Perinatology.
2019 Sep;30(3):160-170. 10.14734/PN.2019.30.3.160.
Levothyroxine Sodium Administration and Late Circulatory Collapse in Premature Infants with Thyroid Dysfunction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Gyeongsang National University Changwon Hospital, Changwon, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea. csassi@hanmail.net
- 3Institute of Health Science, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 2460030
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14734/PN.2019.30.3.160
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Levothyroxine sodium (LT4) is considered safe, and widely administered to premature infants with thyroid dysfunction. Late circulatory collapse (LCC) has not been defined clearly, but it has been characterized as refractory hypotension in premature infants. Recently, LCC after LT4 administration was reported in Japan. However, there is controversy on the aspect of LT4 as a risk factor of LCC. The purpose of this study was to investigate relations between LT4 administration and LCC in premature infants.
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed medical records of premature infants (≤32 weeks gestation) admitted in Gyeongsang National University Hospital between 2011 and 2018. To investigate the relation between LT4 supplementation and LCC, clinical and laboratory findings were reviewed and compared between premature infants with and without LCC.
RESULTS
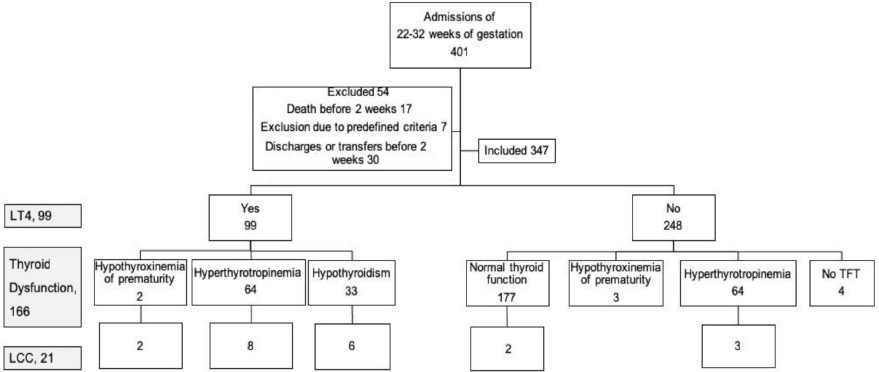
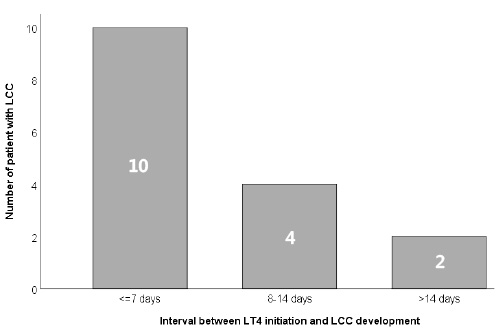
Among 347 premature infants, LCC occurred in 21 (6.1%) on median 19.0th day. Sixteen (76.2%) of 21 infants with LCC were receiving LT4 and LCC was developed on median 3.0 days after LT4 initiation. Gestational age ≤28 weeks, birth weight <1.5 kg, hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus, culture proven sepsis, necrotizing enterocolitis, congenital hypothyroidism, use of LT4 and diuretics, values of serum thyroid stimulating hormone, free thyroxine and sodium were significantly statistically different between LCC and no LCC group. Prematurity ≤28 weeks of gestation and LT4 replacement were risk factors of LCC on multivariate logistic regression analysis.
CONCLUSION
Supplementation of LT4 should be carefully considered in premature infants with thyroid dysfunction and serial monitoring of blood pressure should be warranted if LT4 was administered.
MeSH Terms
-
Birth Weight
Blood Pressure
Congenital Hypothyroidism
Diuretics
Ductus Arteriosus, Patent
Enterocolitis, Necrotizing
Gestational Age
Humans
Hypotension
Infant
Infant, Newborn
Infant, Premature*
Japan
Logistic Models
Medical Records
Pregnancy
Retrospective Studies
Risk Factors
Sepsis
Shock*
Sodium
Thyroid Gland*
Thyrotropin
Thyroxine*
Diuretics
Sodium
Thyrotropin
Thyroxine
Figure
Reference
-
1. Iijima S. Current knowledge of transient hypothyroxinemia of prematurity: to treat or not to treat? J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019; 32:2591–2597.
Article2. Kaluarachchi DC, Colaizy TT, Pesce LM, Tansey M, Klein JM. Congenital hypothyroidism with delayed thyroid-stimulating hormone elevation in premature infants born at less than 30 weeks gestation. J Perinatol. 2017; 37:277–282.
Article3. Lee JH, Kim SW, Jeon GW, Sin JB. Thyroid dysfunction in very low birth weight preterm infants. Korean J Pediatr. 2015; 58:224–229.
Article4. Chung HR, Shin CH, Yang SW, Choi CW, Kim BI, Kim EK, et al. High incidence of thyroid dysfunction in preterm infants. J Korean Med Sci. 2009; 24:627–631.
Article5. La Gamma EF, Korzeniewski SJ, Nigel Paneth PB. Transient hypothyroxinemia of prematurity. Neoreviews. 2016; 17:e394–e402.
Article6. Chung ML, Yoo HW, Kim KS, Lee BS, Pi SY, Lim G, et al. Thyroid dysfunctions of prematurity and their impacts on neurodevelopmental outcome. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 26:449–455.
Article7. Kawai M. Late-onset circulatory collapse of prematurity. Pediatr Int. 2017; 59:391–396.
Article8. Masumoto K, Kusuda S, Aoyagi H, Tamura Y, Obonai T, Yamasaki C, et al. Comparison of serum cortisol concentrations in preterm infants with or without late-onset circulatory collapse due to adrenal insufficiency of prematurity. Pediatr Res. 2008; 63:686–690.
Article9. Lee WJ, Kim MY, Cho HJ, Lee JS, Son DW. Clinical features of late-onset circulatory collapse in preterm infants. Korean J Perinatol. 2013; 24:148–157.
Article10. Takizawa F, Kashimada K, Enomoto K, Miyai K, Ono M, Asada G, et al. Two preterm infants with late onset circulatory collapse induced by levothyroxine sodium. Pediatr Int. 2010; 52:e154–e157.
Article11. Kawai M, Kusuda S, Cho K, Horikawa R, Takizawa F, Ono M, et al. Nationwide surveillance of circulatory collapse associated with levothyroxine administration in very-low-birthweight infants in Japan. Pediatr Int. 2012; 54:177–181.
Article12. Shimokaze T, Saito E, Akaba K. Increased incidence of late-onset circulatory collapse after changing clinical practice: a retrospective investigation of causative factors. Am J Perinatol. 2015; 32:1169–1176.13. Sehgal A, McNamara PJ. Does echocardiography facilitate determination of hemodynamic significance attributable to the ductus arteriosus? Eur J Pediatr. 2009; 168:907–914.
Article14. Bell MJ, Ternberg JL, Feigin RD, Keating JP, Marshall R, Barton L, et al. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Therapeutic decisions based upon clinical staging. Ann Surg. 1978; 187:1–7.15. Papile LA, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. J Pediatr. 1978; 92:529–534.
Article16. Jobe AH, Bancalari E. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001; 163:1723–1729.
Article17. Fierson WM. American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Ophthalmology, American Academy of Ophthalmology, American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus, American Association of Certified Orthoptists. Screening examination of premature infants for retinopathy of prematurity. Pediatrics. 2013; 131:189–195.18. LaFranchi SH. Thyroid hormone studies. In : Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, Geme JS, Schor NF, editors. Nelson textbook of pediatrics. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier;2016. p. 2664.19. Ares S, Quero J, de Escobar GM. Iodine balance, iatrogenic excess, and thyroid dysfunction in premature newborns. Semin Perinatol. 2008; 32:407–412.
Article20. Okada J, Iwata S, Hirose A, Kanda H, Yoshino M, Maeno Y, et al. Levothyroxine replacement therapy and refractory hypotension out of transitional period in preterm infants. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2011; 74:354–364.
Article21. Haugen BR. Drugs that suppress TSH or cause central hypothyroidism. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 23:793–800.
Article22. Kloiber LL, Winn NJ, Shaffer SG, Hassanein RS. Late hyponatremia in very-low-birth-weight infants: incidence and associated risk factors. J Am Diet Assoc. 1996; 96:880–884.23. Kim YJ, Lee JA, Oh S, Choi CW, Kim EK, Kim HS, et al. Risk factors for late-onset hyponatremia and its influence on neonatal outcomes in preterm infants. J Korean Med Sci. 2015; 30:456–462.
Article24. Gokçe İK, Oguz SS. Late onset hyponatremia in preterm newborns: is the sodium content of human milk fortifier insufficient. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018; 09. 20. DOI: 10.1080/14767058.2018.1517314. [Epub].
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Screening and management of thyroid dysfunction in preterm infants
- Clinical Features of Late-Onset Circulatory Collapse in Preterm Infants
- Thyroid Dysfunction in Premature Infants
- Late-onset Hypotension and Late Circulatory Collapse Due to Adrenal Insufficiency in Preterm Infants with Gestational Age Less than 32 Weeks
- Clinical Features of Late-onset Circulatory Collapse in Preterm Infants