Korean J Radiol.
2016 Oct;17(5):695-705. 10.3348/kjr.2016.17.5.695.
Real-Time MRI Navigated Ultrasound for Preoperative Tumor Evaluation in Breast Cancer Patients: Technique and Clinical Implementation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Ansan 15355, Korea. seoboky@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2458061
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.5.695
Abstract
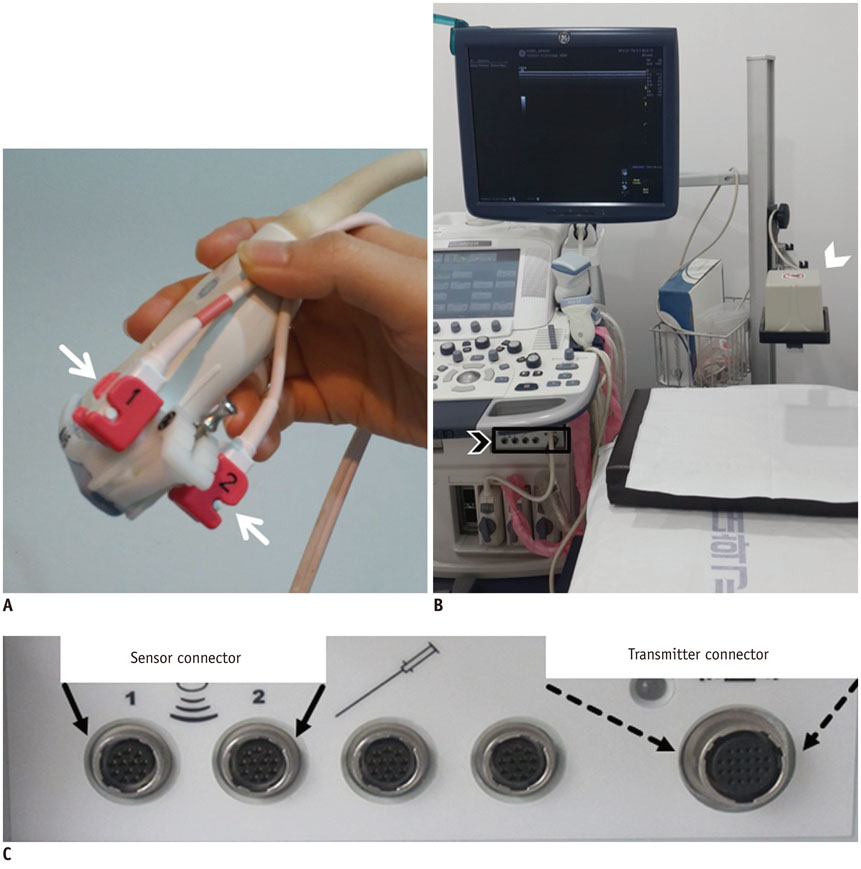
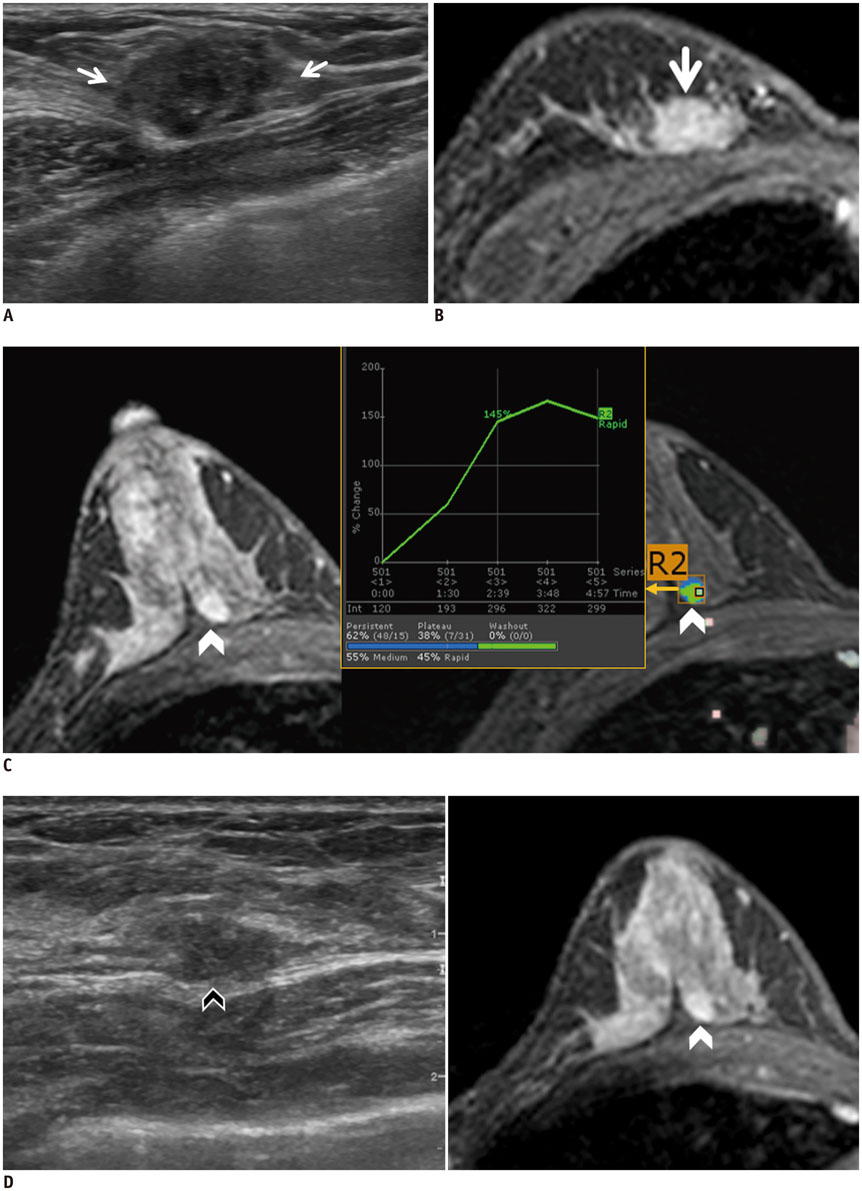
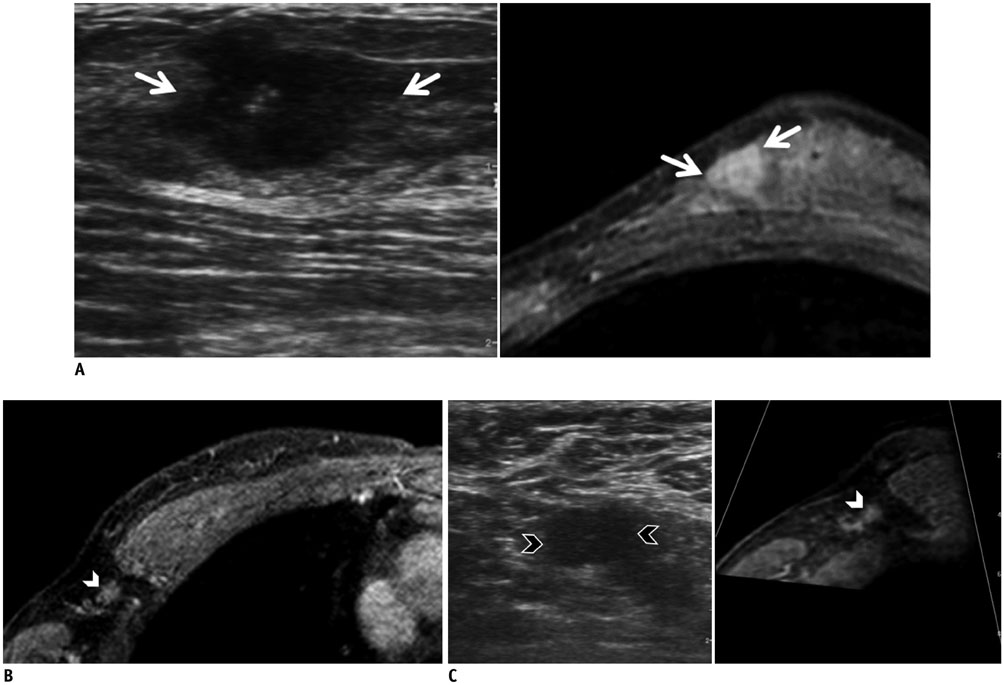
- Real-time magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) navigated ultrasound is an image fusion technique to display the results of both MRI and ultrasonography on the same monitor. This system is a promising technique to improve lesion detection and analysis, to maximize advantages of each imaging modality, and to compensate the disadvantages of both MRI and ultrasound. In evaluating breast cancer stage preoperatively, MRI and ultrasound are the most representative imaging modalities. However, sometimes difficulties arise in interpreting and correlating the radiological features between these two different modalities. This pictorial essay demonstrates the technical principles of the real-time MRI navigated ultrasound, and clinical implementation of the system in preoperative evaluation of tumor extent, multiplicity, and nodal status in breast cancer patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Identification of Preoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Features Associated with Positive Resection Margins in Breast Cancer: A Retrospective Study
Jung-Hyun Kang, Ji Hyun Youk, Jeong-Ah Kim, Hye Mi Gweon, Na Lae Eun, Kyung Hee Ko, Eun Ju Son
Korean J Radiol. 2018;19(5):897-904. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.5.897.
Reference
-
1. Ewertsen C, Săftoiu A, Gruionu LG, Karstrup S, Nielsen MB. Real-time image fusion involving diagnostic ultrasound. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013; 200:W249–W255.2. Maintz JB, Viergever MA. A survey of medical image registration. Med Image Anal. 1998; 2:1–36.3. Lee MW. Fusion imaging of real-time ultrasonography with CT or MRI for hepatic intervention. Ultrasonography. 2014; 33:227–239.4. Stang A, Keles H, Hentschke S, Seydewitz C, Keuchel M, Pohland C, et al. Real-time ultrasonography-computed tomography fusion imaging for staging of hepatic metastatic involvement in patients with colorectal cancer: initial results from comparison to US seeing separate CT images and to multidetector-row CT alone. Invest Radiol. 2010; 45:491–501.5. Okamoto E, Sato S, Sanchez-Siles AA, Ishine J, Miyake T, Amano Y, et al. Evaluation of virtual CT sonography for enhanced detection of small hepatic nodules: a prospective pilot study. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 194:1272–1278.6. Kunishi Y, Numata K, Morimoto M, Okada M, Kaneko T, Maeda S, et al. Efficacy of fusion imaging combining sonography and hepatobiliary phase MRI with Gd-EOB-DTPA to detect small hepatocellular carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012; 198:106–114.7. Lee MW, Rhim H, Cha DI, Kim YJ, Choi D, Kim YS, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: fusion imaging guidance for management of lesions with poor conspicuity at conventional sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012; 198:1438–1444.8. Minami Y, Chung H, Kudo M, Kitai S, Takahashi S, Inoue T, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: value of virtual CT sonography with magnetic navigation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008; 190:W335–W341.9. Nakai M, Sato M, Sahara S, Takasaka I, Kawai N, Minamiguchi H, et al. Radiofrequency ablation assisted by real-time virtual sonography and CT for hepatocellular carcinoma undetectable by conventional sonography. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2009; 32:62–69.10. Yamamoto S, Maeda N, Tamesa M, Nagashima Y, Yoshimura K, Oka M. Prospective ultrasonographic prediction of sentinel lymph node metastasis by real-time virtual sonography constructed with three-dimensional computed tomography-lymphography in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer. 2012; 19:77–82.11. Kuhl CK. The "coming of age" of nonmammographic screening for breast cancer. JAMA. 2008; 299:2203–2205.12. Sardanelli F, Giuseppetti GM, Panizza P, Bazzocchi M, Fausto A, Simonetti G, et al. Sensitivity of MRI versus mammography for detecting foci of multifocal, multicentric breast cancer in Fatty and dense breasts using the whole-breast pathologic examination as a gold standard. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004; 183:1149–1157.13. Kuhl CK, Schrading S, Leutner CC, Morakkabati-Spitz N, Wardelmann E, Fimmers R, et al. Mammography, breast ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging for surveillance of women at high familial risk for breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:8469–8476.14. Sardanelli F, Podo F, D'Agnolo G, Verdecchia A, Santaquilani M, Musumeci R, et al. Multicenter comparative multimodality surveillance of women at genetic-familial high risk for breast cancer (HIBCRIT study): interim results. Radiology. 2007; 242:698–715.15. Nakano S, Kousaka J, Fujii K, Yorozuya K, Yoshida M, Mouri Y, et al. Impact of real-time virtual sonography, a coordinated sonography and MRI system that uses an image fusion technique, on the sonographic evaluation of MRI-detected lesions of the breast in second-look sonography. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012; 134:1179–1188.16. Nakano S, Yoshida M, Fujii K, Yorozuya K, Kousaka J, Mouri Y, et al. Real-time virtual sonography, a coordinated sonography and MRI system that uses magnetic navigation, improves the sonographic identification of enhancing lesions on breast MRI. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2012; 38:42–49.17. Nakano S, Yoshida M, Fujii K, Yorozuya K, Mouri Y, Kousaka J, et al. Fusion of MRI and sonography image for breast cancer evaluation using real-time virtual sonography with magnetic navigation: first experience. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2009; 39:552–559.18. Pons EP, Azcón FM, Casas MC, Meca SM, Espona JL. Real-time MRI navigated US: role in diagnosis and guided biopsy of incidental breast lesions and axillary lymph nodes detected on breast MRI but not on second look US. Eur J Radiol. 2014; 83:942–950.19. Fausto A, Casella D, Mantovani L, Giacalone G, Volterrani L. Clinical value of second-look ultrasound: is there a way to make it objective? Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81:Suppl 1. S36–S40.20. Hong MJ, Cha JH, Kim HH, Shin HJ, Chae EY, Shin JE, et al. Second-look ultrasonography for MRI-detected suspicious breast lesions in patients with breast cancer. Ultrasonography. 2015; 34:125–132.21. Chang JM, Han W, Moon HG, Yi A, Cho N, Koo HR, et al. Evaluation of tumor extent in breast cancer patients using real-time MR navigated ultrasound: preliminary study. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81:3208–3215.22. Rizzatto G, Fausto A. Breast imaging and volume navigation: Mr imaging and ultrasound coregistration. Ultrasound Clin. 2009; 4:261–271.23. Fausto A, Rizzatto G, Preziosa A, Gaburro L, Washburn MJ, Rubello D, et al. A new method to combine contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging during live ultrasound of the breast using volume navigation technique: a study for evaluating feasibility, accuracy and reproducibility in healthy volunteers. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81:e332–e337.24. Erguvan-Dogan B, Whitman G. Breast ultrasound mr imaging correlation. Ultrasound Clin. 2006; 1:593–601.25. McMahon K, Medoro L, Kennedy D. Breast magnetic resonance imaging: an essential role in malignant axillary lymphadenopathy of unknown origin. Australas Radiol. 2005; 49:382–389.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Differences of Tumor Size Measured by Ultrasonography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Compared to Pathological Tumor Size in Primary Breast Cancer
- The Role of Preoperative Breast MRI in Patients With Early-Stage Breast Cancer
- Clinical Applications of Breast MRI
- Fusion Imaging of MRI and US for Evaluating Breast Lesions
- The Clinical Significance of Preoperative MRI for Determination of Surgery in Breast Cancer