Ann Surg Treat Res.
2019 Nov;97(5):266-269. 10.4174/astr.2019.97.5.266.
Cut-down method for perm catheter insertion in patients with completely occluded internal jugular vein
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Soonchunhyang University Seoul Hospital, Seoul, Korea. ultravascsurg@gmail.com
- KMID: 2461903
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2019.97.5.266
Abstract
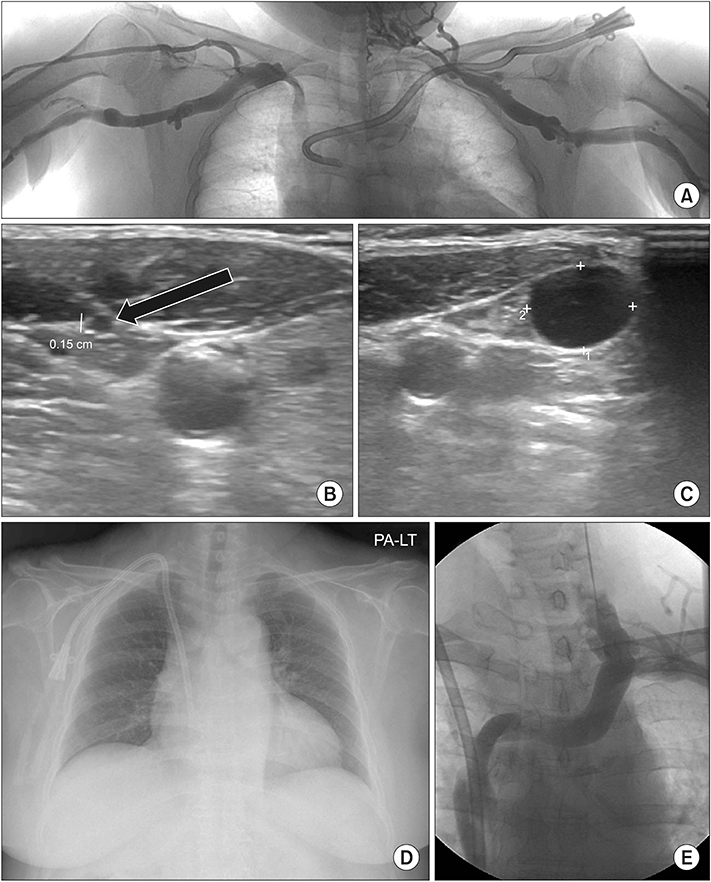
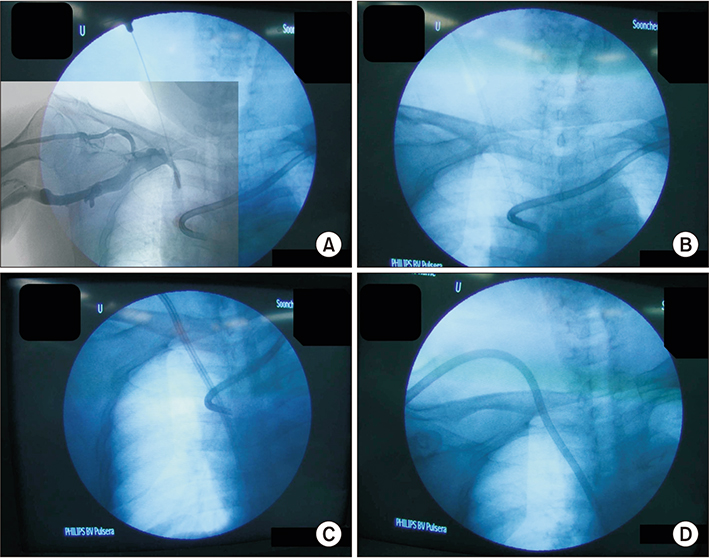
- The primary site for a hemodialysis catheter insertion is the right internal jugular vein (IJV) followed by the left IJV and subclavian vein. In cases when veins of the upper extremities are exhausted, femoral veins are an alternative insertion location. Femoral catheter insertions should only be used for short periods because of the increased risk of infection. There is a percutaneous technique to recanalize occluded central veins for hemodialysis catheter insertion. We experienced success with a cut-down method for permcath through a completely occluded IJV. We, therefore, find surgical recanalization to be better than percutaneous method in terms of cost and safety.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schmidli J, Widmer MK, Basile C, de Donato G, Gallieni M, Gibbons CP, et al. Editor's choice - vascular access: 2018 clinical practice guidelines of the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS). Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2018; 55:757–818.
Article2. Vascular Access 2006 Work Group. Clinical practice guidelines for vascular access. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006; 48 Suppl 1:S176–S247.3. Rahman S, Kuban JD. Dialysis catheter placement in patients with exhausted access. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017; 20:65–74.
Article4. Funaki B, Zaleski GX, Leef JA, Lorenz JN, Van Ha T, Rosenblum JD. Radiologic placement of tunneled hemodialysis catheters in occluded neck, chest, or small thyrocervical collateral veins in central venous occlusion. Radiology. 2001; 218:471–476.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Secondary migration of a pre-existing central venous catheter due to a Swan-Ganz catheter insertion – A case report –
- Posterior triangle approach for lateral in-plane technique during hemodialysis catheter insertion via the internal jugular vein
- Osteomyelitis of the Rib Following Internal Jugular Vein Catheter Insertion
- Malposition of a Subclavian Catheter in the Internal Jugular Vein Due to the Direction of a J-type Guidewire End
- The Usefulness of Cephalic Vein Cut-Down for Totally Implantable Central Venous Port in Children