J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2019 Oct;54(5):440-446. 10.4055/jkoa.2019.54.5.440.
Myxoid Liposarcoma: A Single Institute Experience
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Korea Cancer Center Hospital, Seoul, Korea. wssongmd@gmail.com
- 2Department of Pathology, Korea Cancer Center Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2461234
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2019.54.5.440
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study assessed the treatment outcomes of myxoid liposarcoma in the extremities and investigate the prognostic factors.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 91 patients with myxoid liposarcoma (83 primary, 8 recurrent) between 2001 and 2015 were reviewed retrospectively. The local recurrence and metastasis after treatment were examined. The survival rates and prognostic factors affecting the survival were investigated. The mean follow-up was 84 months (range, 5-196 months).
RESULTS
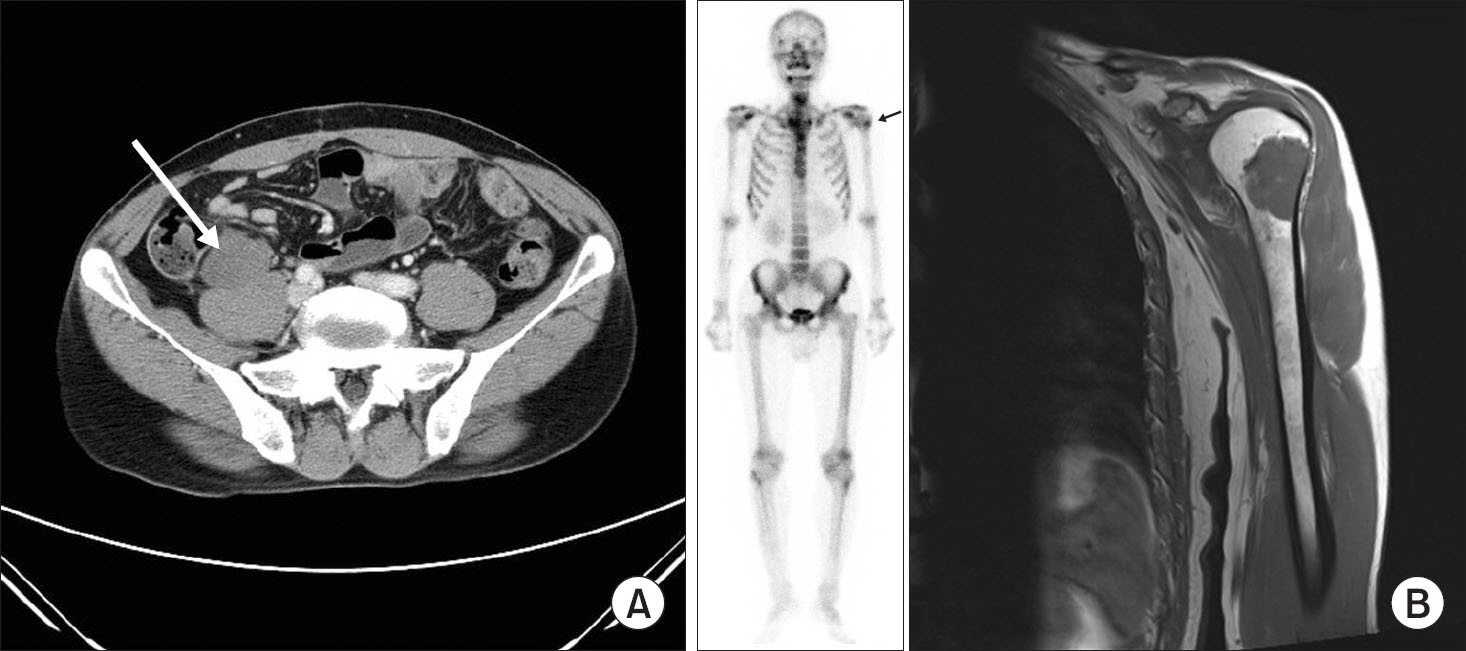
The overall survival rates at 5-yr and 10-yr were 82% and 74%, respectively. The tumor size (p=0.04), round cell component (p<0.0001), grade (p=0.0002), and local recurrence (p=0.006) affected survival in primary patients. Extrapulmonary metastases were observed in 75.0% (18/24) of metastatic patients and the mean post metastasis survival was 26 months (range, 2-72 months).
CONCLUSION
Myxoid liposarcoma developed mainly at the lower extremities. The tumor size, grade, component of round cells, and local recurrence were associated with the prognosis. The unique feature of extrapulmonary metastasis in myxoid liposarcoma should be noted in the treatment and follow-up.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016. 66:7–30.
Article2. Linch M, Miah AB, Thway K, Judson IR, Benson C. Systemic treatment of soft-tissue sarcoma-gold standard and novel therapies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2014. 11:187–202.
Article3. Fletcher CD. The evolving classification of soft tissue tumours - an update based on the new 2013 WHO classification. Histopathology. 2014. 64:2–11.
Article4. ten Heuvel SE, Hoekstra HJ, van Ginkel RJ, Bastiaannet E, Suurmeijer AJ. Clinicopathologic prognostic factors in myxoid liposarcoma: a retrospective study of 49 patients with long-term follow-up. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007. 14:222–9.5. Dalal KM, Antonescu CR, Singer S. Diagnosis and management of lipomatous tumors. J Surg Oncol. 2008. 97:298–313.
Article6. Narendra S, Valente A, Tull J, Zhang S. DDIT3 gene break-apart as a molecular marker for diagnosis of myxoid liposarcoma: assay validation and clinical experience. Diagn Mol Pathol. 2011. 20:218–24.7. Cheng EY, Springfield DS, Mankin HJ. Frequent incidence of extrapulmonary sites of initial metastasis in patients with liposarcoma. Cancer. 1995. 75:1120–7.
Article8. Estourgie SH, Nielsen GP, Ott MJ. Metastatic patterns of extremity myxoid liposarcoma and their outcome. J Surg Oncol. 2002. 80:89–93.
Article9. Lee SH, Cho IJ, Yang WI, Suh JS, Shin KH. Liposarcoma in the extremity. J Korean Bone Joint Tumor Soc. 2010. 16:62–8.
Article10. Chung YG, Kang YK, Bahk WJ. . Prognostic factors in liposarcomas: a retrospective study of 52 patients. J Korean Bone Joint Tumor Soc. 2010. 16:14–20.
Article11. Fiore M, Grosso F, Lo Vullo S. . Myxoid/round cell and pleomorphic liposarcomas: prognostic factors and survival in a series of patients treated at a single institution. Cancer. 2007. 109:2522–31.12. Antonescu CR, Tschernyavsky SJ, Decuseara R. . Prognostic impact of P53 status, TLS-CHOP fusion transcript structure, and histological grade in myxoid liposarcoma: a molecular and clinicopathologic study of 82 cases. Clin Cancer Res. 2001. 7:3977–87.13. Knebel C, Lenze U, Pohlig F. . Prognostic factors and outcome of liposarcoma patients: a retrospective evaluation over 15 years. BMC Cancer. 2017. 17:410.
Article14. Beane JD, Yang JC, White D, Steinberg SM, Rosenberg SA, Rudloff U. Efficacy of adjuvant radiation therapy in the treatment of soft tissue sarcoma of the extremity: 20-year follow-up of a randomized prospective trial. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014. 21:2484–9.
Article15. Engström K, Bergh P, Cederlund CG. . Irradiation of myxoid/round cell liposarcoma induces volume reduction and lipoma-like morphology. Acta Oncol. 2007. 46:838–45.
Article16. Guadagnolo BA, Zagars GK, Ballo MT. . Excellent local control rates and distinctive patterns of failure in myxoid liposarcoma treated with conservation surgery and radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008. 70:760–5.
Article17. Gronchi A, Bui BN, Bonvalot S. . Phase II clinical trial of neoadjuvant trabectedin in patients with advanced localized myxoid liposarcoma. Ann Oncol. 2012. 23:771–6.
Article18. Grosso F, Jones RL, Demetri GD. . Efficacy of trabectedin (ecteinascidin-743) in advanced pretreated myxoid liposarcomas: a retrospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2007. 8:595–602.
Article19. Di Giandomenico S, Frapolli R, Bello E. . Mode of action of trabectedin in myxoid liposarcomas. Oncogene. 2014. 33:5201–10.20. Lee ATJ, Thway K, Huang PH, Jones RL. Clinical and molecular spectrum of liposarcoma. J Clin Oncol. 2018. 36:151–9.
Article21. Fuglø HM, Maretty-Nielsen K, Hovgaard D, Keller JØ, Safwat AA, Petersen MM. Metastatic pattern, local relapse, and survival of patients with myxoid liposarcoma: a retrospective study of 45 patients. Sarcoma. 2013. 2013:548–628.
Article22. Nishida Y, Tsukushi S, Nakashima H, Ishiguro N. Clinicopathologic prognostic factors of pure myxoid liposarcoma of the extremities and trunk wall. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010. 468:3041–6.
Article23. Schwab JH, Boland PJ, Antonescu C, Bilsky MH, Healey JH. Spinal metastases from myxoid liposarcoma warrant screening with magnetic resonance imaging. Cancer. 2007. 110:1815–22.
Article24. Conill C, Setoain X, Colomo L. . Diagnostic efficacy of bone scintigraphy, magnetic resonance imaging, and positron emission tomography in bone metastases of myxoid liposarcoma. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008. 27:625–8.
Article