Yonsei Med J.
2019 Oct;60(10):944-951. 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.10.944.
Various Treatment Modalities in Hepatic Hydrothorax: What Is Safe and Effective?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Chonnam National University Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. choisk@jnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, Chonnam National University Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Hwasun, Korea.
- 4Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Chonnam National University Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. yochuni@naver.com
- KMID: 2459147
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2019.60.10.944
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Hepatic hydrothorax is a complication of decompensated liver cirrhosis that is difficult and complex to manage. Data concerning the optimal treatment method, other than liver transplantation, are limited. This study aimed to compare the clinical features and outcomes of patients treated with various modalities, while focusing on surgical management and pigtail drainage.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
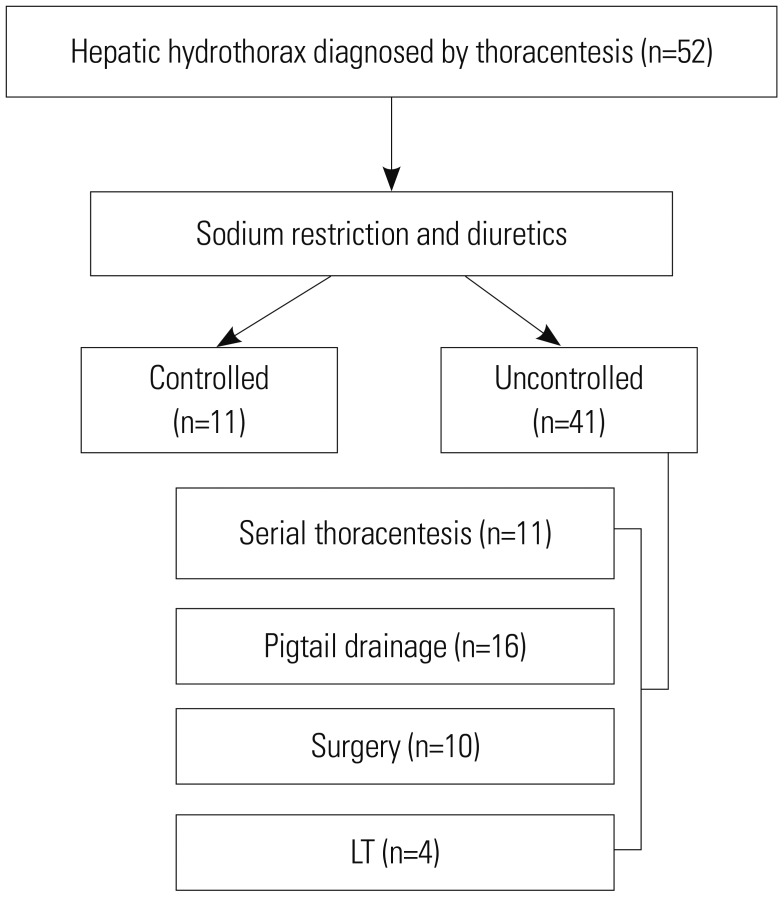
Forty-one patients diagnosed with refractory hepatic hydrothorax between January 2013 and December 2017 were enrolled.
RESULTS
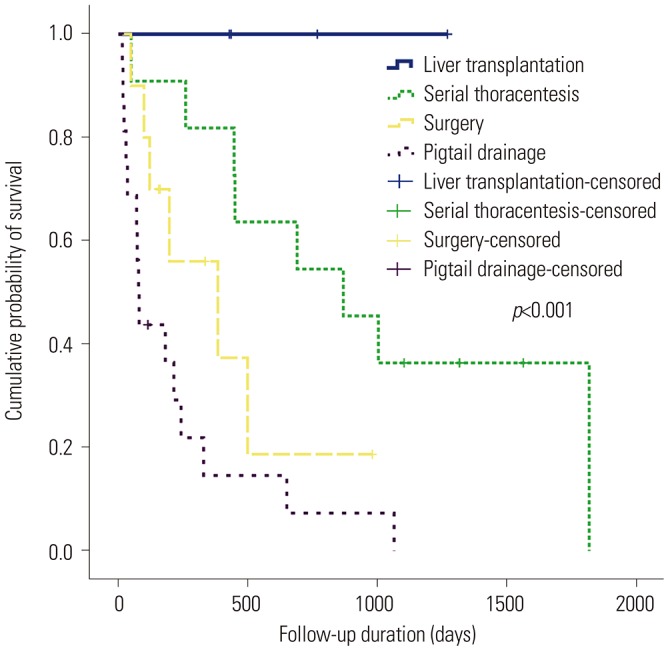
The mean Child-Turcotte-Pugh and model for end stage liver disease scores of the enrolled patients were 10.1 and 19.7, respectively. The patients underwent four modalities: serial thoracentesis (n=11, 26.8%), pigtail drainage (n=16, 39.0%), surgery (n=10, 24.4%), and liver transplantation (n=4, 9.8%); 12-month mortality rate/median survival duration was 18.2%/868 days, 87.5%/79 days, 70%/179 days, and 0%/601.5 days, respectively. Regarding the management of refractory hepatic hydrothorax, surgery group required less frequent needle puncture (23.5 times in pigtail group vs. 9.3 times in surgery group), had a lower occurrence of hepatorenal syndrome (50% vs. 30%), and had a non-inferior cumulative overall survival (402.1 days vs. 221.7 days) compared to pigtail group. On multivariate analysis for poor survival, body mass index <19 kg/m², refractory hepatic hydrothorax not managed with liver transplantation, Child-Turcotte-Pugh score >10, and history of severe encephalopathy (grade >2) were associated with poor survival.
CONCLUSION
Serial thoracentesis may be recommended for management of hepatic hydrothorax and surgical management can be a useful option in patients with refractory hepatic hydrothorax, alternative to pigtail drainage.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Diagnosis and Management of Hepatic Hydrothorax
Amie Vidyani, Citra Indriani Sibarani, Budi Widodo, Herry Purbayu, Husin Thamrin, Muhammad Miftahussurur, Poernomo Boedi Setiawan, Titong Sugihartono, Ulfa Kholili, Ummi Maimunah
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2024;83(2):45-53. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2023.107.
Reference
-
1. Malagari K, Nikita A, Alexopoulou E, Brountzos E, Papathanasiou M, Mitromaras J, et al. Cirrhosis-related intrathoracic disease. Imaging features in 1038 patients. Hepatogastroenterology. 2005; 52:558–562. PMID: 15816477.2. Foschi FG, Piscaglia F, Pompili M, Corbelli C, Marano G, Righini R, et al. Real-time contrast-enhanced ultrasound--a new simple tool for detection of peritoneal-pleural communications in hepatic hydrothorax. Ultraschall Med. 2008; 29:538–542. PMID: 19241513.3. Rubinstein D, McInnes IE, Dudley FJ. Hepatic hydrothorax in the absence of clinical ascites: diagnosis and management. Gastroenterology. 1985; 88(1 Pt 1):188–191. PMID: 3964765.
Article4. Xiol X, Tremosa G, Castellote J, Gornals J, Lama C, Lopez C, et al. Liver transplantation in patients with hepatic hydrothorax. Transpl Int. 2005; 18:672–675. PMID: 15910292.
Article5. Lazaridis KN, Frank JW, Krowka MJ, Kamath PS. Hepatic hydrothorax: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. Am J Med. 1999; 107:262–267. PMID: 10492320.
Article6. The Korean Association for the Study of the Liver (KASL). KASL clinical practice guidelines for liver cirrhosis: ascites and related complications. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2018; 24:230–277. PMID: 29991196.7. Machicao VI, Balakrishnan M, Fallon MB. Pulmonary complications in chronic liver disease. Hepatology. 2014; 59:1627–1637. PMID: 24089295.
Article8. Moore KP, Wong F, Gines P, Bernardi M, Ochs A, Salerno F, et al. The management of ascites in cirrhosis: report on the consensus conference of the International Ascites Club. Hepatology. 2003; 38:258–266. PMID: 12830009.
Article9. Hsu SL, Tseng CW. Comparison of treatment of hepatic hydrothorax with catheter drainage versus serial thoracentesis. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2018; 24:392–397. PMID: 29521656.
Article10. Badillo R, Rockey DC. Hepatic hydrothorax: clinical features, management, and outcomes in 77 patients and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2014; 93:135–142. PMID: 24797168.11. Hung TH, Tseng CW, Tsai CC, Hsieh YH, Tseng KC, Tsai CC. Mortality following catheter drainage versus thoracentesis in cirrhotic patients with pleural effusion. Dig Dis Sci. 2017; 62:1080–1085. PMID: 28130709.
Article12. Peters TJ, Martin F, Ward K. Chronic alcoholic skeletal myopathy--common and reversible. Alcohol. 1985; 2:485–489. PMID: 3161521.
Article13. Porcel JM. Management of refractory hepatic hydrothorax. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2014; 20:352–357. PMID: 24811830.
Article14. Mouroux J, Perrin C, Venissac N, Blaive B, Richelme H. Management of pleural effusion of cirrhotic origin. Chest. 1996; 109:1093–1096. PMID: 8635335.
Article15. Milanez de Campos JR, Andrade Filho LO, de Campos Werebe E, Pandulo FL, Filomeno LT, Jatene FB. Hepatic hydrothorax. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2001; 22:665–674. PMID: 16088711.
Article16. Milanez de Campos JR, Filho LO, de Campos Werebe E, Sette H Jr, Fernandez A, Filomeno LT, et al. Thoracoscopy and talc poudrage in the management of hepatic hydrothorax. Chest. 2000; 118:13–17. PMID: 10893352.
Article17. Nakamura Y, Iwazaki M, Yasui N, Seki H, Matsumoto H, Masuda R, et al. Diaphragmatic repair of hepatic hydrothorax with VATS after abdominal insufflation with CO(2). Asian J Endosc Surg. 2012; 5:141–144. PMID: 22823172.
Article18. Luh SP, Chen CY. Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) for the treatment of hepatic hydrothorax: report of twelve cases. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2009; 10:547–551. PMID: 19585673.
Article19. Strauss RM, Boyer TD. Hepatic hydrothorax. Semin Liver Dis. 1997; 17:227–232. PMID: 9308127.
Article20. Alberts WM, Salem AJ, Solomon DA, Boyce G. Hepatic hydrothorax. Cause and management. Arch Intern Med. 1991; 151:2383–2388. PMID: 1746994.
Article21. Cardenas A, Kelleher T, Chopra S. Review article: hepatic hydrothorax. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004; 20:271–279. PMID: 15274663.22. Emerson PA, Davies JH. Hydrothorax complicating ascites. Lancet. 1955; 268:487–488. PMID: 13234425.
Article23. Bhattacharya A, Mittal BR, Biswas T, Dhiman RK, Singh B, Jindal SK, et al. Radioisotope scintigraphy in the diagnosis of hepatic hydrothorax. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001; 16:317–321. PMID: 11339424.
Article24. Alonso JC. Pleural effusion in liver disease. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2010; 31:698–705. PMID: 21213201.
Article25. Degawa M, Hamasaki K, Yano K, Nakao K, Kato Y, Sakamoto I, et al. Refractory hepatic hydrothorax treated with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. J Gastroenterol. 1999; 34:128–131. PMID: 10204623.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Complete Remission of Refractory Hepatic Hydrothorax in Patient with Advanced Liver Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt
- A Case of Refractory Hepatic Hydrothorax That Was Not Treated by Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt
- A Case of the Hepatic Hydrothorax in the Absence of Ascites Confirmed by Tc-99m Macroaggregated Serum Albumin Scan
- Diagnosis and Management of Hepatic Hydrothorax
- A case of hepatic hydrothorax