J Liver Cancer.
2019 Sep;19(2):128-135. 10.17998/jlc.19.2.128.
Tenofovir and Entecavir Have Similar Renal Adverse Events on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Treated with Transarterial Chemoembolization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine and Liver Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ydoctor2@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2463613
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.128
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) is potentially nephrotoxic in chronic hepatitis B patients. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients treated using transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) are at an increased risk of renal injury. The aim of this study was to determine whether TDF is associated with more renal adverse events than entecavir (ETV) in HCC patients treated with TACE.
METHODS
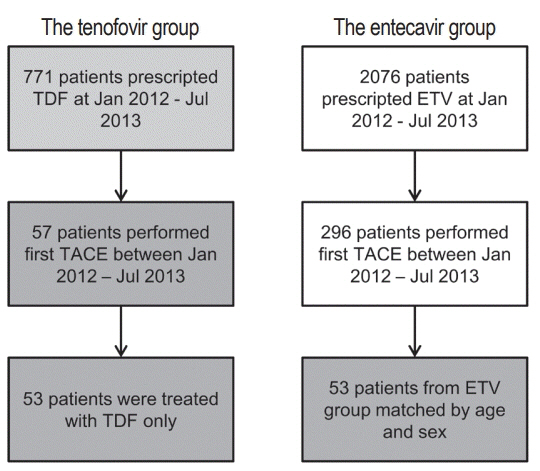
In this retrospective single-center study, we selected 53 HCC patients who were treated with TDF from January 2012 to July 2013 and had their first TACE procedure in the same period. These patients were matched by age and sex to patients treated with ETV.
RESULTS
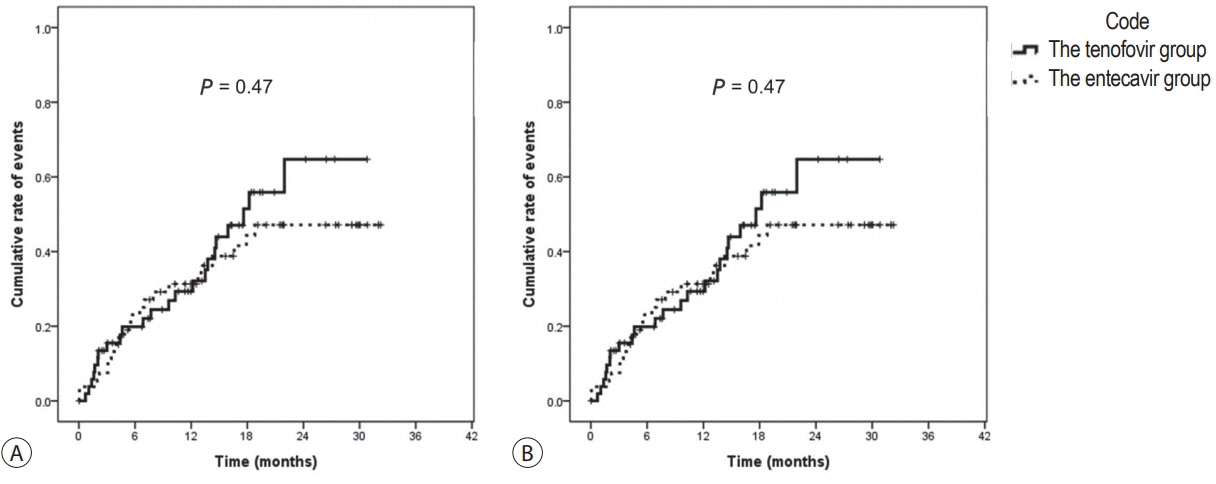
There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics, including HCC factors, and nephrotoxic drug use, between the two groups. The median follow-up period was 17.0 and 20.0 months for the TDF and ETV groups, respectively. There was no difference during the follow-up period between the TDF and ETV groups in the increase in creatinine over 0.5 mg/dL (17.0% and 17.0%, P=1.00, respectively) and the decrease in eGFR over 25% (43.4% and 41.5%, P=0.84, respectively). Multivariate analysis revealed that Child-Pugh class over B (hazard ratio [HR], 7.30; 95% confidence interval [CI] 2.79-19.10; P<0.01) was associated with increase in creatinine, and Child-Pugh class over B (HR, 82.74; 95% CI 12.31-555.83; P<0.01) and Barcelona-Clinic Liver Cancer stage over B (HR, 14.93; 95% CI 1.60-139.51; P=0.02) were associated with decrease in eGFR.
CONCLUSIONS
TDF has comparable safety to that of ETV for HCC patients undergoing TACE.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee WM. Hepatitis B virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1997; 337:1733–1745.2. Lok AS, McMahon BJ, Brown RS Jr, Wong JB, Ahmed AT, Farah W, et al. Antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis B viral infection in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology. 2016; 63:284–306.3. Bristol-Myers Squibb. Archived drug label, [Internet]. United States: Bristol-Myers Squibb;[cited Jan 1 2019]. Available from: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/archives/fdaDrugInfo.cfm?archiveid=10048.4. Gish RG, Clark MD, Kane SD, Shaw RE, Mangahas MF, Baqai S. Similar risk of renal events among patients treated with tenofovir or entecavir for chronic hepatitis B. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 10:941–946.5. Hall AM, Hendry BM, Nitsch D, Connolly JO. Tenofovir-associated kidney toxicity in HIV-infected patients: a review of the evidence. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011; 57:773–780.6. Hwang HS, Park CW, Song MJ. Tenofovir-associated Fanconi syndrome and nephrotic syndrome in a patient with chronic hepatitis B monoinfection. Hepatology. 2015; 62:1318–1320.7. Cho H, Cho Y, Cho EJ, Lee JH, Yu SJ, Oh KH, et al. Tenofovirassociated nephrotoxicity in patients with chronic hepatitis B: two cases. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2016; 22:286–291.8. Yu SJ. A concise review of updated guidelines regarding the management of hepatocellular carcinoma around the world: 2010-2016. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2016; 22:7–17.9. Park JW, Chen M, Colombo M, Roberts LR, Schwartz M, Chen PJ, et al. Global patterns of hepatocellular carcinoma management from diagnosis to death: the BRIDGE Study. Liver Int. 2015; 35:2155–2166.10. Zhou C, Wang R, Ding Y, Du L, Hou C, Lu D, et al. Prognostic factors for acute kidney injury following transarterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014; 7:2579–2586.11. Korean Association for the Study of the Liver. KASL clinical practice guidelines: management of chronic hepatitis B. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2016; 22:18–75.12. Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF 3rd, Feldman HI, et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. 2009; 150:604–612.13. Koklu S, Gulsen MT, Tuna Y, Koklu H, Yuksel O, Demir M, et al. Differences in nephrotoxicity risk and renal effects among antiviral therapies against hepatitis B. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015; 41:310–319.14. Riveiro-Barciela M, Tabernero D, Calleja JL, Lens S, Manzano ML, Rodriguez FG, et al. Effectiveness and safety of entecavir or tenofovir in a spanish cohort of chronic hepatitis b patients: validation of the page-b score to predict hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 2017; 62:784–793.15. Hao JF, Zhang LW, Bai JX, Li YJ, Liu JN, Zhang XL, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and prognosis of acute kidney injury following transarterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective cohort study. Indian J Cancer. 2015; 51 Suppl 2:e3–e8.16. Monteagudo-Chu MO, Chang MH, Fung HB, Bräu N. Renal toxicity of long-term therapy with tenofovir in HIV-infected patients. J Pharm Pract. 2012; 25:552–559.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy of Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy and Radiofrequency Ablation against Hepatocellular Carcinoma Refractory to Transarterial Chemoembolization and Vascular Variation: A Case Study
- Transarterial Chemoembolization in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Extrahepatic Metastasis
- Complications Related to Transarterial Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review
- Entecavir versus tenofovir in patients with chronic hepatitis B: Enemies or partners in the prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Antiviral Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis B