J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2019 Oct;60(10):922-928. 10.3341/jkos.2019.60.10.922.
Comparison of Corneal Astigmatism and Higher-order Aberrations between Color Light-emitting Diode Topographer and Scheimpflug Imager
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. chungsh@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2460509
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2019.60.10.922
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare corneal astigmatism, keratometry and corneal higher order aberrations between the light emitting diode corneal topography analyzer and Scheimpflug Imager.
METHODS
This prospective study involved 45 patients (45 eyes) who visited Seoul St. Mary's hospital before cataract surgery from June 7, 2017, to August 2, 2017. For each eye, keratometry, astigmatism and its axis of cornea, higher-order aberrations were evaluated with a Scheimpflug Imager (Pentacam HR®, Oculus, Wetzlar, Germany) and a color-LED corneal topographer (Cassini®, i-Optics, Den Haag, The Netherlands).
RESULTS
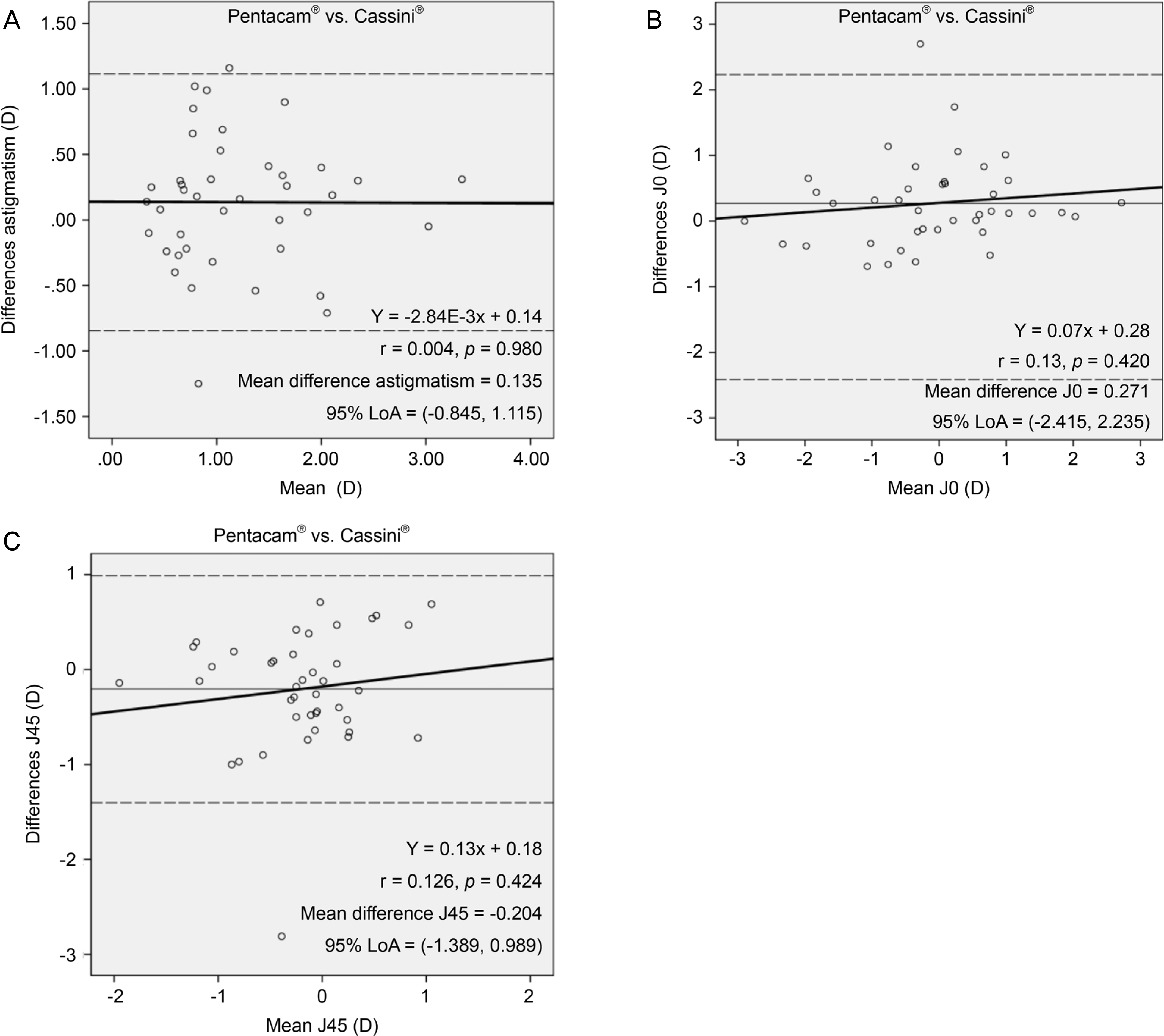
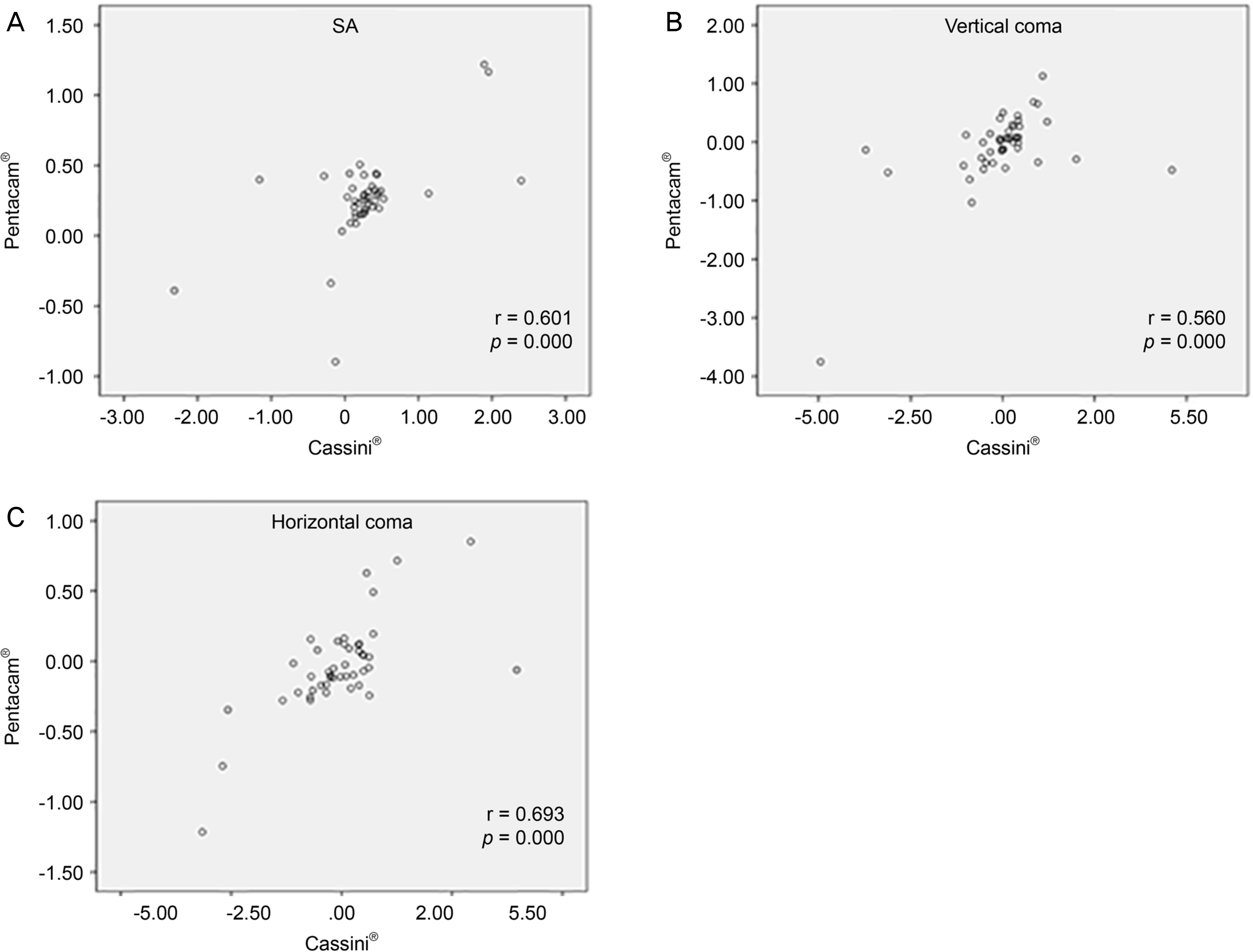
Astigmatism magnitude measured using Cassini® and Pentacam® showed no statistically differences but anterior and total astigmatic axes were significantly different, as measured by the two devices (p < 0.05). Anterior and total mean keratometry were statistically significantly different, as measured by the two devices (p < 0.05). J0 and J45 vectors of anterior and total cornea were statistically different (p < 0.05). In addition, Cassini® and Pentacam® showed discrepancies between total corneal astigmatism, total J0 and J45 vectors. Corneal anterior spherical aberration, vertical and horizontal coma, and oblique and horizontal trefoil aberrations were not statistically different between the two devices.
CONCLUSIONS
Astigmatic axes obtained from the two devices based on different principles showed statistically significant differences. Astigmatism magnitude was not statistically different but showed a discrepancy between the two devices.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ferreira TB, Ribeiro FJ. A novel color-LED corneal topographer to assess astigmatism in pseudophakic eyes. Clin Ophthalmol. 2016; 10:1521–9.
Article2. Lombardo M, Lombardo G. Wave aberration of human eyes and new descriptors of image optical quality and visual performance. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:313–31.
Article3. Artal P, Berrio E, Guirao A, Piers P. Contribution of the cornea and internal surfaces to the change of ocular aberrations with age. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis. 2002; 19:137–43.
Article4. Bellucci R, Morselli S, Piers P. Comparison of wavefront abdominals and optical quality of eyes implanted with five different abdominal lenses. J Refract Surg. 2004; 20:297–306.5. Ventura BV, Wang L, Ali SF, et al. Comparison of corneal power, astigmatism, and wavefront aberration measurements obtained by a point-source color light-emitting diode-based topographer, a Placido-disk topographer, and a combined Placido and dual Scheimpflug device. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2015; 41:1658–71.
Article6. Kanellopoulos AJ, Asimellis G. Color light-emitting diode abdominal topography: validation of keratometric repeatability in a large sample of wide cylindrical-range corneas. Clin Ophthalmol. 2015; 9:245–52.7. Barkana Y, Gerber Y, Elbaz U, et al. Central corneal thickness measurement with the Pentacam Scheimpflug system, optical low-coherence reflectometry pachymeter, and ultrasound pachymetry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:1729–35.
Article8. Koch DD, Ali SF, Weikert MP, et al. Contribution of posterior abdominal astigmatism to total corneal astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:2080–7.9. Kanellopoulos AJ, Asimellis G. Distribution and repeatability of corneal astigmatism measurements (magnitude and axis) evaluated with color light emitting diode reflection topography. Cornea. 2015; 34:937–44.
Article10. Klijn S, Reus NJ, van der Sommen CM, Sicam VA. Accuracy of total corneal astigmatism measurements with a scheimpflug imager and a color light-emitting diode corneal topographer. Am J Ophthalmol. 2016; 167:72–8.
Article11. Davison JA, Potvin R. Refractive cylinder outcomes after abdominal toric intraocular lens cylinder power using total corneal abdominal power. Clin Ophthalmol. 2015; 9:1511–7.12. Klijn S, Reus NJ, Sicam VA. Evaluation of keratometry with a abdominal color-LED corneal topographer. J Refract Surg. 2015; 31:249–56.13. Mejía-Barbosa Y, Malacara-Hernández D. A review of methods for measuring corneal topography. Optom Vis Sci. 2001; 78:240–53.
Article14. Hoffmann PC, Abraham M, Hirnschall N, Findl O. Prediction of residual astigmatism after cataract surgery using swept source fourier domain optical coherence tomography. Current Eye Res. 2014; 39:1178–86.
Article15. Elliott M, Simpson T, Richter D, Fonn D. Repeatability and abdominal of automated refraction: a comparison of the Nikon NRK-8000, the Nidek AR-1000, and subjective refraction. Optom Vis Sci. 1997; 74:434–8.16. Choi YJ, Kang NH, Jun RM. Comparison of corneal higher-order aberrations measured with two instruments using scheimpflug camera system. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015; 56:1497–504.
Article17. Shin JY, Lee MY, Chung SH. Comparison of keratometry and abdominal higher order aberrations between scout videokeratoscope and pentacam scheimpflug camera. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014; 55:1758–64.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Power Vector and Aberrations Using Corneal Topographer and Wavefront Aberrometer Before and After Pterygium Surgery
- Changes in Corneal Higher-order Aberrations and Astigmatism after Upper Eyelid Surgery
- Changes in Higher-order Aberrations after Superior-incision Cataract Surgery in Patients with Positive Vertical Coma
- Surgically Induced Astigmatism and Corneal Higher Order Aberrations in Microcoaxial and Conventional Cataract Surgery
- Comparing Changes in Corneal Astigmatism Using Scheimpflug Camera after Epiblepharon Correction Surgery