High Proportion of Adult Cases and Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Population in Korea: A Nationwide Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jaehyeon@skku.edu
- 3Department of Biostatistic, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Statistics and Actuarial Science, Soongsil University, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Clinical Research Design and Evaluation, Samsung Advanced Institute for Health Sciences and Technology, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2460974
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0048
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) in all age groups and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in patients with T1DM in Korea were estimated.
METHODS
The incidence and prevalence of T1DM between 2007 and 2013 were calculated using the Korean National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) datasets of claims. Clinical characteristics and prevalence of metabolic syndrome in individuals with T1DM between 2009 and 2013 were determined using the database of NHIS preventive health checkups.
RESULTS
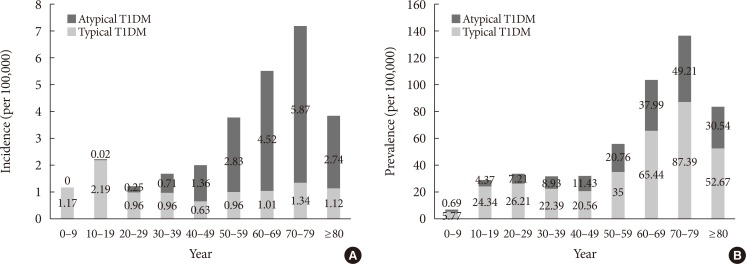
The prevalence of T1DM in Korea between 2007 and 2013 was 0.041% to 0.047%. The annual incidence rate of T1DM in Korea in 2007 to 2013 was 2.73 to 5.02/100,000 people. Although the incidence rate of typical T1DM was highest in teenagers, it remained steady in adults over 30 years of age. In contrast, the incidence rate of atypical T1DM in 2013 was higher in people aged 40 years or older than in younger age groups. Age- and sex-adjusted prevalence of metabolic syndrome in patients with T1DM was 51.65% to 55.06% between 2009 and 2013.
CONCLUSION
T1DM may be more common in Korean adults than previously believed. Metabolic syndrome may be a frequent finding in individuals with T1DM in Korea.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 7 articles
-
Management of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in Adults
Hye Ryoung Yun
J Korean Diabetes. 2020;21(3):156-160. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2020.21.3.156.New Insulin Pumps and Open Source Artificial Pancreas System in Korea
Jae Hyeon Kim
J Korean Diabetes. 2020;21(4):197-203. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2020.21.4.197.Age at Diagnosis and the Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Jong Ha Baek, Woo Je Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Soo Kyoung Kim, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(1):46-54. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2019.0134.Age at Diagnosis and the Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (
Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:46-54)
Ye Seul Yang, Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(2):277-278. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0028.Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Microvascular Complications in Chinese Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Qianwen Huang, Daizhi Yang, Hongrong Deng, Hua Liang, Xueying Zheng, Jinhua Yan, Wen Xu, Xiangwen Liu, Bin Yao, Sihui Luo, Jianping Weng
Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):93-103. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0240.Comparison of Insulin-Treated Patients with Ambiguous Diabetes Type with Definite Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Subjects: A Clinical Perspective
Insa Laspe, Juris J. Meier, Michael A. Nauck
Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):140-146. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0322.Risk of Depression according to Cumulative Exposure to a Low-Household Income Status in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
So Hee Park, You-Bin Lee, Kyu-na Lee, Bongsung Kim, So Hyun Cho, So Yoon Kwon, Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Kyungdo Han, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):290-301. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0299.
Reference
-
1. Song SO, Song YD, Nam JY, Park KH, Yoon JH, Son KM, Ko Y, Lim DH. Epidemiology of type 1 diabetes mellitus in Korea through an investigation of the national registration project of type 1 diabetes for the reimbursement of glucometer strips with additional analyses using claims data. Diabetes Metab J. 2016; 40:35–45. PMID: 26912154.
Article2. Thorn LM, Forsblom C, Waden J, Saraheimo M, Tolonen N, Hietala K, Groop PH. Finnish Diabetic Nephropathy (FinnDiane) Study Group. Metabolic syndrome as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease, mortality, and progression of diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:950–952. PMID: 19196885.
Article3. Park Y, Wintergerst KA, Zhou Z. Clinical heterogeneity of type 1 diabetes (T1D) found in Asia. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2017; 33.
Article4. Kim JH, Lee CG, Lee YA, Yang SW, Shin CH. Increasing incidence of type 1 diabetes among Korean children and adolescents: analysis of data from a nationwide registry in Korea. Pediatr Diabetes. 2016; 17:519–524. PMID: 26420382.
Article5. Zhao Z, Sun C, Wang C, Li P, Wang W, Ye J, Gu X, Wang X, Shen S, Zhi D, Lu Z, Ye R, Cheng R, Xi L, Li X, Zheng Z, Zhang M, Luo F. Rapidly rising incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes in Chinese population: epidemiology in Shanghai during 1997-2011. Acta Diabetol. 2014; 51:947–953. PMID: 24777734.
Article6. Lin WH, Wang MC, Wang WM, Yang DC, Lam CF, Roan JN, Li CY. Incidence of and mortality from type I diabetes in Taiwan from 1999 through 2010: a nationwide cohort study. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e86172. PMID: 24465941.
Article7. Ko KW, Yang SW, Cho NH. The incidence of IDDM in Seoul from 1985 to 1988. Diabetes Care. 1994; 17:1473–1475. PMID: 7882820.
Article8. Shin CH. Epidemiologic characteristics of type 1 diabetes in children aged 14 years or under in Korea, 1985-2000. Korean J Pediatr. 2008; 51:569–575.
Article9. Bruno G, Runzo C, Cavallo-Perin P, Merletti F, Rivetti M, Pinach S, Novelli G, Trovati M, Cerutti F, Pagano G. Piedmont Study Group for Diabetes Epidemiology. Incidence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in adults aged 30-49 years: the population-based registry in the province of Turin, Italy. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28:2613–2619. PMID: 16249528.10. Molbak AG, Christau B, Marner B, Borch-Johnsen K, Nerup J. Incidence of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in age groups over 30 years in Denmark. Diabet Med. 1994; 11:650–655. PMID: 7955989.11. Thomas NJ, Jones SE, Weedon MN, Shields BM, Oram RA, Hattersley AT. Frequency and phenotype of type 1 diabetes in the first six decades of life: a cross-sectional, genetically stratified survival analysis from UK Biobank. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018; 6:122–129. PMID: 29199115.
Article12. Kilpatrick ES, Rigby AS, Atkin SL. Insulin resistance, the metabolic syndrome, and complication risk in type 1 diabetes: “double diabetes” in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Diabetes Care. 2007; 30:707–712. PMID: 17327345.13. Thorn LM, Forsblom C, Fagerudd J, Thomas MC, Pettersson-Fernholm K, Saraheimo M, Waden J, Ronnback M, Rosengard-Barlund M, Bjorkesten CG, Taskinen MR, Groop PH. FinnDiane Study Group. Metabolic syndrome in type 1 diabetes: association with diabetic nephropathy and glycemic control (the FinnDiane study). Diabetes Care. 2005; 28:2019–2024. PMID: 16043748.14. Lee YH, Han K, Ko SH, Ko KS, Lee KU. Taskforce Team of Diabetes Fact Sheet of the Korean Diabetes Association. Data analytic process of a nationwide population-based study using national health information database established by National Health Insurance Service. Diabetes Metab J. 2016; 40:79–82. PMID: 26912157.
Article15. Seok H, Jung CH, Kim SW, Lee MJ, Lee WJ, Kim JH, Lee BW. Clinical characteristics and insulin independence of Koreans with new-onset type 2 diabetes presenting with diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2013; 29:507–513. PMID: 23653323.
Article16. Jin SM, Baek JH, Suh S, Jung CH, Lee WJ, Park CY, Yang HK, Cho JH, Lee BW, Kim JH. Factors associated with greater benefit of a national reimbursement policy for blood glucose test strips in adult patients with type 1 diabetes: a prospective cohort study. J Diabetes Investig. 2018; 9:549–557.
Article17. Alberti KG, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, Fruchart JC, James WP, Loria CM, Smith SC Jr. International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention. Hational Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. American Heart Association. World Heart Federation. International Atherosclerosis Society. International Association for the Study of Obesity. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation. 2009; 120:1640–1645. PMID: 19805654.18. Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH, Franklin BA, Gordon DJ, Krauss RM, Savage PJ, Smith SC Jr, Spertus JA, Costa F. American Heart Association. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation. 2005; 112:2735–2752. PMID: 16157765.19. Noh J, Han KD, Ko SH, Ko KS, Park CY. Trends in the pervasiveness of type 2 diabetes, impaired fasting glucose and co-morbidities during an 8-year-follow-up of nationwide Korean population. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:46656. PMID: 28425463.
Article20. Guglielmi C, Palermo A, Pozzilli P. Latent autoimmune diabetes in the adults (LADA) in Asia: from pathogenesis and epidemiology to therapy. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2012; 28(Suppl 2):40–46.
Article21. Imagawa A, Hanafusa T. Fulminant type 1 diabetes: an important subtype in East Asia. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2011; 27:959–964. PMID: 22069293.22. Cho YM, Kim JT, Ko KS, Koo BK, Yang SW, Park MH, Lee HK, Park KS. Fulminant type 1 diabetes in Korea: high prevalence among patients with adult-onset type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2007; 50:2276–2279. PMID: 17724575.
Article23. Rogers MAM, Kim C, Banerjee T, Lee JM. Fluctuations in the incidence of type 1 diabetes in the United States from 2001 to 2015: a longitudinal study. BMC Med. 2017; 15:199. PMID: 29115947.
Article24. Atkinson MA, Eisenbarth GS, Michels AW. Type 1 diabetes. Lancet. 2014; 383:69–82. PMID: 23890997.
Article25. Blohme G, Nystrom L, Arnqvist HJ, Lithner F, Littorin B, Olsson PO, Schersten B, Wibell L, Ostman J. Male predominance of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus in young adults: results from a 5-year prospective nationwide study of the 15-34-year age group in Sweden. Diabetologia. 1992; 35:56–62. PMID: 1541382.
Article26. Casu A, Pascutto C, Bernardinelli L, Songini M. Type 1 diabetes among Sardinian children is increasing: the Sardinian diabetes register for children aged 0-14 years (1989-1999). Diabetes Care. 2004; 27:1623–1629. PMID: 15220238.27. Kyvik KO, Nystrom L, Gorus F, Songini M, Oestman J, Castell C, Green A, Guyrus E, Ionescu-Tirgoviste C, McKinney PA, Michalkova D, Ostrauskas R, Raymond NT. The epidemiology of type 1 diabetes mellitus is not the same in young adults as in children. Diabetologia. 2004; 47:377–384. PMID: 14762657.
Article28. Bruno G, Cerutti F, Merletti F, Cavallo-Perin P, Gandolfo E, Rivetti M, Runzo C, Pinach S, Pagano G. Piedmont Study Group for Diabetes Epidemiology. Residual beta-cell function and male/female ratio are higher in incident young adults than in children: the registry of type 1 diabetes of the province of Turin, Italy, 1984-2000. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28:312–317. PMID: 15677785.29. Almahfoodh D, Alabbood M, Alali A, Mansour A. Epidemiology of type 1 diabetes mellitus in Basrah, Southern Iraq: a retrospective study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017; 133:104–108. PMID: 28926733.
Article30. Shaltout AA, Moussa MA, Qabazard M, Abdella N, Karvonen M, Al-Khawari M, Al-Arouj M, Al-Nakhi A, Tuomilehto J, El-Gammal A. Kuwait Diabetes Study Group. Further evidence for the rising incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes in Kuwait. Diabet Med. 2002; 19:522–525. PMID: 12109439.
Article31. Zayed H. Genetic epidemiology of type 1 diabetes in the 22 Arab countries. Curr Diab Rep. 2016; 16:37. PMID: 26983625.
Article32. Kim MK, Lee SH, Kim JH, Lee JI, Kim JH, Jang EH, Yoon KH, Lee KW, Song KH. Clinical characteristics of Korean patients with new-onset diabetes presenting with diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2009; 85:e8–11. PMID: 19477546.
Article33. WHO Expert Consultation. Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet. 2004; 363:157–163. PMID: 14726171.34. Guy J, Ogden L, Wadwa RP, Hamman RF, Mayer-Davis EJ, Liese AD, D'Agostino R Jr, Marcovina S, Dabelea D. Lipid and lipoprotein profiles in youth with and without type 1 diabetes: the SEARCH for diabetes in youth case-control study. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:416–420. PMID: 19092167.35. Wadwa RP, Kinney GL, Maahs DM, Snell-Bergeon J, Hokanson JE, Garg SK, Eckel RH, Rewers M. Awareness and treatment of dyslipidemia in young adults with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28:1051–1056. PMID: 15855566.
Article36. Jellinger PS, Handelsman Y, Rosenblit PD, Bloomgarden ZT, Fonseca VA, Garber AJ, Grunberger G, Guerin CK, Bell DSH, Mechanick JI, Pessah-Pollack R, Wyne K, Smith D, Brinton EA, Fazio S, Davidson M. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology guidelines for management of dyslipidemia and prevention of cardiovascular disease. Endocr Pract. 2017; 23(Suppl 2):1–87.
Article37. Lim S, Shin H, Song JH, Kwak SH, Kang SM, Won Yoon J, Choi SH, Cho SI, Park KS, Lee HK, Jang HC, Koh KK. Increasing prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Korea: the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey for 1998-2007. Diabetes Care. 2011; 34:1323–1328. PMID: 21505206.38. Kazumi T, Vranic M, Bar-On H, Steiner G. Portal v peripheral hyperinsulinemia and very low density lipoprotein triglyceride kinetics. Metabolism. 1986; 35:1024–1028. PMID: 3534515.39. Taskinen MR. Quantitative and qualitative lipoprotein abnormalities in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1992; 41(Suppl 2):12–17.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome
- Clinical Predictive Factors for Metabolic Syndrome in Obese Children and Adolescents
- Hyperuricemia is Associated With an Increased Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in a General Population and a Decreased Prevalence of Diabetes in Men
- Sex differences in Risk of Cardiovascular Disease, Depression and Self-Care Activities in Type 2 Diabetes with Metabolic Syndrome
- Therapeutic approaches to obesity and metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents