Hip Pelvis.
2019 Dec;31(4):224-231. 10.5371/hp.2019.31.4.224.
Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of Rectangular Tapered Cementless Stem According to Proximal Femoral Geometry in Elderly Asian Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea. kangjoon@inha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2464239
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2019.31.4.224
Abstract
- PURPOSE
A retrospective analysis of mid- to long-term clinical and radiological outcomes of Korean patients over 60 years of age who underwent hip arthroplasty using a cementless rectangular tapered stem according to Dorr proximal femur geography.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January 2007 to December 2013, 107 patients (112 hips) underwent hip arthroplasty using the C2 stem. The mean age of patients was 77.4 years (range, 60-91 years) and the mean follow-up duration was 91.1 months (range, 60-116 months). All patients were evaluated clinically and radiologically with special attention to Dorr femoral bone classification, implant fixation, radiolucent line (RLL), and thigh pain.
RESULTS
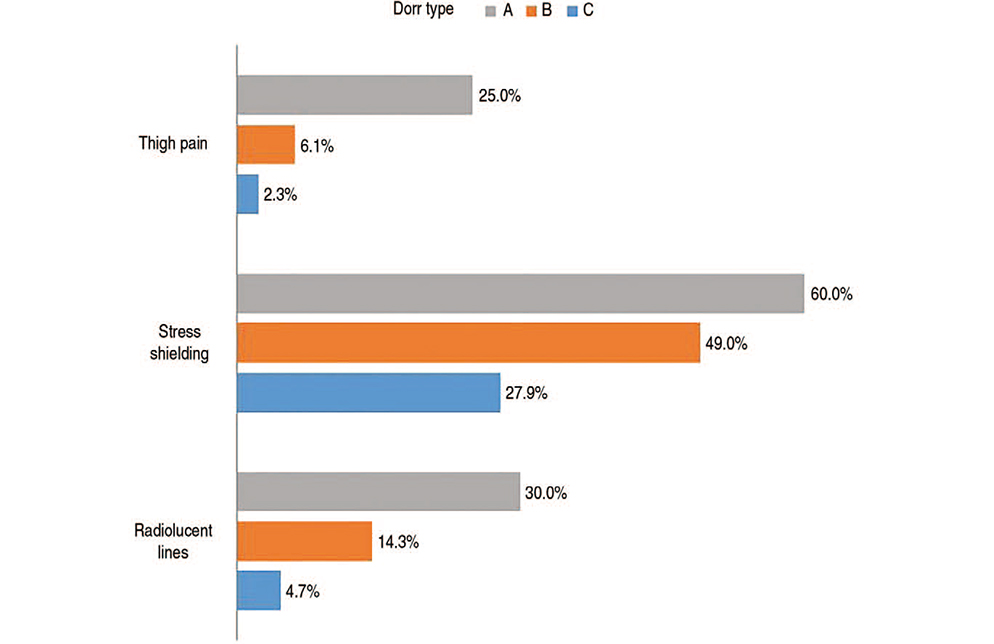
All implants demonstrated radiographic evidence of stable fixation by bone ingrowth without any change in position. The mean Harris hip score improved from 65.5±16.0 (preoperative) to 90.5±15.9 (final follow-up) (P<0.001). Incidence of RLLs, stress shielding, and thigh pain was highest in patients with Dorr type A (RLL, P=0.021; stress shielding, P=0.030; thigh pain, P<0.001). One stem revision was performed due to deep infection. The Kaplan-Meier survival rate of the femoral stem was 97.6%.
CONCLUSION
The overall survival rate of the C2 stems was greater than 97%; there were no significant differences in survival of the C2 stem according to the Dorr classification. The incidences of RLL of thigh pain and RLL were significantly different among Dorr classifications and (highest in patients with Dorr type A).
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Simpson DJ, Kendrick BJ, Hughes M, et al. The migration patterns of two versions of the Furlong cementless femoral stem: a randomised, controlled trial using radiostereometric analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010; 92:1356–1362.2. Kim YH, Oh JH. A comparison of a conventional versus a short, anatomical metaphyseal-fitting cementless femoral stem in the treatment of patients with a fracture of the femoral neck. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012; 94:774–781.3. Incavo SJ, Beynnon BD, Coughlin KM. Total hip arthroplasty with the Secur-Fit and Secur-Fit plus femoral stem design a brief follow-up report at 5 to 10 years. J Arthroplasty. 2008; 23:670–676.
Article4. Lee JM, Sim YS, Choi DS. Hip arthroplasty using the Bencox® Hip System: an evaluation of a consecutive series of one thousand cases. Hip Pelvis. 2018; 30:210–218.
Article5. Huo MH, Martin RP, Zatorski LE, Keggi KJ. Total hip arthroplasty using the Zweymuller stem implanted without cement. A prospective study of consecutive patients with minimum 3-year follow-up period. J Arthroplasty. 1995; 10:793–799.
Article6. Kim JT, Yoo JJ. Implant design in cementless hip arthroplasty. Hip Pelvis. 2016; 28:65–75.
Article7. Suckel A, Geiger F, Kinzl L, Wulker N, Garbrecht M. Long-term results for the uncemented Zweymuller/Alloclassic hip endoprosthesis. A 15-year minimum follow-up of 320 hip operations. J Arthroplasty. 2009; 24:846–853.
Article8. Korovessis P, Repantis T. High medium-term survival of Zweymüller SLR-plus stem used in femoral revision. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009; 467:2032–2040.
Article9. Korovessis P, Repantis T, Zafiropoulos A. High medium-term survivorship and durability of Zweymüller-Plus total hip arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011; 131:603–611.
Article10. Kim HJ, Yoo JJ, Seo W, Kim MN, Kang T. Cementless total hip arthroplasty using the COREN hip system: a minimum five-year follow-up study. Hip Pelvis. 2018; 30:162–167.
Article11. Zweymüller KA, Schwarzinger UM, Steindl MS. Radiolucent lines and osteolysis along tapered straight cementless titanium hip stems: a comparison of 6-year and 10-year follow-up results in 95 patients. Acta Orthop. 2006; 77:871–876.
Article12. Delaunay C, Bonnomet F, North J, Jobard D, Cazeau C, Kempf JF. Grit-blasted titanium femoral stem in cementless primary total hip arthroplasty: a 5- to 10-year multicenter study. J Arthroplasty. 2001; 16:47–54.
Article13. Swanson TV. The tapered press fit total hip arthroplasty: a European alternative. J Arthroplasty. 2005; 20:4 Suppl 2. 63–67.14. Khanuja HS, Vakil JJ, Goddard MS, Mont MA. Cementless femoral fixation in total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011; 93:500–509.
Article15. Dorr LD, Faugere MC, Mackel AM, Gruen TA, Bognar B, Malluche HH. Structural and cellular assessment of bone quality of proximal femur. Bone. 1993; 14:231–242.
Article16. Dorr LD, Wan Z. Comparative results of a distal modular sleeve, circumferential coating, and stiffness relief using the Anatomic Porous Replacement II. J Arthroplasty. 1996; 11:419–428.
Article17. Dorr LD, Lewonowski K, Lucero M, Harris M, Wan Z. Failure mechanisms of anatomic porous replacement I cementless total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997; (334):157–167.
Article18. Gruen TA, McNeice GM, Amstutz HC. “Modes of failure” of cemented stem-type femoral components: a radiographic analysis of loosening. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979; (141):17–27.19. Engh CA, Bobyn JD. The influence of stem size and extent of porous coating on femoral bone resorption after primary cementless hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; (231):7–28.
Article20. Grübl A, Chiari C, Giurea A, et al. Cementless total hip arthroplasty with the rectangular titanium Zweymuller stem. A concise follow-up, at a minimum of fifteen years, of a previous report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88:2210–2215.
Article21. Schmotzer H, Clausen JD. Primary stability - the first step in successful cementless total hip replacement. In : Friedrich NF, Santore RF, editors. 25 years of biologic fixation: K. Zweymüller. München: Elsevier, Urban & Fischer;2007. p. 113–118.22. Swanson TV. Benefits of posterior single-incision less-invasive THA using the SL-PLUS cementless stem. In : Friedrich NF, Santore RF, editors. 25 years of biologic fixation: K. Zweymüller. München: Elsevier, Urban & Fischer;2007. p. 179–190.23. Turchetto L. Experience with the SL-PLUS system in special conditions. In : Friedrich NF, Santore RF, editors. 25 years of biologic fixation: K. Zweymüller. München: Elsevier, Urban & Fischer;2007. p. 107–111.24. Choy WS, Ahn JH, Jeong HJ, et al. Cementless bipolar hemiarthroplasty for femoral neck fractures in elderly patients. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2008; 43:703–709.
Article25. Park MS, Cho HM, Kim JH, Shin WJ. Cementless bipolar hemiarthroplasty using a rectangular cross-section stem for unstable intertrochanteric fractures. Hip Int. 2013; 23:316–322.
Article26. Vresilovic EJ, Hozack WJ, Rothman RH. Incidence of thigh pain after uncemented total hip arthroplasty as a function of femoral stem size. J Arthroplasty. 1996; 11:304–311.
Article27. Campbell AC, Rorabeck CH, Bourne RB, Chess D, Nott L. Thigh pain after cementless hip arthroplasty. Annoyance or ill omen. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992; 74:63–66.
Article28. Brown TE, Larson B, Shen F, Moskal JT. Thigh pain after cementless total hip arthroplasty: evaluation and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2002; 10:385–392.
Article29. Woo J, Li M, Lau E. Population bone mineral density measurements for Chinese women and men in Hong Kong. Osteoporos Int. 2001; 12:289–295.
Article30. Walker MD, Babbar R, Opotowsky AR, et al. A referent bone mineral density database for Chinese American women. Osteoporos Int. 2006; 17:878–887.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cementless Hip Arthroplasty Using a Long Double-Tapered Rectangular Stem in Patients with Osteoporotic Proximal Femoral Fractures or Reoperation
- Radiological Analysis of the Tapered Femoral Stem after Cementless Hip Arthroplasty: Minimum 5 years follow-up
- Radiological Analysis of the Proximal Femoral Geometry in Korean Adults and the Design of the Cementless Femoral Stem
- Ultra-Short Bone Conserving Cementless Femoral Stem
- Cementless Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty for Femoral Neck Fractures in Elderly Patients