J Korean Radiol Soc.
1985 Dec;21(6):963-968. 10.3348/jkrs.1985.21.6.963.
CT findings of tuberculous lymphadenitis in the abdominal cavity
- KMID: 2462395
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jkrs.1985.21.6.963
Abstract
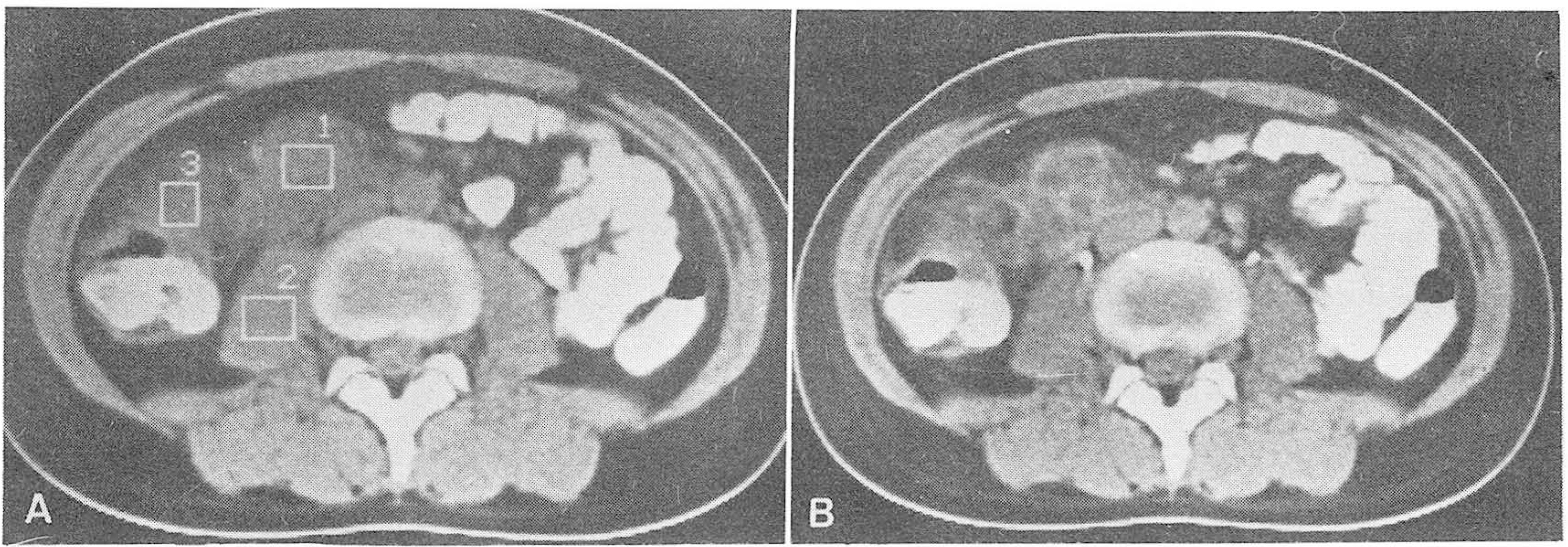
- Authors analyzed CT findings of 8 patients with tuberculous lymphadenitis and one case of tuberculous abscessdiagnosed surgically or clinically. The results were as follows; 1. Soft tissue density masses were noted in 8patients in paraaortic, mesenteric, peripancreatic, celiac, porta hepatis, and esophagogastric junction areas inorder of frequency, and these correspond to lylmph node groups of the same name. On contrast enhanced CT, rimenhancement with multilocular low dinsties indicating caseous necrosis were noted in 3 patients, ill defined lowdensities were seen in 3 patients, and no definite changes were noted in 2 patients. 2. Two or more lymph nodegroups were involved in 6 patients, and one lymph node group was involved in two patients. 3. A huge cystic masswith relatively irregular rim enhancement and small anount of solid component occupied nearly entire upper abdomenin 1 patient and this was confiremd as tuberculous abscess in peritoneum. 4. In 2 cases, bowel wall thickening wassuggested in cecum, ascending colon, and terminal ileum.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.We rb el off L., Novis BH., Bank S, et al. Radiology of tuberculosis of the gastronistestinal tract. Br J Radio. 45:329–336. 1973.2.Amerson JR., Martin JD. Tuberculosis of the alimentary tract. Am J Surg. 107:340–345. 1964.
Article3.Bhansali SK. Abdominal tuberculsis. Am J Gastroentero. 67:324–337. 7977.4.Stanley RJ. Fluid characterization with computed tomography. Moss ΑΔ, Goldgberg HI, editors. eds.Computed tomography, ultrasound and X-ray: an integrated approach. New York: Academic Press;p. 65–66. 1980.5.Epstein BM., Mann JH. CT of abdominal tuberculosis. AJR. 139:861–866. 1982.
Article6.Dahlene DH., Stanley RJ., Koehler RE, et al. Abdominal tuberculosis; CT findings. Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography. 8:443–445. 1984.
Article7.Hanson RD., Η니nter TB. Tuberculous peritonitis: CT appearance. AJR. 144:931–932. 1985.
Article8.Borgia G., Ciampi R., Nappa S, et al. Tuberculous mesenteric lymphadenitis clinically presenting as abdominal mass; CT and sonographic findings. J Clin Ultrasound. 13:491–493. 1985.
Article9.Bocluis HL. Tuberculosis of the intestines. In: Gastroenterolgy,. 3rd ed.2. Philadelphia: Saunders;p. 750–777. 1976.10.Thoeni RF., Margulis AR. Gastrointestinal tuberculosis. Seminars in Roentgenology. 14:283–294. 7979.
Article11.Auerbach O. Pleural, peritoneal and pericardial tuberculosis; review of 209 cases uncomplicated by treatment of secondary infection. Am Rev Tuberc. 61:845–861. 1950.12.Krudy AG., Donnick WR., Magrath IT, et al. CT of American Burkitt lymphoma. AJR. 136:747–754. 1981.
Article13.Yeh H., Chahinian P. Ultrasonography and computed tomography of peritoneal mesothelioma. 135:705–712. 1980.14.Mayes BG., Ch니ang VP., Fisher RE. CT of pseudomyxoma peritonei. AJR. 136:807–808. 1981.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- CT menifestations of cervical tuberculous lymphadenitis
- Computed Tomographic Differential Diagnosis of Cervical Lymphadenopathy: Tuberculous versus Metastatic
- Nodo-Colonic Fistula Caused by Intra-Abdominal Tuberculous Lymphadenitis during Treatment with Anti-Tuberculous Medication: A Case Report
- Computed tomographic findings of cervical tuberculous lymphadenitis
- A Case of Intestinal Tuberculosis with Tuberculous Mesenteric Lymphadenitis Simulating Neoplasm