J Rheum Dis.
2019 Oct;26(4):278-281. 10.4078/jrd.2019.26.4.278.
A Case of Rapid Progressive Neurosyphilis in Patient with Ankylosing Spondylitis Who Is Treating Anti-interleukin 17A Monoclonal Antibody, Secukinumab
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea. dream1331@naver.com
- 2Division of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Neuroradiology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2459453
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2019.26.4.278
Abstract
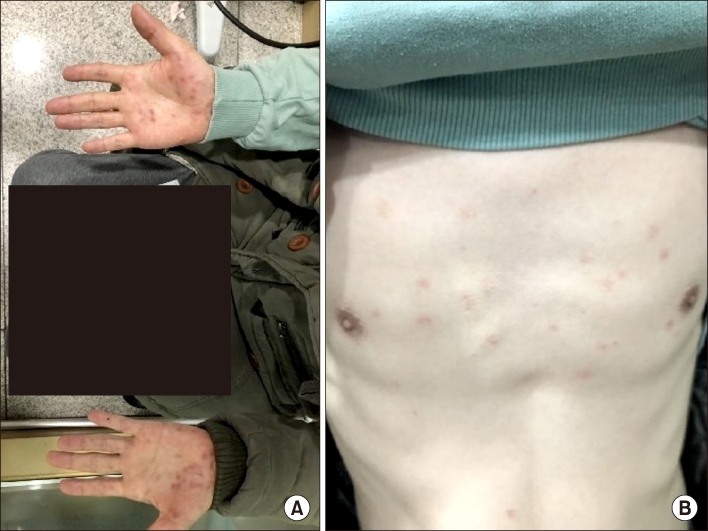
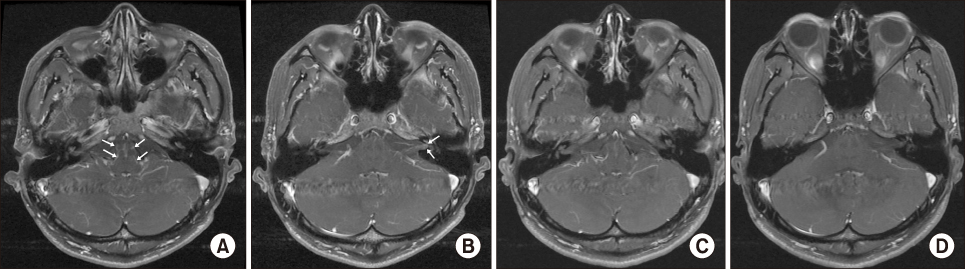
- Anti-interleukin 17A agent, secukinumab is remarkably effective for treating patients with ankylosing spondylitis. However, the main safety concern of secukinumab is an increased risk of infection. Generally, neurosyphilis occurs a few years after the primary syphilitic infection. Rare cases of progressing to neurosyphilis with a much lower latency were reported. We report a case of rapid progressive neurosyphilis involving hearing loss in both ears in a patient with ankylosing spondylitis who was treated with secukinumab.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Timmermans M, Carr J. Neurosyphilis in the modern era. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004; 75:1727–1730.2. Marra CM. Neurosyphilis. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2015; 21(6 Neuroinfectious Disease):1714–1728.
Article3. Langley RG, Kimball AB, Nak H, Xu W, Pangallo B, Osuntokun OO, et al. Long-term safety profile of ixekizumab in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: an integrated analysis from 11 clinical trials. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019; 33:333–339.4. Iglesias-Plaza A, Iglesias-Sancho M, Quintana-Codina M, García-Miguel J, Salleras-Redonnet M. Syphilis in the setting of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy. Reumatol Clin. 2018; 02. 03. DOI: 10.1016/j.reuma.2017.12.008. [Epub].
Article5. Bories-Haffner C, Buche S, Paccou J. Secondary syphilis occurring under anti-TNFalpha therapy. Joint Bone Spine. 2010; 77:364–365.6. Assikar S, Doffoel-Hantz V, Sparsa A, Bonnetblanc JM. Early neurosyphilis with etanercept treatment. Eur J Dermatol. 2013; 23:901–902.
Article7. Drago F, Merlo G, Ciccarese G, Agnoletti AF, Cozzani E, Rebora A, et al. Changes in neurosyphilis presentation: a survey on 286 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016; 30:1886–1900.8. Nagappa M, Sinha S, Taly AB, Rao SL, Nagarathna S, Bindu PS, et al. Neurosyphilis: MRI features and their phenotypic correlation in a cohort of 35 patients from a tertiary care university hospital. Neuroradiology. 2013; 55:379–388.
Article9. Pastuszczak M, Jakiela B, Wielowieyska-Szybinska D, Jaworek AK, Zeman J, Wojas-Pelc A. Elevated cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-17A and interferon-γ levels in early asymptomatic neurosyphilis. Sex Transm Dis. 2013; 40:808–812.10. Stary G, Klein I, Brüggen MC, Kohlhofer S, Brunner PM, Spazierer D, et al. Host defense mechanisms in secondary syphilitic lesions: a role for IFN-gamma-/IL-17-producing CD8+ T cells? Am J Pathol. 2010; 177:2421–2432.11. Sadeghani K, Kallini JR, Khachemoune A. Neurosyphilis in a man with human immunodeficiency virus. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014; 7:35–40.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Sensorineural Hearing Loss Caused by Neurosyphilis in Patient Who Is Treated by Anti-Interleukin 17A Monoclonal Antibody
- A Case of Nummular Eczema-Like Eruption after Secukinumab Treatment
- A New Medical Therapy for Axial Spondyloarthritis
- Eczematous Vesicular Rruption and Exacerbation of Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria Associated with Secukinumab
- Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Secukinumab and Adalimumab in Patients with Active Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Bayesian Network Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials