Chonnam Med J.
2018 Jan;54(1):78-79. 10.4068/cmj.2018.54.1.78.
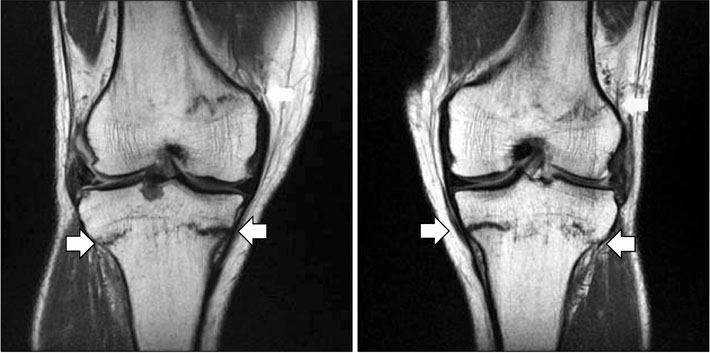
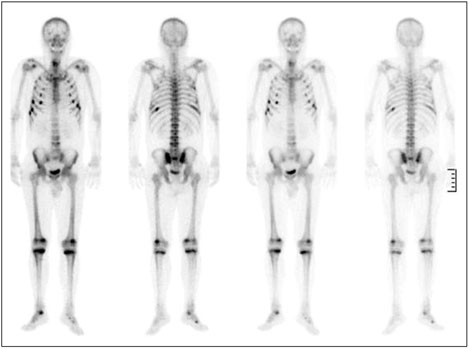
Hypophosphatemic Osteomalacia with Multiple Bone Fractures: ADV-Induced Fanconi's Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Research Institute of Clinical Medicine, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea. kaleey@jbnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2458591
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4068/cmj.2018.54.1.78
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Izzedine H, Launay-Vacher V, Isnard-Bagnis C, Deray G. Drug-induced Fanconi's syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003; 41:292–309.
Article2. Eguchi H, Tsuruta M, Tani J, Kuwahara R, Hiromatsu Y. Hypophosphatemic osteomalacia due to drug-induced Fanconi's syndrome associated with adefovir dipivoxil treatment for hepatitis B. Intern Med. 2014; 53:233–237.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pathologic Femoral Neck Fracture Due to Fanconi Syndrome Induced by Adefovir Dipivoxil Therapy for Hepatitis B
- Sporadic Nonfamilial Hypophosphatemic Osteomalacia
- An Uncommon Case of Bilateral Pathologic Hip Fractures: Antiviral Drug-induced Osteomalacia in a Patient with Hepatitis B
- Three Cases of Osteomalacia with Fractures Induced by Adefovir in Chronic Hepatitis B
- Fanconi's Syndrome Associated with Prolonged Adefovir Dipivoxil Therapy in a Hepatitis B Virus Patient