J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc.
2019 Nov;58(4):331-338. 10.4306/jknpa.2019.58.4.331.
Assessment of Functional Impairments in Male Children and Adolescents with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Oppositional Defiant Disorder
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Psychiatry, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea. irenelee@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 2465053
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4306/jknpa.2019.58.4.331
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Many studies have demonstrated comorbidities and overlapping symptoms in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and oppositional defiant disorder (ODD). The purpose of this study was to examine the functional impairment in subjects with ADHD, ODD, and in those with both ADHD and ODD.
METHODS
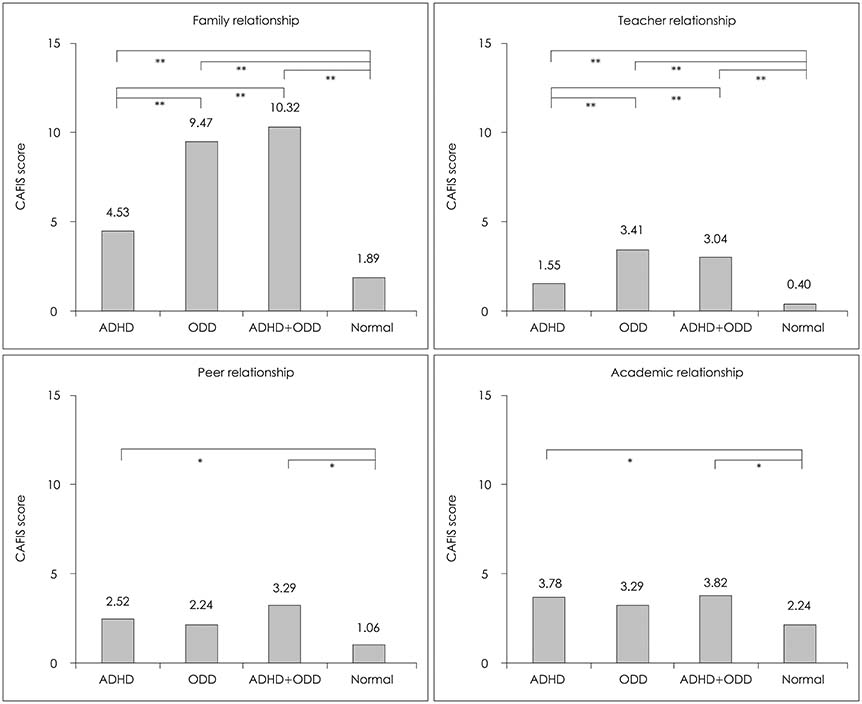
172 male subjects, aged 6 to 15 years old, were enrolled in this study. Based on diagnoses made by applying the Kiddie-Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia-Present and Lifetime (K-SADS-PL), the subjects were categorized into four groups: ADHD group (n=64), ODD group (n=17), ADHD+ODD group (n=28), and control group (n=63). The Child and Adolescent Functioning Impairment Scale (CAFIS) was used to measure the functional impairment of the subjects. CAFIS consists of four subscales : Family relationship, Teacher relationship, Peer relationship, and Academic achievement scales. A high CAFIS score implies high functional impairment. Analysis of covariance was conducted to compare the scores between the four groups.
RESULTS
Both the ODD and the ADHD+ODD groups had significantly high scores for Parent relationship compared to that of the ADHD group. Compared to the control group, both the ADHD and the ADHD+ODD group had significantly higher scores for Peer relationship and Academic achievement, whereas, the ODD group showed no significant difference from the control group on those two subscales.
CONCLUSION
The present study showed that subjects with ADHD and ODD have different functional impairment characteristics. The subjects' relationships with their parents were worsened by the presence of ODD. Peer relationships and Academic achievements were significantly affected by the presence of ADHD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. American Psychiatry Association. DSM-5. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th edition. Arlington, VA: American Psychaitry Association;2013.2. Biederman J. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a selective overview. Biol Psychiatry. 2005; 57:1215–1220.
Article3. Brassett-Harknett A, Butler N. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: an overview of the etiology and a review of the literature relating to the correlates and lifecourse outcomes for men and women. Clin Psychol Rev. 2007; 27:188–210.
Article4. Barkley RA, Cunningham CE, Gordon M, Faraone SV, Lewandowski L, Murphy KR. ADHD symptoms vs. impairment: revisited. ADHD Report. 2006; 14:1–9.
Article5. Burke JD, Rowe R, Boylan K. Functional outcomes of child and adolescent oppositional defiant disorder symptoms in young adult men. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2014; 55:264–272.
Article6. Nock MK, Kazdin AE, Hiripi E, Kessler RC. Lifetime prevalence, correlates, and persistence of oppositional defiant disorder: results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2007; 48:703–713.
Article7. Angold A, Costello EJ, Erkanli A. Comorbidity. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1999; 40:57–87.
Article8. Waschbusch DA. A meta-analytic examination of comorbid hyperactive-impulsive-attention problems and conduct problems. Psychol Bull. 2002; 128:118–150.
Article9. Becker SP, Langberg JM, Evans SW, Girio-Herrera E, Vaughn AJ. Differentiating anxiety and depression in relation to the social functioning of young adolescents with ADHD. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2015; 44:1015–1029.
Article10. Pardini DA, Fite PJ. Symptoms of conduct disorder, oppositional defiant disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and callous-unemotional traits as unique predictors of psychosocial maladjustment in boys: advancing an evidence base for DSM-V. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2010; 49:1134–1144.
Article11. Kaufman J, Birmaher B, Brent D, Rao U, Ryan N. Diagnostic Interview: Kiddie-Sads-Present and Lifetime version 1.0. [online]. 1996. 10. cited 2019 Apr 25. Available from: http://www.icctc.org/August2013/PMM%20Handouts/Kiddie-SADS.pdf.12. Park JH, Lee SI, Schachar RJ. Reliability and validity of the Child and Adolescent Functioning Impairment Scale in children with attentiondeficit/ hyperactivity disorder. Psychiatry Investig. 2011; 8:113–122.
Article13. Shaffer D, Gould MS, Brasic J, Ambrosini P, Fisher P, Bird H, et al. A Children's Global Assessment Scale (CGAS). Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1983; 40:1228–1231.
Article14. Byoun SY, Lee SY, Lee YH. Functional impairment across subtypes of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. J Korean Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2010; 21:72–79.
Article15. Wechsler D. WISC-III Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-third edition manual. San Antonio, TX: The Psychological Corporation of America;1991.16. Fischer M. Parenting stress and the child with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 1990; 19:337–346.
Article17. Lifford KJ, Harold GT, Thapar A. Parent-child relationships and ADHD symptoms: a longitudinal analysis. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2008; 36:285–296.
Article18. Hoza B. Peer functioning in children with ADHD. Ambul Pediatr. 2007; 7:101–106.
Article19. Zeigler Dendy CA. Teaching teens with ADD and ADHD: a quick reference guide for teachers and parents. Bethesda, MD: Woodbine House;2000.20. Barkley RA. Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: a handbook for diagnosis and treatment. 4th ed. New York, NY: Guilford Publications;2015.21. Liu CY, Huang WL, Kao WC, Gau SS. Influence of disruptive behavior disorders on academic performance and school functions of youths with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2017; 48:870–880.
Article22. Lahey BB, Loeber R, Quay HC, Frick PJ, Grimm J. Oppositional defiant and conduct disorders: issues to be resolved for DSM-IV. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1992; 31:539–546.
Article23. Mackler JS, Kelleher RT, Shanahan L, Calkins SD, Keane SP, O'Brien M. Parenting stress, parental reactions, and externalizing behavior from ages 4 to 10. J Marriage Fam. 2015; 77:388–406.
Article24. Henricsson L, Rydell AM. Elementary school children with behavior problems: teacher-child relations and self-perception A prospective study. Merrill-Palmer Quarterl. 2004; 50:111–138.
Article25. Obsuth I, Murray AL, Malti T, Sulger P, Ribeaud D, Eisner M. A nonbipartite propensity score analysis of the effects of teacher-student relationships on adolescent problem and prosocial behavior. J Youth Adolesc. 2017; 46:1661–1687.
Article26. Leadbeater BJ, Ames ME. The longitudinal effects of oppositional defiant disorder symptoms on academic and occupational functioning in the transition to young adulthood. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2017; 45:749–763.
Article27. Li L, Lin X, Hinshaw SP, Du H, Qin S, Fang X. Longitudinal associations between oppositional defiant symptoms and interpersonal relationships among Chinese children. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2018; 46:1267–1281.
Article28. Paap MC, Haraldsen IR, Breivik K, Butcher PR, Hellem FM, Stormark KM. The link between peer relations, prosocial behavior, and ODD/ADHD symptoms in 7-9-year-old children. Psychiatry J. 2013; 2013:319874.
Article29. Johnston C. Parent characteristics and parent-child interactions in families of nonproblem children and ADHD children with higher and lower levels of oppositional-defiant behavior. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1996; 24:85–104.
Article30. Frazier TW, Demaree HA, Youngstrom EA. Meta-analysis of intellectual and neuropsychological test performance in attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder. Neuropsychology. 2004; 18:543–555.
Article31. Noordermeer SD, Luman M, Buitelaar JK, Hartman CA, Hoekstra PJ, Franke B, et al. Neurocognitive deficits in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder with and without comorbid oppositional defiant disorder. J Atten Disord. 2015; 1087054715606216.
Article32. Gaub M, Carlson CL. Gender differences in ADHD: a meta-analysis and critical review. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1997; 36:1036–1045.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comorbid Psychiatric Symptom Associated With Oppositional Defiant Symptom in Community School-Age Children
- Emotional Regulation and Executive Function Deficits in Unmedicated Chinese Children with Oppositional Defiant Disorder
- Impact of Comorbid Oppositional Defiant Disorder on the Clinical and Neuropsychological Characteristics of Korean Children With Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
- Psychiatric Disorders in Adolescence
- Characteristics Related to Depression in Adolescent Conduct Disorder and Oppositional Defiant Disorder