Intest Res.
2019 Oct;17(4):554-560. 10.5217/ir.2018.00148.
Primary epiploic appendagitis: compared with diverticulitis and focused on obesity and recurrence
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea. drgreen@gilhospital.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2465821
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2018.00148
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
There is limited data to compare the clinical characteristics and recurrence rates between left-sided primary epiploic appendagitis (PEA) versus left-sided acute colonic diverticulitis (ACD), and right-sided PEA versus right-sided ACD, respectively.
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records and radiologic images of the patients who presented with left-sided or right-sided acute abdominal pain and had computer tomography performed at the time of presentation showing radiological signs of PEA or ACD between January 2004 and December 2014. We compared the clinical characteristics of left PEA versus left ACD and right PEA versus right ACD, respectively.
RESULTS
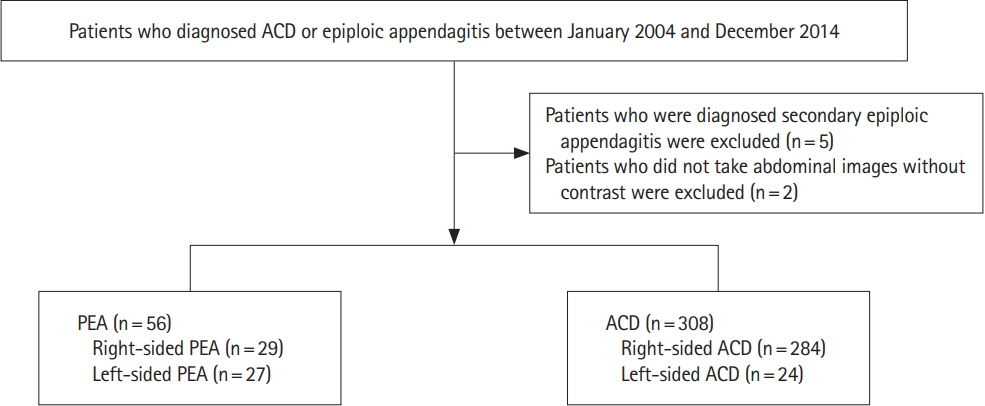
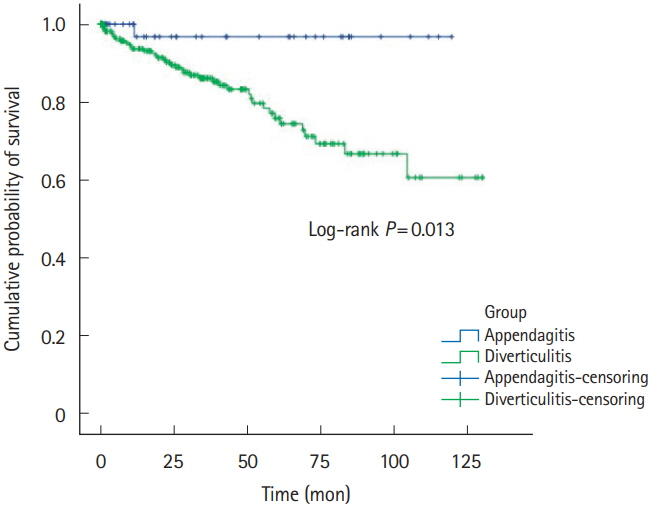
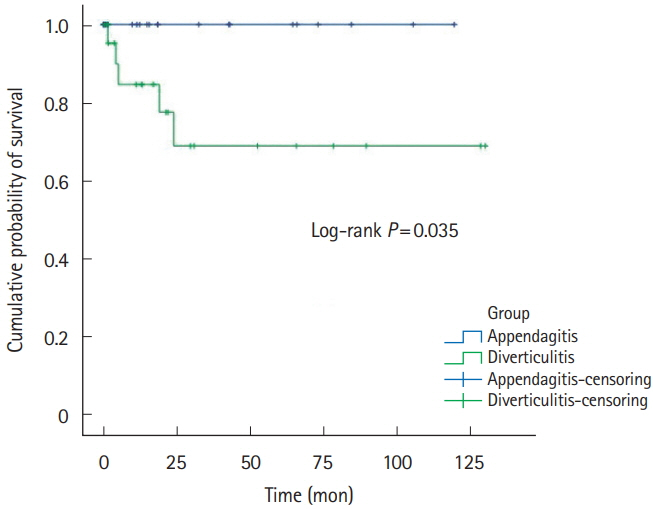
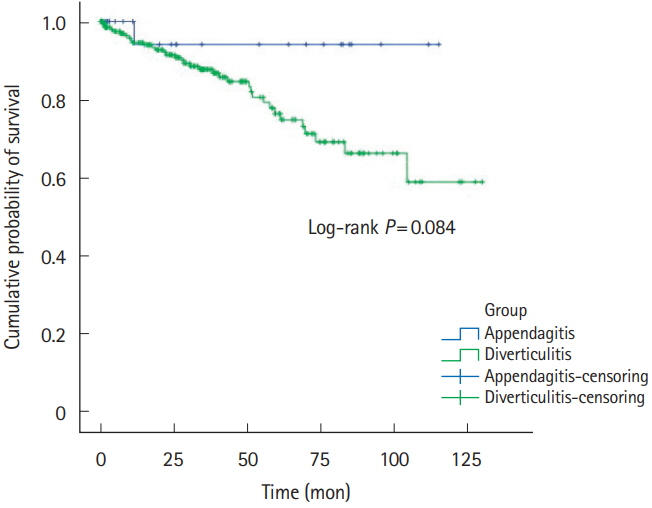
Fifty-six patients (left:right = 27:29) and 308 patients (left:right = 24:284) were diagnosed with symptomatic PEA and ACD, respectively. Left-sided PEA were statistically significantly younger (50.2 ± 15.4 years vs. 62.1 ± 15.8 years, P= 0.009), more obese (body mass index [BMI]: 26.3 ± 2.9 kg/m² vs. 22.3 ± 3.1 kg/m² , P< 0.001), and had more tendencies with normal or mildly elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) (1.2 ± 1.3 mg/dL vs. 8.4 ± 7.9 mg/dL, P< 0.001) than patients with left-sided ACD. The discriminative function of age, BMI and CRP between left-sided PEA versus left-sided ACD was 0.71 (cutoff: age ≤ 59 years, sensitivity of 66.7%, specificity of 77.8%), 0.84 (cutoff: BMI > 24.5 kg/m² , sensitivity of 80.0%, specificity of 80.0%) and 0.80 (cutoff: CRP < 1.8 mg/dL, sensitivity of 72.2%, specificity of 85.7%).
CONCLUSIONS
If patients with left lower quadrant abdominal pain are less than 60 years, obese (BMI > 24.5 kg/m² ) with or without normal to mild elevated CRP levels (CRP < 1.8 mg/dL), it might be necessary for clinicians to suspect the diagnosis of PEA rather than ACD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Boardman J, Kaplan KJ, Hollcraft C, Bui-Mansfield LT. Radiologic-pathologic conference of Keller Army Community Hospital at West Point, the United States Military Academy: torsion of the epiploic appendage. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003; 180:748.2. Ghahremani GG, White EM, Hoff FL, Gore RM, Miller JW, Christ ML. Appendices epiploicae of the colon: radiologic and pathologic features. Radiographics. 1992; 12:59–77.3. Sand M, Gelos M, Bechara FG, et al. Epiploic appendagitis: clinical characteristics of an uncommon surgical diagnosis. BMC Surg. 2007; 7:11.4. Subramaniam R. Acute appendagitis: emergency presentation and computed tomographic appearances. Emerg Med J. 2006; 23:e53.5. Ross JA. Vascular loops in the appendices epiploicae; their anatomy and surgical significance, with a review of the surgical pathology of appendices epiploicae. Br J Surg. 1950; 37:464–466.6. Ng KS, Tan AG, Chen KK, Wong SK, Tan HM. CT features of primary epiploic appendagitis. Eur J Radiol. 2006; 59:284–288.
Article7. Son HJ, Lee SJ, Lee JH, et al. Clinical diagnosis of primary epiploic appendagitis: differentiation from acute diverticulitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2002; 34:435–438.8. Legome EL, Sims C, Rao PM. Epiploic appendagitis: adding to the differential of acute abdominal pain. J Emerg Med. 1999; 17:823–826.9. Vinson DR. Epiploic appendagitis: a new diagnosis for the emergency physician. Two case reports and a review. J Emerg Med. 1999; 17:827–832.10. Carmichael DH, Organ CH Jr. Epiploic disorders: conditions of the epiploic appendages. Arch Surg. 1985; 120:1167–1172.11. Dockerty MB, Lynn TE, Waugh JM. A clinicopathologic study of the epiploic appendages. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1956; 103:423–433.12. Legome EL, Belton AL, Murray RE, Rao PM, Novelline RA. Epiploic appendagitis: the emergency department presentation. J Emerg Med. 2002; 22:9–13.13. Rioux M, Langis P. Primary epiploic appendagitis: clinical, US, and CT findings in 14 cases. Radiology. 1994; 191:523–526.14. Rao PM, Rhea JT, Wittenberg J, Warshaw AL. Misdiagnosis of primary epiploic appendagitis. Am J Surg. 1998; 176:81–85.15. Rao PM, Wittenberg J, Lawrason JN. Primary epiploic appendagitis: evolutionary changes in CT appearance. Radiology. 1997; 204:713–717.
Article16. Hasbahceci M, Erol C, Seker M. Epiploic appendagitis: is there need for surgery to confirm diagnosis in spite of clinical and radiological findings? World J Surg. 2012; 36:441–446.
Article17. Choi YU, Choi PW, Park YH, et al. Clinical characteristics of primary epiploic appendagitis. J Korean Soc Coloproctol. 2011; 27:114–121.18. Chen JH, Wu CC, Wu PH. Epiploic appendagitis: an uncommon and easily misdiagnosed disease. J Dig Dis. 2011; 12:448–452.19. Horton KM, Corl FM, Fishman EK. CT evaluation of the colon: inflammatory disease. Radiographics. 2000; 20:399–418.
Article20. Pereira JM, Sirlin CB, Pinto PS, Jeffrey RB, Stella DL, Casola G. Disproportionate fat stranding: a helpful CT sign in patients with acute abdominal pain. Radiographics. 2004; 24:703–715.21. Kim JA, Choi CJ, Yum KS. Cut-off values of visceral fat area and waist circumference: diagnostic criteria for abdominal obesity in a Korean population. J Korean Med Sci. 2006; 21:1048–1053.22. Examination Committee of Criteria for ‘Obesity Disease’ in Japan. Japan Society for the Study of Obesity: new criteria for ‘obesity disease’ in Japan. Circ J. 2002; 66:987–992.23. Oka R, Kobayashi J, Yagi K, et al. Reassessment of the cutoff values of waist circumference and visceral fat area for identifying Japanese subjects at risk for the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008; 79:474–481.24. Hwang JA, Kim SM, Song HJ, et al. Differential diagnosis of left-sided abdominal pain: primary epiploic appendagitis vs colonic diverticulitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:6842–6848.25. Ozkurt H, Karatag O, Karaarslan E, Rozanes I, Basak M, Bavbek C. CT findings in epiploic appendagitis. Surgery. 2007; 141:530–532.26. Ozdemir S, Gulpinar K, Leventoglu S, et al. Torsion of the primary epiploic appendagitis: a case series and review of the literature. Am J Surg. 2010; 199:453–458.
Article27. Patel VG, Rao A, Williams R, Srinivasan R, Fortson JK, Weaver WL. Cecal epiploic appendagitis: a diagnostic and therapeutic dilemma. Am Surg. 2007; 73:828–830.28. Lien WC, Lai TI, Lin GS, Wang HP, Chen WJ, Cheng TY. Epiploic appendagitis mimicking acute cholecystitis. Am J Emerg Med. 2004; 22:507–508.29. Ortega-Cruz HD, Martínez-Souss J, Acosta-Pumarejo E, Toro DH. Epiploic appendagitis, an uncommon cause of abdominal pain: a case series and review of the literature. P R Health Sci J. 2015; 34:219–221.30. Cho MS, Hwang-Bo S, Choi UY, Kim HS, Hahn SH. A case of epiploic appendagitis with acute gastroenteritis. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2014; 17:263–265.31. Hiller N, Berelowitz D, Hadas-Halpern I. Primary epiploic appendagitis: clinical and radiological manifestations. Isr Med Assoc J. 2000; 2:896–898.32. Theodoropoulou A, Koutroubakis IE. Ischemic colitis: clinical practice in diagnosis and treatment. World J Gastroenterol. 2008; 14:7302–7308.33. Choi SR, Jee SR, Song GA, et al. Predictive factors for severe outcomes in ischemic colitis. Gut Liver. 2015; 9:761–766.34. Danielson K, Chernin MM, Amberg JR, Goff S, Durham JR. Epiploic appendicitis: CT characteristics. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1986; 10:142–143.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Incidentally Diagnosed Colon Cancer by Ultrasound due to Acute Abdomen Caused by Primary Epiploic Appendagitis
- A Case of Epiploic Appendagitis after COVID-19
- A Case of Primary Epiploic Appendagitis
- Seven Cases of Epiploic Appendagitis: Retrograde Analysis of Clinical Characteristics
- A Case of Epiploic Appendagitis Presented with Right Lower Quadrant Pain of Abdomen