Ann Rehabil Med.
2019 Aug;43(4):465-473. 10.5535/arm.2019.43.4.465.
Effect of Pre-training and Post-training Nordic Exercise on Hamstring Injury Prevention, Recurrence, and Severity in Soccer Players
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Basic Science, Faculty of Physical Therapy, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt. dr_ahmed_elerian77@cu.edu.eg
- 2Department of Physical Therapy, Alexandria General Hospital, Alexandria, Egypt.
- KMID: 2457755
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2019.43.4.465
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the effect of adding Nordic exercise as post-training in decreasing hamstring initial, recurrent injuries rates, and their severity.
METHODS
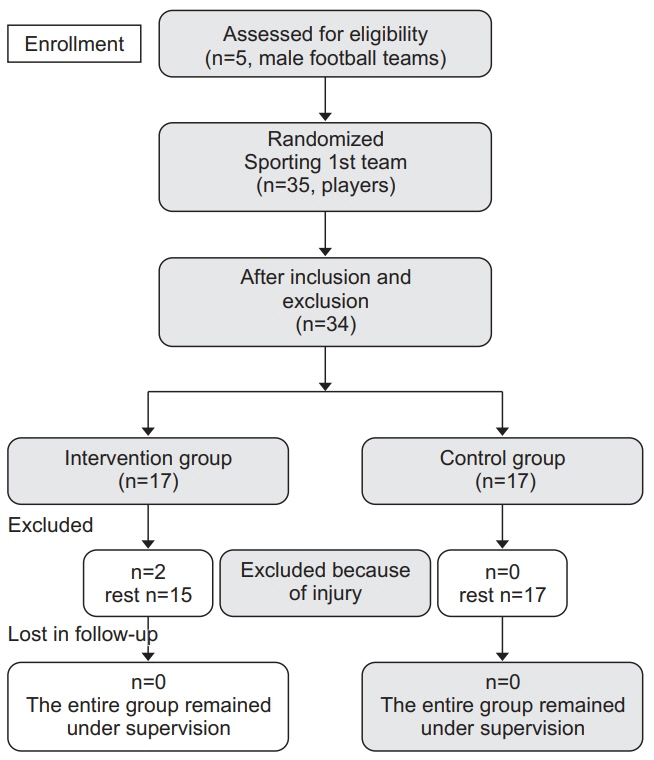
In this randomly controlled trial study, 34 professional football players aged 21 to 35 years were randomly assigned into two groups (17 players each) from Sporting clubs at Alexandria, Egypt. For group one, Nordic hamstring exercise (NHE) was performed pre-training and post-training. For group two, NHE was only performed pre-training. The control group was the same team during the previous season. Length of the trial was 12 weeks. The Australian football association injury form was used to collect incidence of injuries for each subject in both groups.
RESULTS
Pooled results based on total injuries showed that group one had significantly less hamstring initial injuries (92% less) than the previous season, while group two had 80% less initial injuries and 85% less recurrent injuries than previous season. Regarding the severity of injuries in term of mean number of absent days, it was 1 day for group one and 2.7 days for group two while it was 7.95 days for the previous season during total risk time of 116.3±13.2 and 117.6±5.7 exposure hours for group one and group two, respectively.
CONCLUSION
The use of NHE as a prevention protocol was effective in reducing all hamstring injuries with the use of NHE during pre-training and post-training having the greatest effect.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lovell R, Knox M, Weston M, Siegler JC, Brennan S, Marshall PW. Hamstring injury prevention in soccer: before or after training? Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2018; 28:658–66.
Article2. Al Attar WS, Soomro N, Sinclair PJ, Pappas E, Muaidi QI, Sanders RH. Implementation of an evidence-based injury prevention program in professional and semi-professional soccer. Int J Sports Sci Coach. 2018; 13(1):113–21.
Article3. van Beijsterveldt AM, van de Port IG, Vereijken AJ, Backx FJ. Risk factors for hamstring injuries in male soccer players: a systematic review of prospective studies. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2013; 23:253–62.
Article4. Wan X, Qu F, Garrett WE, Liu H, Yu B. The effect of hamstring flexibility on peak hamstring muscle strain in sprinting. J Sport Health Sci. 2017; 6:283–9.
Article5. Al Attar WS, Soomro N, Sinclair PJ, Pappas E, Sanders RH. Effect of injury prevention programs that include the Nordic hamstring exercise on hamstring injury rates in soccer players: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Sports Med. 2017; 47:907–16.
Article6. Seymore KD, Domire ZJ, DeVita P, Rider PM, Kulas AS. The effect of Nordic hamstring strength training on muscle architecture, stiffness, and strength. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2017; 117:943–53.
Article7. Bourne MN, Opar DA, Williams MD, Al Najjar A, Shield AJ. Muscle activation patterns in the Nordic hamstring exercise: Impact of prior strain injury. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2016; 26:666–74.
Article8. Al Attar WS, Soomro N, Pappas E, Sinclair PJ, Sanders RH. How effective are F-MARC injury prevention programs for soccer players? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2016; 46:205–17.
Article9. Steffen K, Emery CA, Romiti M, Kang J, Bizzini M, Dvorak J, et al. High adherence to a neuromuscular injury prevention programme (FIFA 11+) improves functional balance and reduces injury risk in Canadian youth female football players: a cluster randomised trial. Br J Sports Med. 2013; 47:794–802.
Article10. van der Horst N, Smits DW, Petersen J, Goedhart EA, Backx FJ. The preventive effect of the Nordic hamstring exercise on hamstring injuries in amateur soccer players: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med. 2015; 43:1316–23.
Article11. Al Attar WSA, Soomro N, Pappas E, Sinclair PJ, Sanders RH. Adding a post-training FIFA 11+ exercise program to the pre-training FIFA 11+ injury prevention program reduces injury rates among male amateur soccer players: a cluster-randomised trial. J Physiother. 2017; 63:235–42.
Article12. Arnason A, Andersen TE, Holme I, Engebretsen L, Bahr R. Prevention of hamstring strains in elite soccer: an intervention study. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2008; 18:40–8.
Article13. Ayala F, Calderon-Lopez A, Delgado-Gosalbez JC, Parra-Sanchez S, Pomares-Noguera C, Hernandez-Sanchez S, et al. Acute effects of three neuromuscular warm-up strategies on several physical performance measures in football players. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0169660.
Article14. Machado AF, Ferreira PH, Micheletti JK, de Almeida AC, Lemes IR, Vanderlei FM, et al. Can water temperature and immersion time influence the effect of cold water immersion on muscle soreness? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2016; 46:503–14.
Article15. Meyer T, Wegmann M, Poppendieck W, Fullagar HH. Regenerative interventions in professional football. Sports Orthop Traumatol. 2014; 30:112–8.
Article16. Thorborg K, Krommes KK, Esteve E, Clausen MB, Bartels EM, Rathleff MS. Effect of specific exercise-based football injury prevention programmes on the overall injury rate in football: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the FIFA 11 and 11+ programmes. Br J Sports Med. 2017; 51:562–71.
Article17. van der Horst N. Preventing hamstring injuries in football through enhanced exercise and RTP strategies. Br J Sports Med. 2018; 52:684–5.
Article18. Ribeiro-Alvares JB, Marques VB, Vaz MA, Baroni BM. Four weeks of Nordic hamstring exercise reduce muscle injury risk factors in young adults. J Strength Cond Res. 2018; 32:1254–62.
Article19. Van Hooren B, Bosch F. Is there really an eccentric action of the hamstrings during the swing phase of highspeed running? Part I. A critical review of the literature. J Sports Sci. 2017; 35:2313–21.
Article20. Guex K, Degache F, Morisod C, Sailly M, Millet GP. Hamstring architectural and functional adaptations following long vs. short muscle length eccentric training. Front Physiol. 2016; 7:340.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Prevention and Rehabilitation of Soccer Injuries
- Effects of Intensive Training on Cardiorespiratory Response to Maximal Exercise Loading in Soccer Players
- Comparisons of Electrocardiograms and Echocardiograms in Soccer Players before and after Intensive Training
- The Effects of 11+ Program on Technical Skills and Balance Ability of High School Soccer Players
- Comparison of Cardiopulmonary Endurance among Positions in Middle School Soccer Players and Their Sports Injuries