Korean J Neurotrauma.
2019 Oct;15(2):110-116. 10.13004/kjnt.2019.15.e25.
Burr Hole Drainage versus Small Craniotomy of Chronic Subdural Hematomas
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea. ywh9868@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2461115
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2019.15.e25
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Chronic subdural hematoma drainage is one of the most common procedures performed in neurosurgical practice. Not only burr hole drainage but also small craniotomy (diameter 3-5 cm) is frequently used neurosurgical treatment of chronic subdural hematomas. We assessed to compare the postoperative recurrence rates between burr hole drainage versus small craniotomy with closed-system drainage for chronic subdural hematomas.
METHODS
From January 2016 to December 2018, 75 patients who were treated with burr hole drainage and small craniotomy with closed system drainage for the symptomatic chronic subdural hematoma were enrolled. Pre and postoperative computed tomography (CT) were used for radiologic evaluation. The choice of procedure was decided by preoperative CT images.
RESULTS
60 patients out of 75 patients underwent burr hole drainage, whereas 15 patients underwent small craniotomy. The overall postoperative recurrence rate was 16%. The recurrence occurred in 8 patients out of 60 patients in burr hole drainage group (13.3%) and 7 patients out of 15 patients in small craniotomy group (46.7%). The number of days of hospitalization was 10.3 days in burr hole drainage group and 15.7 days in small craniotomy group.
CONCLUSION
Burr hole drainage would be sufficient to evacuate chronic subdural hematoma with lower recurrence rate, but small craniotomy was also needed in some cases such as hematoma has solid portion or multiple septum.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
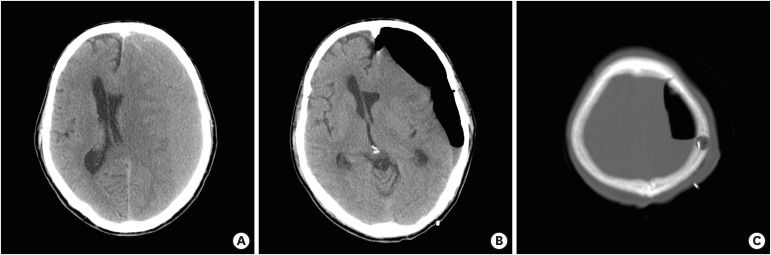
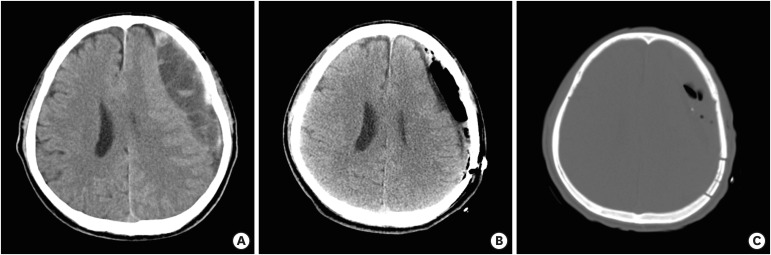
Figure
Reference
-
1. Abouzari M, Rashidi A, Rezaii J, Esfandiari K, Asadollahi M, Aleali H, et al. The role of postoperative patient posture in the recurrence of traumatic chronic subdural hematoma after burr-hole surgery. Neurosurgery. 2007; 61:794–797. PMID: 17986941.
Article2. Adhiyaman V, Asghar M, Ganeshram KN, Bhowmick BK. Chronic subdural haematoma in the elderly. Postgrad Med J. 2002; 78:71–75. PMID: 11807186.3. Amirjamshidi A, Abouzari M, Eftekhar B, Rashidi A, Rezaii J, Esfandiari K, et al. Outcomes and recurrence rates in chronic subdural haematoma. Br J Neurosurg. 2007; 21:272–275. PMID: 17612917.
Article4. Cousseau DH, Echevarría Martín G, Gaspari M, Gonorazky SE. Chronic and subacute subdural haematoma. An epidemiological study in a captive population. Rev Neurol. 2001; 32:821–824. PMID: 11424031.5. Santarius T, Kirkpatrick PJ, Ganesan D, Chia HL, Jalloh I, Smielewski P, et al. Use of drains versus no drains after burr-hole evacuation of chronic subdural haematoma: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2009; 374:1067–1073. PMID: 19782872.
Article6. Ahn SY, Kim JH, Ha SK, Kim JH, Kwon TH, Park YK, et al. Clinical analysis of risk factors associated with the recurrence of chronic subdural hematoma. J Korean Neurotraumatol Soc. 2011; 7:68–73.
Article7. Ernestus RI, Beldzinski P, Lanfermann H, Klug N. Chronic subdural hematoma: surgical treatment and outcome in 104 patients. Surg Neurol. 1997; 48:220–225. PMID: 9290707.
Article8. Frati A, Salvati M, Mainiero F, Ippoliti F, Rocchi G, Raco A, et al. Inflammation markers and risk factors for recurrence in 35 patients with a posttraumatic chronic subdural hematoma: a prospective study. J Neurosurg. 2004; 100:24–32.
Article9. Santarius T, Hutchinson PJ. Chronic subdural haematoma: time to rationalize treatment? Br J Neurosurg. 2004; 18:328–332. PMID: 15702829.
Article10. Gurelik M, Aslan A, Gurelik B, Ozum U, Karadag O, Kars HZ. A safe and effective method for treatment of chronic subdural haematoma. Can J Neurol Sci. 2007; 34:84–87. PMID: 17352353.
Article11. Sambasivan M. An overview of chronic subdural hematoma: experience with 2300 cases. Surg Neurol. 1997; 47:418–422. PMID: 9131021.
Article12. Jeong JE, Kim GK, Park JT, Lim YJ, Kim TS, Rhee BA, et al. A clinical analysis of chronic subdural hematoma according to age factor. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2000; 29:748–753.13. Taussky P, Fandino J, Landolt H. Number of burr holes as independent predictor of postoperative recurrence in chronic subdural haematoma. Br J Neurosurg. 2008; 22:279–282. PMID: 18348026.
Article14. Kim HY, Kwon SC, Kim TH, Shin HS, Hwang YS, Park SK. Analysis of management according to CT findings in chronic subdural hematoma. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2005; 37:96–100.15. Ko BS, Lee JK, Seo BR, Moon SJ, Kim JH, Kim SH. Clinical analysis of risk factors related to recurrent chronic subdural hematoma. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2008; 43:11–15. PMID: 19096538.
Article16. Krupp WF, Jans PJ. Treatment of chronic subdural haematoma with burr-hole craniostomy and closed drainage. Br J Neurosurg. 1995; 9:619–627. PMID: 8561934.
Article17. Kurokawa Y, Ishizaki E, Inaba K. Bilateral chronic subdural hematoma cases showing rapid and progressive aggravation. Surg Neurol. 2005; 64:444–449. PMID: 16253697.
Article18. Kuroki T, Katsume M, Harada N, Yamazaki T, Aoki K, Takasu N. Strict closed-system drainage for treating chronic subdural haematoma. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2001; 143:1041–1044. PMID: 11685612.
Article19. Zakaraia AM, Adnan JS, Haspani MS, Naing NN, Abdullah JM. Outcome of 2 different types of operative techniques practiced for chronic subdural hematoma in Malaysia: an analysis. Surg Neurol. 2008; 69:608–615. PMID: 18486703.
Article20. Lee SH, Ha SK, Kim JH, Kim JH, Kwon TH, Park YK. Age-specific characteristics in chronic subdural hematoma patients. J Korean Neurotraumatol Soc. 2011; 7:83–87.
Article21. Lega BC, Danish SF, Malhotra NR, Sonnad SS, Stein SC. Choosing the best operation for chronic subdural hematoma: a decision analysis. J Neurosurg. 2010; 113:615–621. PMID: 19877806.
Article22. Yamamoto H, Hirashima Y, Hamada H, Hayashi N, Origasa H, Endo S. Independent predictors of recurrence of chronic subdural hematoma: results of multivariate analysis performed using a logistic regression model. J Neurosurg. 2003; 98:1217–1221. PMID: 12816267.
Article23. Weigel R, Schmiedek P, Krauss JK. Outcome of contemporary surgery for chronic subdural haematoma: evidence based review. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2003; 74:937–943. PMID: 12810784.
Article24. Weber G. Chronic subdural hematoma. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1969; 99:1483–1488. PMID: 4310306.25. Wakai S, Hashimoto K, Watanabe N, Inoh S, Ochiai C, Nagai M. Efficacy of closed-system drainage in treating chronic subdural hematoma: a prospective comparative study. Neurosurgery. 1990; 26:771–773. PMID: 2352594.
Article26. Mohamed EE. Chronic subdural haematoma treated by craniotomy, durectomy, outer membranectomy and subgaleal suction drainage. Personal experience in 39 patients. Br J Neurosurg. 2003; 17:244–247. PMID: 14565521.
Article27. Mondorf Y, Abu-Owaimer M, Gaab MR, Oertel JM. Chronic subdural hematoma--craniotomy versus burr hole trepanation. Br J Neurosurg. 2009; 23:612–616. PMID: 19922275.
Article28. Murakami H, Hirose Y, Sagoh M, Shimizu K, Kojima M, Gotoh K, et al. Why do chronic subdural hematomas continue to grow slowly and not coagulate? Role of thrombomodulin in the mechanism. J Neurosurg. 2002; 96:877–884. PMID: 12005395.
Article29. Nakaguchi H, Tanishima T, Yoshimasu N. Relationship between drainage catheter location and postoperative recurrence of chronic subdural hematoma after burr-hole irrigation and closed-system drainage. J Neurosurg. 2000; 93:791–795. PMID: 11059659.
Article30. Oishi M, Toyama M, Tamatani S, Kitazawa T, Saito M. Clinical factors of recurrent chronic subdural hematoma. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2001; 41:382–386. PMID: 11561348.
Article31. Okada Y, Akai T, Okamoto K, Iida T, Takata H, Iizuka H. A comparative study of the treatment of chronic subdural hematoma--burr hole drainage versus burr hole irrigation. Surg Neurol. 2002; 57:405–409. PMID: 12176202.
Article32. Quinones-Hinojosa A. Schmidek and sweet operative neurosurgical techniques. ed 6. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders;2012.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cerebellar Hemorrhage after Burr Hole Drainage of Supratentorial Chronic Subdural Hematoma
- Chronic Subdural Hematomas : A Comparative Study of Three Types of Operative Procedures
- Remote Hemorrhage after Burr Hole Drainage of Chronic Subdural Hematoma
- Evolution of Chronic Subdural Hematoma based on Brain CT findings and Appropriate Treatment Methods
- Clinical Observation, of Chronic Subdural Hematomas (Burr hole, Drainage and Craniotomy, Membranectomy)