Cancer Res Treat.
2019 Oct;51(4):1336-1346. 10.4143/crt.2018.504.
Changes of Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes after Core Needle Biopsy and the Prognostic Implications in Early Stage Breast Cancer: A Retrospective Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Comprehensive Breast Health Center, Ruijin Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China. kwshen@medmail.com.cn
- 2Department of Pathology, Ruijin Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
- KMID: 2460583
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2018.504
Abstract
- PURPOSE
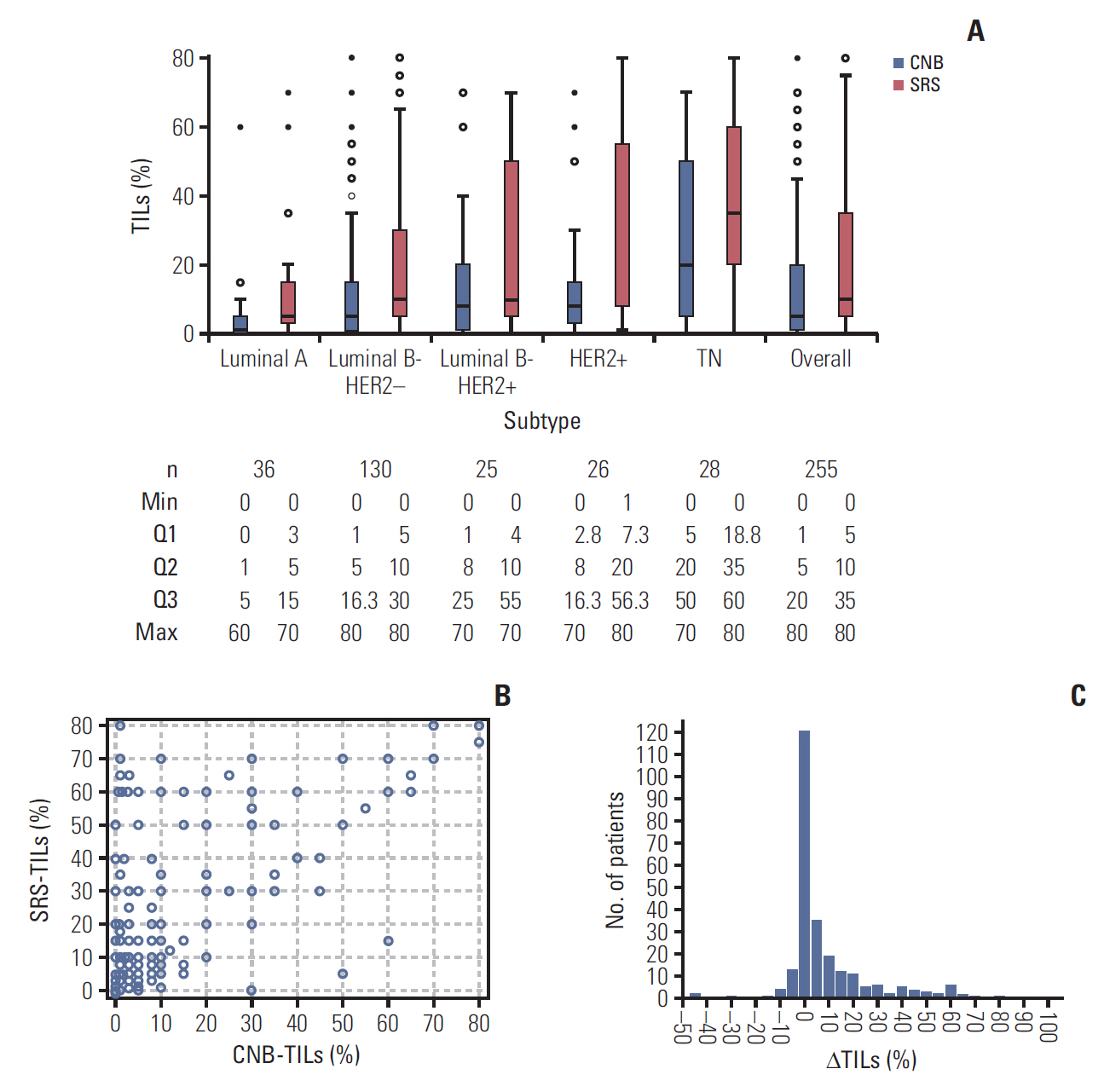
The purpose of this study was to investigate the changes of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) between core needle biopsy (CNB) and surgery removed sample (SRS) in early stage breast cancer patients and to identify the correlating factors and prognostic significance of TILs changes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A retrospective study was carried out on 255 patients who received CNB and underwent surgical resection for invasive breast cancer. Stromal TILs levels of CNB and SRS were evaluated respectively. Tumors with ≥50% stromal TILs were defined as lymphocyte-predominant breast cancer (LPBC). Clinicopathological variables were analyzed to determine whether there were factors associated with TILs changes. Log-rank tests and Cox proportional hazards models were used to analyze the influences of TILs and TILs changes on survival.
RESULTS
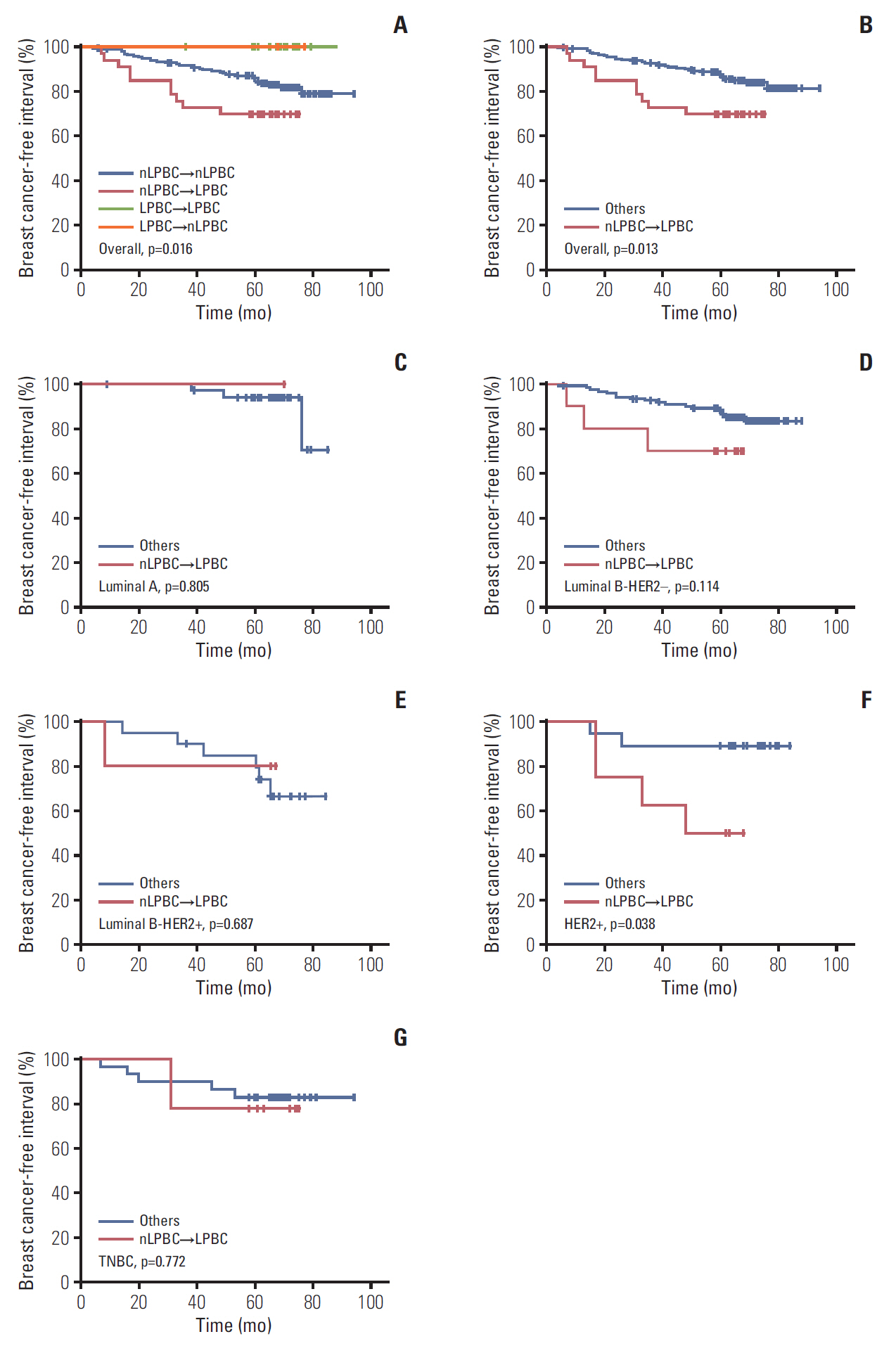
SRS-TILs (median, 10.0%) were significant higher than CNB-TILs (median, 5.0%; p<0.001). Younger age (<60 years, p=0.016) and long surgery time interval (STI, ≥4 days; p=0.003) were independent factors correlating with higher TILs changes. CNB-LPBC patients showed better breast cancer-free interval (BCFI, p=0.021) than CNB-non-LPBC (CNB-nLPBC) patients. Patients were categorized into four groups according to the LPBC change pattern from CNB to SRS: LPBC→LPBC, LPBC→nLPBC, nLPBC→LPBC, and nLPBC→nLPBC, with estimated 5-year BCFI 100%, 100%, 69.7%, and 86.0% (p=0.016). nLPBC→LPBC pattern was an independent prognostic factor of worse BCFI (hazard ratio, 2.19; 95% confidence interval, 1.06 to 4.53; p=0.035) compared with other patterns.
CONCLUSION
TILs were significantly higher in SRS than in CNB. Higher TILs changes were associated with younger age and long STI. Changing from nLPBC to LPBC after CNB indicated a worse BCFI, which needs further validation.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Lee HJ, Seo JY, Ahn JH, Ahn SH, Gong G. Tumor-associated lymphocytes predict response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. J Breast Cancer. 2013; 16:32–9.
Article2. Loi S, Michiels S, Salgado R, Sirtaine N, Jose V, Fumagalli D, et al. Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes are prognostic in triple negative breast cancer and predictive for trastuzumab benefit in early breast cancer: results from the FinHER trial. Ann Oncol. 2014; 25:1544–50.
Article3. Adams S, Gray RJ, Demaria S, Goldstein L, Perez EA, Shulman LN, et al. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancers from two phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trials: ECOG 2197 and ECOG 1199. J Clin Oncol. 2014; 32:2959–66.4. Loi S, Sirtaine N, Piette F, Salgado R, Viale G, Van Eenoo F, et al. Prognostic and predictive value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in a phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trial in node-positive breast cancer comparing the addition of docetaxel to doxorubicin with doxorubicin-based chemotherapy: BIG 02-98. J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31:860–7.
Article5. Pruneri G, Vingiani A, Bagnardi V, Rotmensz N, De Rose A, Palazzo A, et al. Clinical validity of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes analysis in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2016; 27:249–56.
Article6. Denkert C, Loibl S, Noske A, Roller M, Muller BM, Komor M, et al. Tumor-associated lymphocytes as an independent predictor of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:105–13.
Article7. Denkert C, von Minckwitz G, Brase JC, Sinn BV, Gade S, Kronenwett R, et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with or without carboplatin in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive and triple-negative primary breast cancers. J Clin Oncol. 2015; 33:983–91.
Article8. Salgado R, Denkert C, Campbell C, Savas P, Nuciforo P, Aura C, et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and associations with pathological complete response and event-free survival in HER2-positive early-stage breast cancer treated with lapatinib and trastuzumab: a secondary analysis of the NeoALTTO Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2015; 1:448–54.9. Ingold Heppner B, Untch M, Denkert C, Pfitzner BM, Lederer B, Schmitt W, et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes: a predictive and prognostic biomarker in neoadjuvant-treated HER2-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2016; 22:5747–54.
Article10. Salgado R, Denkert C, Demaria S, Sirtaine N, Klauschen F, Pruneri G, et al. The evaluation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer: recommendations by an International TILs Working Group 2014. Ann Oncol. 2015; 26:259–71.
Article11. Denkert C, Wienert S, Poterie A, Loibl S, Budczies J, Badve S, et al. Standardized evaluation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer: results of the ring studies of the international immuno-oncology biomarker working group. Mod Pathol. 2016; 29:1155–64.
Article12. Dowsett M, Smith IE, Ebbs SR, Dixon JM, Skene A, A'Hern R, et al. Prognostic value of Ki67 expression after short-term presurgical endocrine therapy for primary breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007; 99:167–70.
Article13. von Minckwitz G, Schmitt WD, Loibl S, Muller BM, Blohmer JU, Sinn BV, et al. Ki67 measured after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for primary breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2013; 19:4521–31.
Article14. Dieci MV, Criscitiello C, Goubar A, Viale G, Conte P, Guarneri V, et al. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes on residual disease after primary chemotherapy for triple-negative breast cancer: a retrospective multicenter study. Ann Oncol. 2014; 25:611–8.
Article15. Hamy AS, Pierga JY, Sabaila A, Laas E, Bonsang-Kitzis H, Laurent C, et al. Stromal lymphocyte infiltration after neoadjuvant chemotherapy is associated with aggressive residual disease and lower disease-free survival in HER2-positive breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2017; 28:2233–40.
Article16. Garcia-Martinez E, Gil GL, Benito AC, Gonzalez-Billalabeitia E, Conesa MA, Garcia Garcia T, et al. Tumor-infiltrating immune cell profiles and their change after neoadjuvant chemotherapy predict response and prognosis of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2014; 16:488.
Article17. Watanabe T, Hida AI, Inoue N, Imamura M, Fujimoto Y, Akazawa K, et al. Abundant tumor infiltrating lymphocytes after primary systemic chemotherapy predicts poor prognosis in estrogen receptor-positive/HER2-negative breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018; 168:135–45.
Article18. Miyashita M, Sasano H, Tamaki K, Hirakawa H, Takahashi Y, Nakagawa S, et al. Prognostic significance of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ and FOXP3+ lymphocytes in residual tumors and alterations in these parameters after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer: a retrospective multicenter study. Breast Cancer Res. 2015; 17:124.
Article19. Arnedos M, Nerurkar A, Osin P, A'Hern R, Smith IE, Dowsett M. Discordance between core needle biopsy (CNB) and excisional biopsy (EB) for estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PgR) and HER2 status in early breast cancer (EBC). Ann Oncol. 2009; 20:1948–52.
Article20. Chen X, Zhu S, Fei X, Garfield DH, Wu J, Huang O, et al. Surgery time interval and molecular subtype may influence Ki67 change after core needle biopsy in breast cancer patients. BMC Cancer. 2015; 15:822.
Article21. Mann GB, Fahey VD, Feleppa F, Buchanan MR. Reliance on hormone receptor assays of surgical specimens may compromise outcome in patients with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:5148–54.
Article22. Karn T, Metzler D, Ruckhaberle E, Hanker L, Gatje R, Solbach C, et al. Data-driven derivation of cutoffs from a pool of 3,030 Affymetrix arrays to stratify distinct clinical types of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010; 120:567–79.23. Tagliabue E, Agresti R, Carcangiu ML, Ghirelli C, Morelli D, Campiglio M, et al. Role of HER2 in wound-induced breast carcinoma proliferation. Lancet. 2003; 362:527–33.
Article24. Goldhirsch A, Winer EP, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thurlimann B, et al. Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer: highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2013. Ann Oncol. 2013; 24:2206–23.25. Jeselsohn RM, Werner L, Regan MM, Fatima A, Gilmore L, Collins LC, et al. Digital quantification of gene expression in sequential breast cancer biopsies reveals activation of an immune response. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e64225.
Article26. Mathenge EG, Dean CA, Clements D, Vaghar-Kashani A, Photopoulos S, Coyle KM, et al. Core needle biopsy of breast cancer tumors increases distant metastases in a mouse model. Neoplasia. 2014; 16:950–60.
Article27. Vaupel P, Mayer A. Tumor oxygenation status: facts and fallacies. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017; 977:91–9.
Article28. Globerson A, Effros RB. Ageing of lymphocytes and lymphocytes in the aged. Immunol Today. 2000; 21:515–21.
Article29. Mao Y, Qu Q, Chen X, Huang O, Wu J, Shen K. The prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0152500.
Article30. Khan AM, Yuan Y. Biopsy variability of lymphocytic infiltration in breast cancer subtypes and the ImmunoSkew score. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:36231.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pseudoaneurysm of the Breast after Core Needle Biopsy: A Case Report
- Screening and Diagnosis for Breast Cancers
- Track Seeding in a Breast Cancer Patient after a 14-Gauge Core Needle Biopsy: A Case Report
- Changes of Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocytes in Breast Cancer after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
- Breast Lesions with Discordant Results on Ultrasound-guided Core Needle Biopsy