Imaging Sci Dent.
2019 Sep;49(3):229-234. 10.5624/isd.2019.49.3.229.
Diagnostic considerations in central odontogenic fibroma of the maxilla: 2 case reports
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Graduate School, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. ohbbang50@gmail.com
- KMID: 2458372
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2019.49.3.229
Abstract
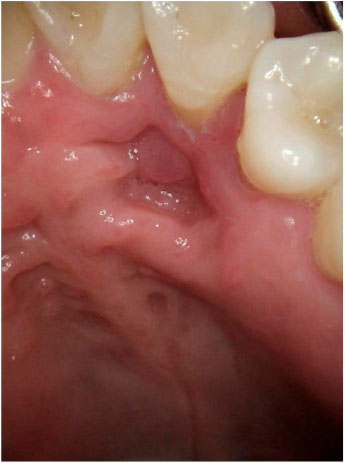
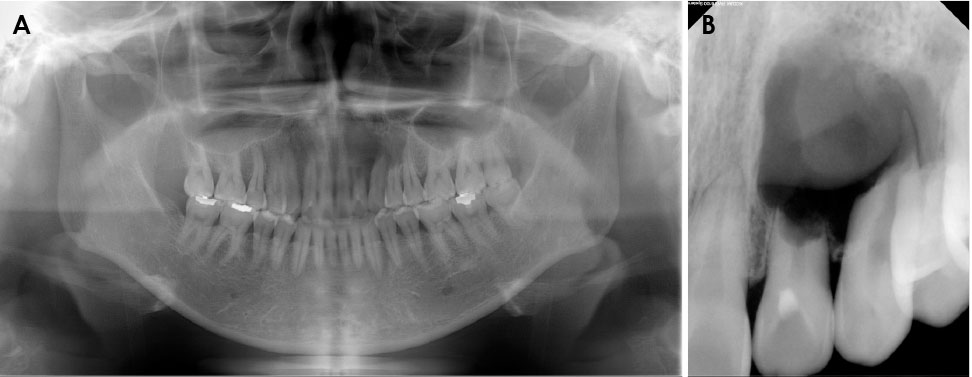
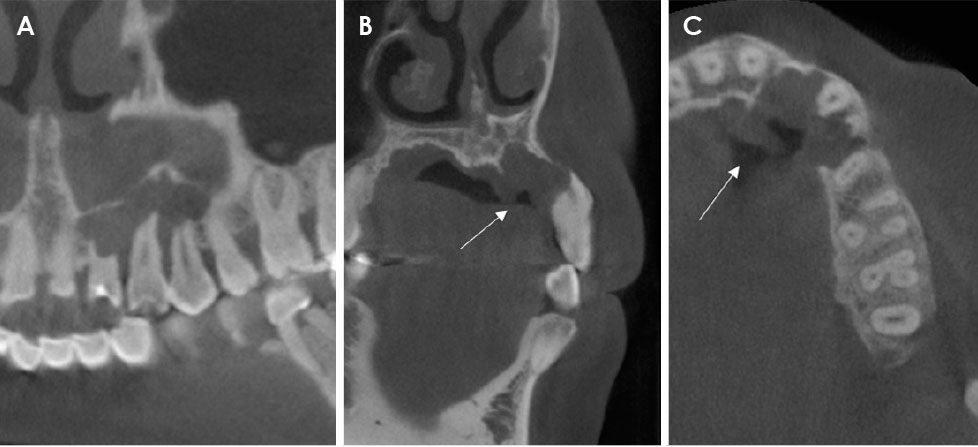
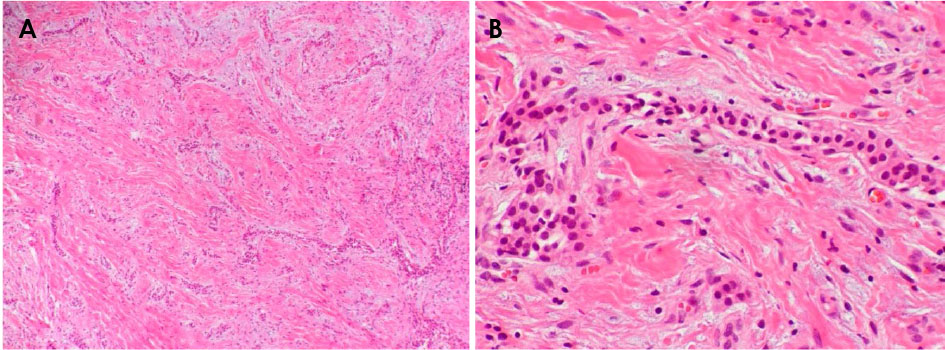
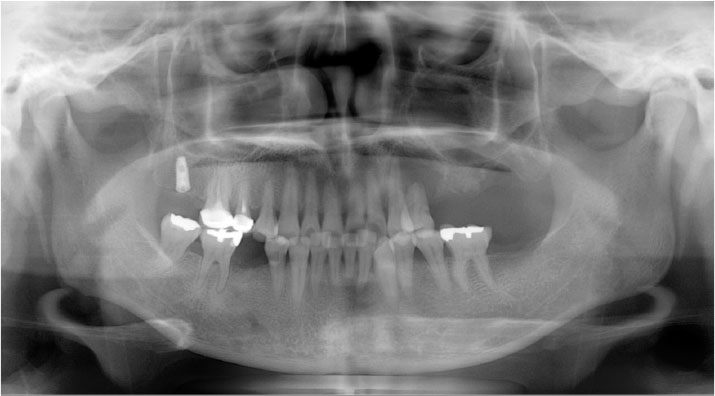
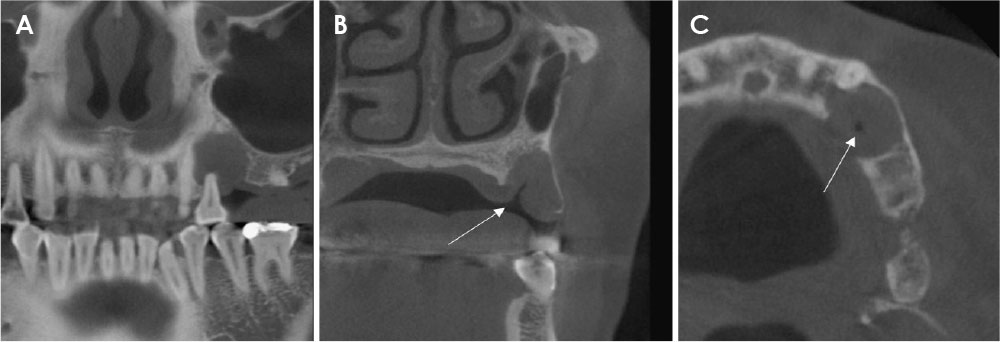
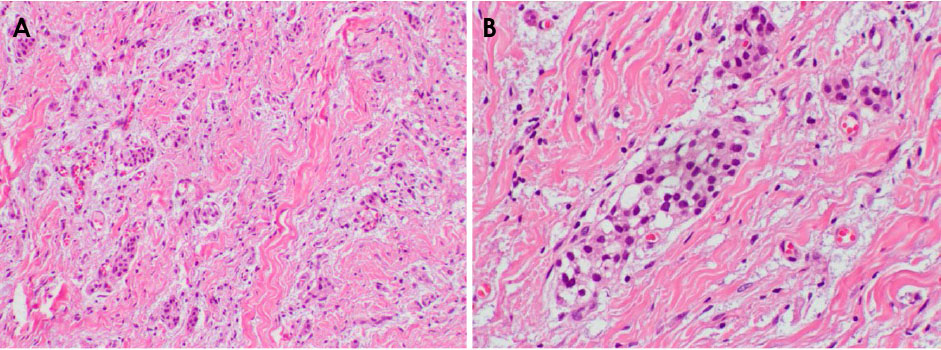
- Central odontogenic fibroma (COF) is defined as a fibroblastic odontogenic tumor characterized by varying density of the tooth epithelium. It is an extremely rare benign neoplasm that occurs in the maxilla and the mandible; only a few reports of COF are available in the literature. Diagnosis of the lesion based only on the radiological features of COF is difficult due to variation in the findings regarding this condition. This report describes 2 clinical cases of middle-aged women with COF. Clinical examination revealed palatal mucosal depression; additionally, oral examination, as well as panoramic radiographs, intraoral radiographs, and computed tomography scans, revealed severe root resorption. This report highlights the clinical and radiological imaging features of COF, with the goal of enabling straightforward differential diagnosis of the lesion by the clinician and thereby appropriate treatment of the patient.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wesley RK, Wysocki GP, Mintz SM. The central odontogenic fibroma. Clinical and morphologic studies. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1975; 40:235–245.2. Philipsen HP, Reichart PA. Classification of odontogenic tumours. A historical review. J Oral Pathol Med. 2006; 35:525–529.
Article3. Covani U, Crespi R, Perrini N, Barone A. Central odontogenic fibroma: a case report. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2005; 10 Suppl 2:E154–E157.4. Ramer M, Buonocore P, Krost B. Central odontogenic fibroma - report of a case and review of the literature. Periodontal Clin Investig. 2002; 24:27–30.5. Handlers JP, Abrams AM, Melrose RJ, Danforth R. Central odontogenic fibroma: clinicopathologic features of 19 cases and review of the literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1991; 49:46–54.
Article6. Huey MW, Bramwell JD, Hutter JW, Kratochvil FJ. Central odontogenic fibroma mimicking a lesion of endodontic origin. J Endod. 1995; 21:625–627.
Article7. Rebai-Chabchoub N, Marbaix E, Iriarte Ortabe JI, Reychler H. Central odontogenic fibroma. Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 1993; 94:271–275.8. Daniels JS. Central odontogenic fibroma of mandible: a case report and review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2004; 98:295–300.
Article9. Kaffe I, Buchner A. Radiologic features of central odontogenic fibroma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1994; 78:811–818.
Article10. Hara M, Matsuzaki H, Katase N, Yanagi Y, Unetsubo T, Asaumi J, et al. Central odontogenic fibroma of the jawbone: 2 case reports describing its imaging features and an analysis of its DCE-MRI findings. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2012; 113:e51–e58.
Article11. Kawai N, Wakasa T, Asaumi J, Kishi K. A radiographic study on resorption of tooth root associated with malignant tumors. Oral Radiol. 2000; 16:55–65.
Article12. Hirschberg A, Buchner A, Dayan D. The central odontogenic fibroma and the hyperplastic dental follicle: study with Picrosirius red and polarizing microscopy. J Oral Pathol Med. 1996; 25:125–127.
Article13. Iordanidis S, Poulopoulos A, Epivatianos A, Zouloumis L. Central odontogenic fibroma: report of case with immunohistochemical study. Indian J Dent Res. 2013; 24:753–755.
Article14. Vered M, Shohat I, Buchner A, Dayan D. Myofibroblasts in stroma of odontogenic cysts and tumors can contribute to variations in the biological behavior of lesions. Oral Oncol. 2005; 41:1028–1033.
Article15. Cercadillo-Ibarguren I, Berini-Aytés L, Marco-Molina V, Gay-Escoda C. Locally aggressive central odontogenic fibroma associated to an inflammatory cyst: a clinical, histological and immunohistochemical study. J Oral Pathol Med. 2006; 35:513–516.
Article16. Veeravarmal V, Madhavan RN, Nassar MM, Amsaveni R. Central odontogenic fibroma of the maxilla. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2013; 17:319.
Article17. Mosqueda-Taylor A, Martínez-Mata G, Carlos-Bregni R, Vargas PA, Toral-Rizo V, Cano-Valdéz AM, et al. Central odontogenic fibroma: new findings and report of a multicentric collaborative study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011; 112:349–358.
Article