J Korean Soc Radiol.
2019 Jul;80(4):788-792. 10.3348/jksr.2019.80.4.788.
Heterotopic Pancreas with Abundant Fat Tissue in the Stomach: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Korea Cancer Center Hospital, Seoul, Korea. lcf0666@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2457459
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2019.80.4.788
Abstract
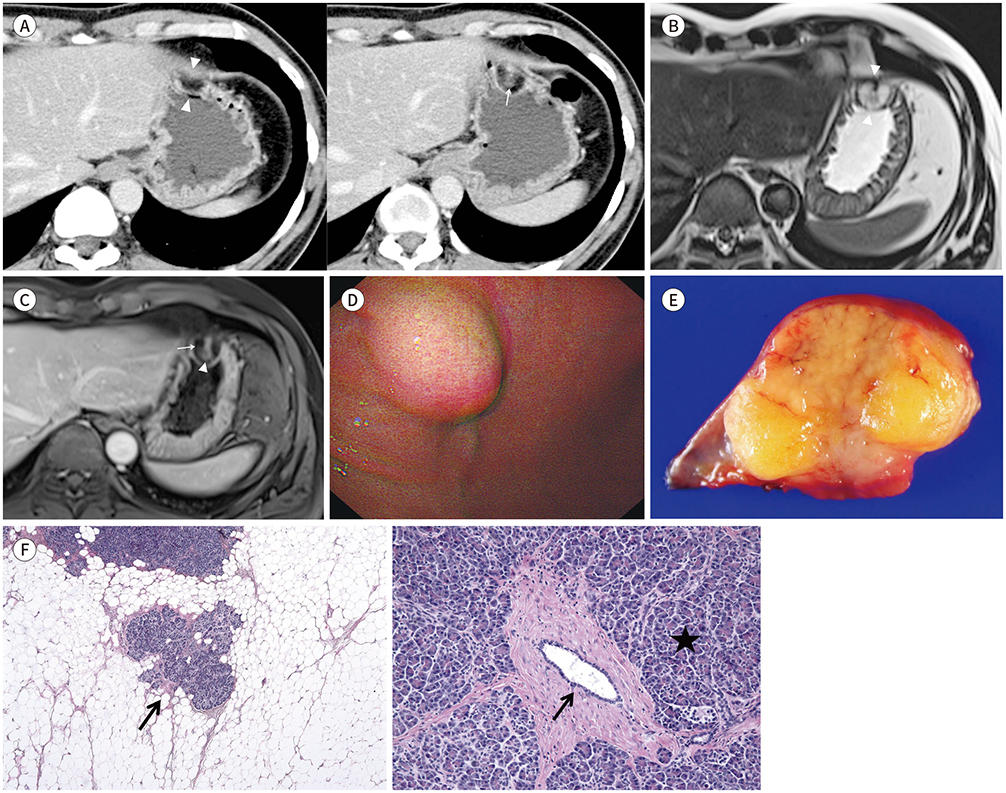
- Heterotopic pancreas is often an incidental finding and can be found at the stomach. However, heterotopic pancreas containing abundant fat is very rare. Fatty replacement of the pancreas is the most frequent pathologic finding, but the precise etiology of the entity remains unclear. The pathological findings observed in the pancreas can also occur in the heterotopic pancreas. Here, we present a case of heterotopic pancreas in the stomach. On CT and MR imaging, it manifested as a predominant fat-density submucosal mass with enhancing solid component.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Christodoulidis G, Zacharoulis D, Barbanis S, Katsogridakis E, Hatzitheofilou K. Heterotopic pancreas in the stomach: a case report and literature review. World J Gastroenterol. 2007; 13:6098–6100.
Article2. Rezvani M, Menias C, Sandrasegaran K, Olpin JD, Elsayes KM, Shaaban AM. Heterotopic pancreas: histopathologic features, imaging findings, and complications. Radiographics. 2017; 37:484–499.
Article3. Chuang MT, Tsai KB, Ma CJ, Hsieh TJ. Ileoileal intussusception due to ileal ectopic pancreas with abundant fat tissue mimicking lipoma. Am J Surg. 2010; 200:e25–e27.
Article4. Nam MY, Kim MY, Kim YJ, Suh CH, Choi SJ, Cho JS. Perilesional steatosis in ectopic pancreas mimicking exogastric mass: a case report. J Korean Soc Magn Reson Med. 2013; 17:154–157.5. Moriki T, Ohtsuki Y, Takahashi T, Ueta S, Mitani M, Ichien M, et al. Lipoma-like tumor mass probably arising in the retroperitoneal heterotopic pancreas: a previously undescribed lesion. Pathol Int. 2004; 54:527–531.
Article6. Kim HJ, Byun JH, Park SH, Shin YM, Kim PN, Ha HK, et al. Focal fatty replacement of the pancreas: usefulness of chemical shift MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007; 188:429–432.
Article7. Ferrozzi F, Tognini G, Bova D, Pavone P. Lipomatous tumors of the stomach: CT findings and differential diagnosis. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2000; 24:854–858.
Article8. Thompson WM, Kende AI, Levy AD. Imaging characteristics of gastric lipomas in 16 adult and pediatric patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003; 181:981–985.
Article9. Liu YJ, Karamchandani DM. Gastric angiolipoma: a rare entity. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2017; 141:862–866.
Article10. Kang HC, Menias CO, Gaballah AH, Shroff S, Taggart MW, Garg N, et al. Beyond the GIST: mesenchymal tumors of the stomach. Radiographics. 2013; 33:1673–1690.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Three Cases of Heterotopic Pancreas of the Stomach
- Ductal Adenocarcinoma Arising from Heterotopic Pancreas in the Stomach: A Case Report
- A Case of Heterotopic Pancreas of Gastric Corpus
- A Case of Heterotopic Pancreas on the Fundus of Stomach by Gastrofiberscopy
- A case of symptomatic heterotopic pancreas with huge pseudocyst formation