of peripheral facial nerve palsy: "paresis" versus "paralysis" and sources of ambiguity in study designs. Otol Neurotol. 2010; 2. 31(2):319–327. PMID: 20009779.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Application of FEMA Grading System
- Evaluation of Trigeminal Nerve Involvement Using Blink Reflex Test in Bell's Palsy
- Clinical Analysis of Recurrent Bell's Palsy in One University Hospital
- Acute Peripheral Facial Palsy: Recent Guidelines and a Systematic Review of the Literature
- Prognostic Value of Electroneurography in Bell's Palsy and Ramsay-Hunt's Syndrome