Ann Dermatol.
2019 Aug;31(Suppl):S62-S63. 10.5021/ad.2019.31.S.S62.
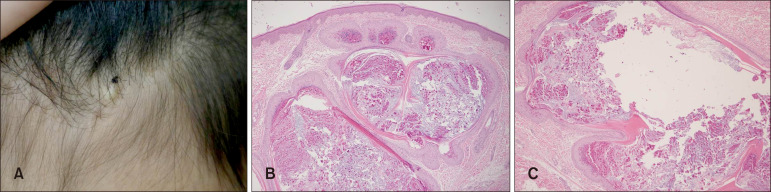
Molluscum Contagiosum Occurring in an Epidermal Cyst Developed on Frontal Hairline
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. bellotte@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2456682
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2019.31.S.S62
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Smith KJ, Yeager J, Skelton H. Molluscum contagiosum: its clinical, histopathologic, and immunohistochemical spectrum. Int J Dermatol. 1999; 38:664–672. PMID: 10517682.
Article2. Hu SC, Chen GS, Tsai KB, Lan CC. Molluscum infestation of an epidermal cyst associated with focal hyperplasia of cyst wall. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2009; 23:353–355. PMID: 18624877.
Article3. Phelps A, Murphy M, Elaba Z, Hoss D. Molluscum contagiosum virus infection in benign cutaneous epithelial cystic lesions-report of 2 cases with different pathogenesis? Am J Dermatopathol. 2010; 32:740–742. PMID: 20700040.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Molluscum Contagiosum Occurring in an Epidermal Cyst Developed on Frontal Hairline
- Molluscum contagiosum occuring in an epidermal cyst
- A Case of Molluscum Contagiosum Occurring in Epidermal Cyst
- Molluscum Contagiosum Virus Infection in an Epidermal Cyst
- A Case of Molluscum Contagiosum Occurring in an Epidermal Cyst