J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2019 Dec;45(6):364-368. 10.5125/jkaoms.2019.45.6.364.
An idiopathic delayed maxillary hemorrhage after orthognathic surgery with Le Fort I osteotomy: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bukyu.lee@gmail.com
- KMID: 2467189
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2019.45.6.364
Abstract
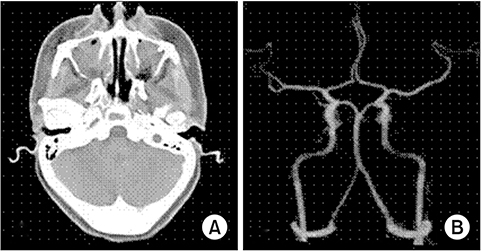
- A Le Fort I osteotomy is a common procedure for correcting dental and facial deformities in orthognathic surgery. In rare cases, a delayed hemorrhage can occur as early as several hours or up to 12 weeks, postoperatively. The most frequently involved blood vessels in a delayed hemorrhage are the descending palatine artery, the internal maxillary artery, and the pterygoid venous plexus of veins. Intraoral bleeding accompanied by severe epistaxis in these cases makes it difficult to locate the precise bleeding focus. Eventual uncontrolled bleeding would require Merocel packing or surgical intervention. In general, a severe late postoperative hemorrhage is most effectively managed by angiography and embolization. Herein we describe a delayed hemorrhage case in which the cause was not evident on angiography. We were able to detect the bleeding point through an endoscopic nasal approach and treat it using direct cauterization.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Epistaxis in dental and maxillofacial practice: a comprehensive review
George Psillas, Grigorios Georgios Dimas, Despoina Papaioannou, Christos Savopoulos, Jiannis Constantinidis
J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2022;48(1):13-20. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2022.48.1.13.
Reference
-
1. Lee WY, Park YW, Kwon KJ, Kim SG. Change of the airway space in mandibular prognathism after bimaxillary surgery involving maxillary posterior impaction. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016; 38:23.
Article2. Jung HD, Kim SY, Park HS, Jung YS. Orthognathic surgery and temporomandibular joint symptoms. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015; 37:14.
Article3. Avelar RL, Goelzer JG, Becker OE, de Oliveira RB, Raupp EF, de Magalhães PS. Embolization of pseudoaneurysm of the internal maxillary artery after orthognathic surgery. J Craniofac Surg. 2010; 21:1764–1768.
Article4. Shin YM, Lee ST, Kwon TG. Surgical correction of septal deviation after Le Fort I osteotomy. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016; 38:21.
Article5. Panula K, Finne K, Oikarinen K. Incidence of complications and problems related to orthognathic surgery: a review of 655 patients. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2001; 59:1128–1136. discussion 1137.
Article6. Garg S, Kaur S. Evaluation of post-operative complication rate of Le Fort I osteotomy: a retrospective and prospective study. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2014; 13:120–127.
Article7. Bykowski MR, Hill A, Garland C, Tobler W, Losee JE, Goldstein JA. Ruptured pseudoaneurysm of the maxillary artery and its branches following Le Fort I osteotomy: evidence-based guidelines. J Craniofac Surg. 2018; 29:998–1001.
Article8. Politis C. Life-threatening haemorrhage after 750 Le Fort I osteotomies and 376 SARPE procedures. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012; 41:702–708.
Article9. Procopio O, Fusetti S, Liessi G, Ferronato G. False aneurysm of the sphenopalatine artery after a Le Fort I osteotomy: report of 2 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003; 61:520–524. discussion 524–5.
Article10. Zachariades N, Rallis G, Papademetriou G, Papakosta V, Spanomichos G, Souelem M. Embolization for the treatment of pseudoaneurysm and transection of facial vessels. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2001; 92:491–494.
Article11. Krempl GA, Noorily AD. Pseudoaneurysm of the descending palatine artery presenting as epistaxis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1996; 114:453–456.
Article12. Silva AC, O'Ryan F, Beckley ML, Young HY, Poor D. Pseudoaneurysm of a branch of the maxillary artery following mandibular sagittal split ramus osteotomy: case report and review of the literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007; 65:1807–1816.
Article13. Fernández-Prieto A, García-Raya P, Burgueño M, Muñoz-Caro J, Frutos R. Endovascular treatment of a pseudoaneurysm of the descending palatine artery after orthognathic surgery: technical note. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005; 34:321–323.
Article14. Viehweg TL, Roberson JB, Hudson JW. Epistaxis: diagnosis and treatment. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006; 64:511–518.
Article15. Ellinas A, Jervis P, Kenyon G, Flood LM. Endoscopic sphenopalatine artery ligation for acute idiopathic epistaxis. Do anatomical variation and a limited evidence base raise questions regarding its place in management? J Laryngol Otol. 2017; 131:290–297.
Article16. McClurg SW, Carrau R. Endoscopic management of posterior epistaxis: a review. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2014; 34:1–8.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case report of surgical correction of mandibular prognathism with midfacial deficiency using Le Fort III osteotomy
- Salvage rapid maxillary expansion for the relapse of maxillary transverse expansion after Le Fort I with parasagittal osteotomy
- Le Fort I osteotomy as treatment for traumatic class III malocclusion caused by Le Fort III fracture: A case report
- Post-Operative Maxillary Cyst after Maxillary Orthognathic Surgery: Report of an Unusual Case
- Repetitive Postoperative Infection after Le Fort I Osteotomy in a Patient with a History of Non-allergic Rhinitis