Transl Clin Pharmacol.
2019 Sep;27(3):87-88. 10.12793/tcp.2019.27.3.87.
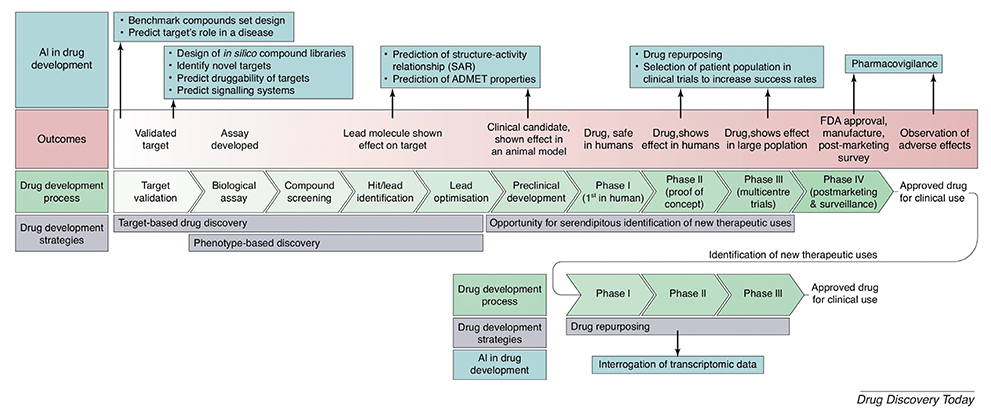
Artificial intelligence in drug development: clinical pharmacologist perspective
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics College of Medicine, Seoul National University and Seoul National University Hospital, Clinical Trials Center, SNU Hospital, Seoul 03080, Korea. ijjang@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2458946
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12793/tcp.2019.27.3.87
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Esteva A, Robicquet A, Ramsundar B, Kuleshov V, DePristo M, Chou K, et al. A guide to deep learning in healthcare. Nat Med. 2019; 25:24–29. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-018-0316-z.
Article2. Bakkar N, Kovalik T, Lorenzini I, Spangler S, Lacoste A, Sponaugle K, et al. Artificial intelligence in neurodegenerative disease research: use of IBM Watson to identify additional RNA-binding proteins altered in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2018; 135:227–247. DOI: 10.1007/s00401-017-1785-8.
Article3. Mak KK, Pichika MR. Artificial intelligence in drug development: present status and future prospects. Drug Discov Today. 2019; 24:773–780. DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2018.11.014.
Article4. Harrer S, Shah P, Antony B, Hu J. Artificial Intelligence for Clinical Trial Design. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2019; 40:577–591. DOI: 10.1016/j.tips.2019.05.005.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Role of medical doctor in the era of artificial intelligence
- Role of Artificial Intelligence in Achieving Universal Health Coverage: A Mongolian Perspective
- Crew Resource Management in Industry 4.0: Focusing on Human-Autonomy Teaming
- Artificial Intelligence in Pathology
- Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Mammography from a Development and Validation Perspective