Anat Cell Biol.
2019 Sep;52(3):255-261. 10.5115/acb.19.021.
Restoration and conservation of anatomic pieces
- Affiliations
-
- 1Medicine Program, Universidad de Ciencias de Aplicadas y Ambientales U.D.C.A, Bogotá, Colombia. Camcardenas@udca.edu.co
- 2Department of Human Morphology, Faculty of Medicine, Universidad de Ciencias Aplicadas y Ambientales U.D.C.A, Bogotá, Colombia.
- KMID: 2459540
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.19.021
Abstract
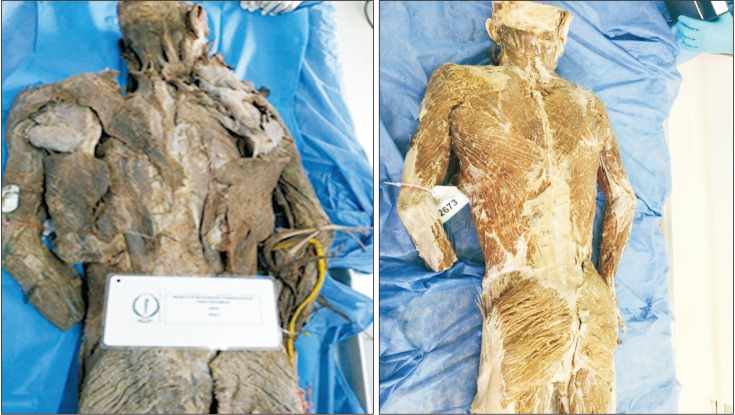
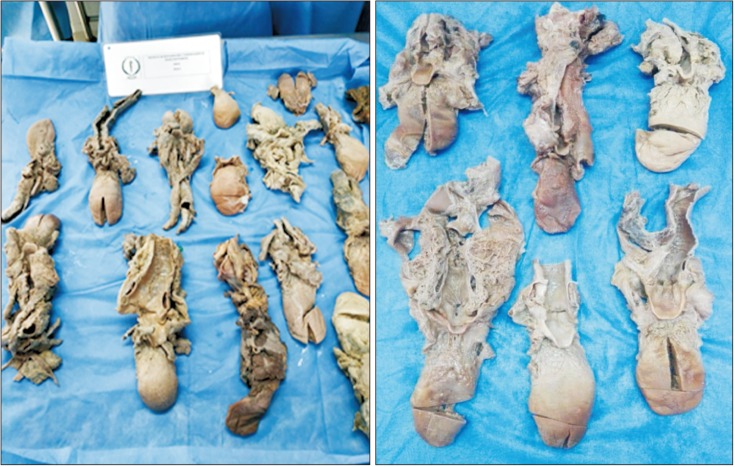
- In this study, a restoration process was developed with potassium hydroxide (KOH), in order to improve each of the structures for their posterior fixation, through the use of new methods such as the Chilean conservative fixative solution (SFCCh), with exceptional results. Restore anatomical pieces corresponding to corpse and organs, being these last set with the SFCCh. In this work dealt with processes of restoration with potassium hydroxide, sodium chloride, and sodium hypochlorite, the process began with the cleanliness and suture of the structures for subsequent fixing in Chilean conservative fixative solution, making use of a corpse and different anatomical parts. Work based on items found in the database, Elsevier, Science Direct, ProQuest, and MEDLINE. At the end of the process of restoration and conservation of the anatomical pieces, was observed an improvement in muscle pigment with decrease of rigidity in the specimen, additionally a recovery of appearance in the vascular-nervous elements was achieved. The organs were much more malleable and the structures facilitate the identification of specific details, its subsequent immersion in SFCCh allows the longer preservation of the obtained results. The restoration with potassium hydroxide allows the improvement in the appearance of the different anatomical structures and simultaneously to facilitate its study. The SFCCh is an alternative that replaces partially the use of formaldehyde. In addition, it presents toxicity reduction.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Condemayta DC, Condemayta ZC, Butrón OO, Rojas MM. Comparative study techniques of anatomical conservation of sheep corpsesat altitude, using formaldehyde solution and prives. Rev Invest Altoandin. 2014; 16:33–38.2. Pulido Guerrero JA, Valderrama Sandoval JA. Determination of the minimum inhibitory concentration of formaldehyde capable of decreasing bacterial growth of strains obtained in cadaveric conservation pools [BS thesis]. Bogota: Pontifical Xavierian University;2007.3. Giménez Mas J. White paper on pathological anatomy in Spain, 2009. Zaragoza: Sociedad Española de Anatomía Patológica;2009.4. Hurtado E, Vallecampo A, De Liévano K, De Artiga B, Vásquez G. Measurements of formaldehyde concentrations in a human anatomy lab compared to internatonal standards. Rev Cientifica Crea Ciencia. 2017; 11:7–13.5. Franco JC. Restauración de piezas anatómicas humanas [dissertation]. Bogota: Universidad Nacional de Colombia;2013.6. Sánchez Carpio C, Andromaco M, Páez R, Barello MD, Pedernera G. Study of new techniques for the preservation of anatomical pieces. Plastination. Rev Salud Publ. 2012; 16:27–32.7. Ortega Orozco LA. Recuperación restauración de componentes anatómicos humanos extremidades superiors [thesis]. Bogota: Universidad Nacional de Colombia;2014.8. Idrobo-Avila EH, Vásquez-López JA, Vargas-Cañas R. Occupational exposure to formaldehyde and new table of occupational diseases. Rev Salud Publica (Bogota). 2017; 19:382–385. PMID: 30183945.9. Gómez CA, Ortiz JA. Preservation and elaboration of anatomic pieces with substances other than formol at La Salle University's Department of Agricultural Sciences. Rev Med Vet. 2011; 22:51–55.10. Muñetón Gómez CA, Ortiz JA. Preparation in glycerin: a technique for prolonged preservation of bodies in veterinary anatomy. Rev Med Vet. 2013; 26:115–122.11. Segura Cavanzo C, Quintero F, Rubio Rincon EA. V Congreso Colombiano de Morfolofía. Int J Morphol. 2010; 28:337–340.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Factors Influencing Health Conservation among Elders
- Conservation Surgery for Hypopharyngeal Cancer
- Influence of Frailty, Nutritional Status, Positive Thinking and Family Function on Health Conservation of the Elderly at Home
- A study on the attitude affecting the preventive behavior for hearing conservation
- The Effects of Elderly Diabetes Mellitus Patients' Self-care Behavior and Health Conservation on Cardiovascular Risk Factors