Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2020 Jan;23(1):105-109. 10.5223/pghn.2020.23.1.105.
Endoscopic Management of Large Peripancreatic Fluid Collections in Two Pediatric Patients by Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided Transmural Drainage
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, PA, USA. lwalsh1@pennstatehealth.psu.edu
- 2Penn State Hershey College of Medicine, Hershey, PA, USA.
- 3Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Penn State Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, Hershey, PA, USA.
- KMID: 2467899
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2020.23.1.105
Abstract
- The incidence of acute pancreatitis (AP) has increased in the pediatric population over the past few decades and it stands to follow that the complications of severe AP, including symptomatic pancreatic fluid collections (PFCs) will increase as well. In adults, the therapeutic options for this situation have undergone a dramatic evolution from mainly surgical approaches to less invasive endoscopic approaches, mainly endoscopic ultrasound-guided transmural drainage (EUS-TD) followed be direct endoscopic necrosectomy if needed. This has proven safe and effective in adults; however, this approach has not been well studied or reported in pediatric populations. Here we demonstrate that EUS-TD seems to offer a safe, efficacious and minimally invasive approach to the management of large PFCs in pediatric patients by reviewing two representative cases at our institution.
MeSH Terms
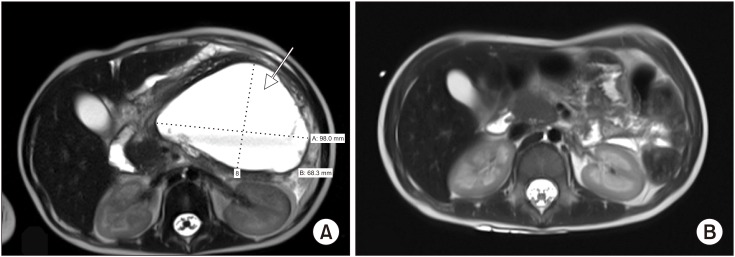
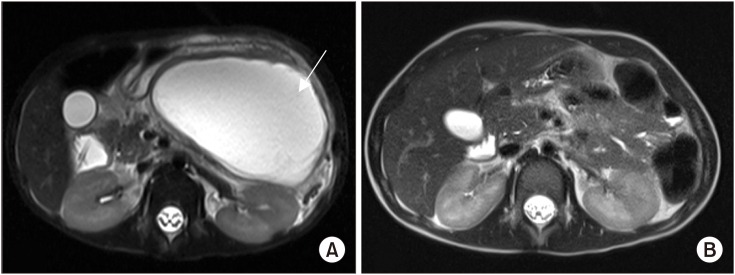
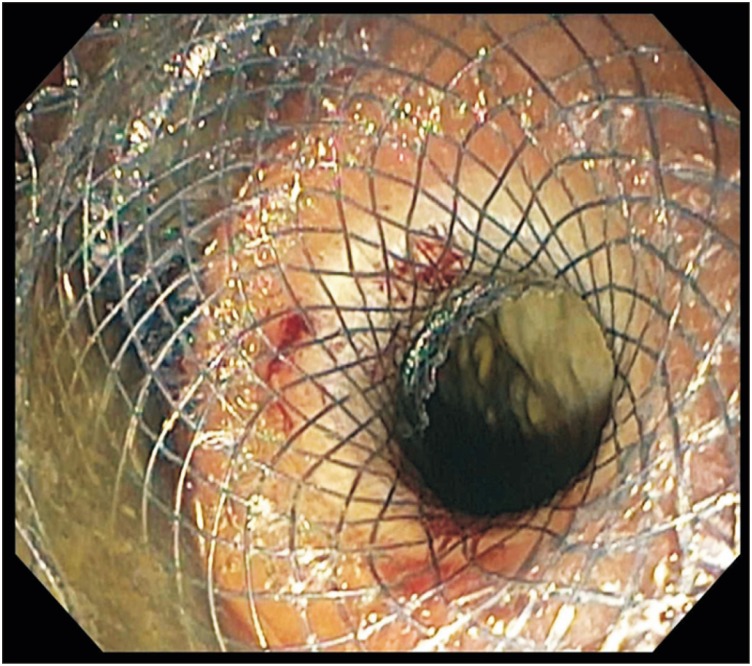
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nydegger A, Heine RG, Ranuh R, Gegati-Levy R, Crameri J, Oliver MR. Changing incidence of acute pancreatitis: 10-year experience at the Royal Children's Hospital, Melbourne. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007; 22:1313–1316. PMID: 17489962.
Article2. Pant C, Deshpande A, Olyaee M, Anderson MP, Bitar A, Steele MI, et al. Epidemiology of acute pancreatitis in hospitalized children in the United States from 2000-2009. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e95552. PMID: 24805879.
Article3. Tyberg A, Karia K, Gabr M, Desai A, Doshi R, Gaidhane M, et al. Management of pancreatic fluid collections: a comprehensive review of the literature. World J Gastroenterol. 2016; 22:2256–2270. PMID: 26900288.
Article4. Bolia R, Srivastava A, Yachha SK, Poddar U, Kumar S. Prevalence, natural history, and outcome of acute fluid collection and pseudocyst in children with acute pancreatitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2015; 61:451–455. PMID: 26029866.
Article5. Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen HG, Johnson CD, Sarr MG, et al. Acute Pancreatitis Classification Working Group. Classification of acute pancreatitis--2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut. 2013; 62:102–111. PMID: 23100216.
Article6. Varadarajulu S, Bang JY, Sutton BS, Trevino JM, Christein JD, Wilcox CM. Equal efficacy of endoscopic and surgical cystogastrostomy for pancreatic pseudocyst drainage in a randomized trial. Gastroenterology. 2013; 145:583–90.e1. PMID: 23732774.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided Drainage in Pancreatobiliary Diseases
- Metal versus Plastic Stent for Transmural Drainage of Pancreatic Fluid Collections
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Drainage of Pancreatic Fluid Collections (with Video)
- Role of EUS in Drainage of Peripancreatic Fluid Collections Not Amenable for Endoscopic Transmural Drainage
- Endoscopic Management of Peri-Pancreatic Fluid Collections