J Rheum Dis.
2019 Oct;26(4):264-272. 10.4078/jrd.2019.26.4.264.
Effect of Drug Adherence on Treatment Outcome in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea. kiwonmoon@kangwon.ac.kr
- 2Department of Biomedical Informatics, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Office of Biostatistics, Ajou Research Institute for Innovative Medicine, Ajou University Medical Center, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2459451
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2019.26.4.264
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The present study aimed to evaluate the effect of drug adherence on treatment outcome in Korean patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
METHODS
A total of 2,694 RA patients who had complete data from annual follow-ups over three years in the Korean Observational Study Network for Arthritis were included in this study. Patients were divided into adherent and non-adherent groups according to data for drug adherence over three years. The European League against Rheumatism response and rate of disease flare were compared between two groups over three years. We also compared continuous variables representing treatment outcomes between the two groups.
RESULTS
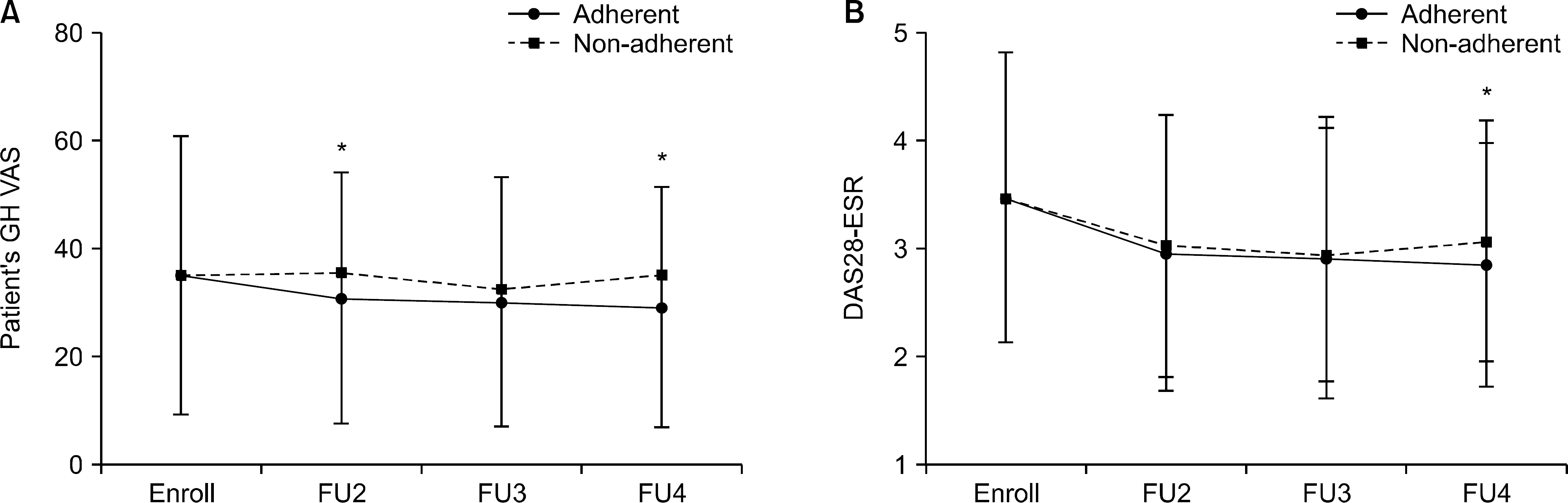
After propensity score matching using a ratio of 1:3, patients were allocated into non-adherent (n=522) and adherent (n=1,447) groups. The rate of non-response was higher in the non-adherent group over three years; however, there were no significant differences between continuous variables related to treatment outcome between the two groups. To evaluate the difference according to disease duration, patients were classified into early and late RA based on 48-month disease duration. In patients with early RA, the adherent group had lower patient's global health visual analog scale and lower disease activity 28 scores at three years compared with the non-adherence group. In patients with late RA, the non-adherent group had a higher rate of disease flare.
CONCLUSION
The adherent group tended to show lower disease activity, especially in early RA, whereas the non-adherence group was associated with non-response and higher risk of disease flare.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Time-integrated Cumulative Parameters Predictive of Radiographic Progression of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Real-world Data From a Prospective Single-center Cohort
Youngjae Park, Mei-Ling Li, Ji-Won Kim, Jung Hee Koh, Yune-Jung Park, Wan-Uk Kim
J Rheum Dis. 2022;29(2):98-107. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2022.29.2.98.
Reference
-
1. Li L, Cui Y, Yin R, Chen S, Zhao Q, Chen H, et al. Medication adherence has an impact on disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2017; 11:1343–56.
Article2. Nakagawa S, Nakaishi M, Hashimoto M, Ito H, Yamamoto W, Nakashima R, et al. Effect of medication adherence on disease activity among Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One. 2018; 13:e0206943.
Article3. Pasma A, van't Spijker A, Hazes JM, Busschbach JJ, Luime JJ. Factors associated with adherence to pharmaceutical treatment for rheumatoid arthritis patients: a systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2013; 43:18–28.
Article4. Sung YK, Cho SK, Choi CB, Park SY, Shim J, Ahn JK, et al. Korean Observational Study Network for Arthritis (KORONA): establishment of a prospective multicenter cohort for rheumatoid arthritis in South Korea. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2012; 41:745–51.
Article5. van Gestel AM, Prevoo ML, van't Hof MA, van Rijswijk MH, van de Putte LB, van Riel PL. Development and validation of the European League Against Rheumatism response criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Comparison with the preliminary American College of Rheumatology and the World Health Organization/International League Against Rheumatism Criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1996; 39:34–40.
Article6. van der Maas A, Lie E, Christensen R, Choy E, de Man YA, van Riel P, et al. Construct and criterion validity of several proposed DAS28-based rheumatoid arthritis flare criteria: an OMERACT cohort validation study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013; 72:1800–5.
Article7. van den Bemt BJ, Zwikker HE, van den Ende CH. Medication adherence in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a critical appraisal of the existing literature. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2012; 8:337–51.
Article8. Pasma A, Schenk CV, Timman R, Busschbach JJ, van den Bemt BJ, Molenaar E, et al. Non-adherence to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs is associated with higher disease activity in early arthritis patients in the first year of the disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015; 17:281.
Article9. Kim D, Choi JY, Cho SK, Choi CB, Bang SY, Cha HS, et al. Prevalence and associated factors for nonadherence in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheum Dis. 2018; 25:47–57.
Article10. Scheiman-Elazary A, Duan L, Shourt C, Agrawal H, Ellashof D, Cameron-Hay M, et al. The rate of adherence to anti-arthritis medications and associated factors among patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic literature review and metaanalysis. J Rheumatol. 2016; 43:512–23.
Article11. de Klerk E, van der Heijde D, Landewé R, van der Tempel H, Urquhart J, van der Linden S. Patient compliance in rheumatoid arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, and gout. J Rheumatol. 2003; 30:44–54.12. Pascual-Ramos V, Contreras-Yáñez I, Villa AR, Cabiedes J, Rull-Gabayet M. Medication persistence over 2 years of follow-up in a cohort of early rheumatoid arthritis patients: associated factors and relationship with disease activity and with disability. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009; 11:R26.
Article13. Fransen J, Laan RF, Van Der Laar MA, Huizinga TW, Van Riel PL. Influence of guideline adherence on outcome in a randomised controlled trial on the efficacy of methotrexate with folate supplementation in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004; 63:1222–6.
Article14. Lathia U, Ewara EM, Nantel F. Impact of adherence to biological agents on health care resource utilization for patients over the age of 65 years with rheumatoid arthritis. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2017; 11:1133–42.
Article15. Wabe NT, Sorich MJ, Wechalekar MD, Cleland LG, McWilliams L, Lee AT, et al. Effect of adherence to proto-colized targeted intensifications of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs on treatment outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis: results from an Australian early arthritis cohort. J Rheumatol. 2016; 43:1643–9.
Article16. Wabe N, Lee A, Wechalekar M, McWilliams L, Proudman S, Wiese M. Adherence to combination DMARD therapy and treatment outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis: a longitudinal study of new and existing DMARD users. Rheumatol Int. 2017; 37:897–904.
Article17. Osterberg L, Blaschke T. Adherence to medication. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:487–97.
Article18. Cannon GW, Mikuls TR, Hayden CL, Ying J, Curtis JR, Reimold AM, et al. Merging veterans affairs rheumatoid arthritis registry and pharmacy data to assess methotrexate adherence and disease activity in clinical practice. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011; 63:1680–90.
Article19. Kumar K, Raza K, Gill P, Greenfield S. The impact of using musculoskeletal ultrasound imaging and other influencing factors on medication adherence in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a qualitative study. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2016; 10:1091–100.
Article20. Jimmy B, Jose J. Patient medication adherence: measures in daily practice. Oman Med J. 2011; 26:155–9.
Article21. de Jongh T, Gurol-Urganci I, Vodopivec-Jamsek V, Car J, Atun R. Mobile phone messaging for facilitating self-management of long-term illnesses. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012; 12:CD007459.
Article22. Mary A, Boursier A, Desailly Henry I, Grados F, Séjourné A, Salomon S, et al. Mobile phone text messages improve treatment adherence in patients taking methotrexate for rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized pilot study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2018 Sep 7; [Epub].DOI: DOI:10.1002/acr.23750.23. Salaffi F, Carotti M, Di Carlo M, Farah S, Gutierrez M. Adherence to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy administered subcutaneously and associated factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2015; 21:419–25.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Factors Affecting Medication Adherence in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Medical Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Can We Calculate Patients' Compliance and Forecast Their Adherence to Medication: Cultural Adaptation of the Korean Version of a Compliance Questionnaire for Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis
- Clinical significance of rheumatoid factor in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis