Ann Dermatol.
2019 Aug;31(Suppl):S52-S53. 10.5021/ad.2019.31.S.S52.
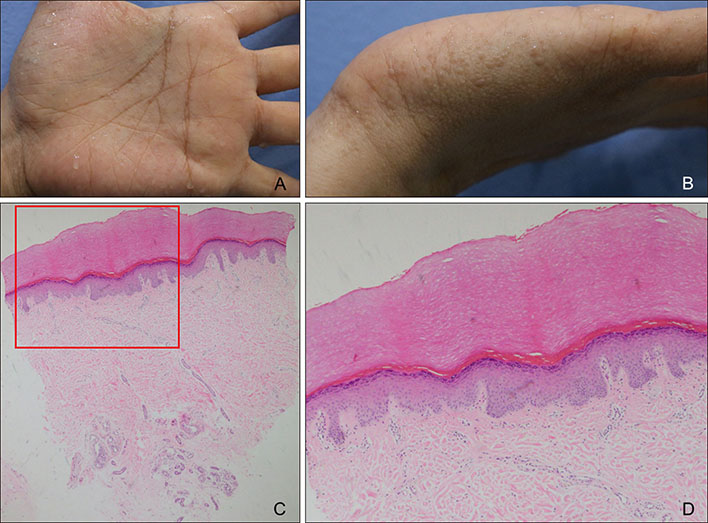
Hereditary Papulotranslucent Acrokeratoderma: Prominent Clinical Presentation after Water Exposure
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- 2Department of Dermatology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. oddung93@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2456678
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2019.31.S.S52
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Onwukwe MF, Mihm MC Jr, Toda K. Hereditary papulotranslucent acrokeratoderma. A new variant of familial punctate keratoderma? Arch Dermatol. 1973; 108:108–110.
Article2. Sun Y, Jia H. Hereditary papulotranslucent acrokeratoderma: a simultaneous presentation in daughter and mother. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013; 79:555.
Article3. Luo DQ, Li Y, Huang YB, Wu LC, He DY. Aquagenic syringeal acrokeratoderma in an adult man: case report and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009; 34:e907–e909.
Article4. Poletti ED, Muñoz-Sandoval R. Images in clinical medicine. Aquagenic keratoderma. N Engl J Med. 2014; 371:952.5. Yan AC, Aasi SZ, Alms WJ, James WD, Heymann WR, Paller AS, et al. Aquagenic palmoplantar keratoderma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001; 44:696–699.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hereditary Papulotranslucent Acrokeratoderma: Prominent Clinical Presentation after Water Exposure
- Hereditary Palpulotranslucent Acrokeratoderma: Report of a Case
- Backpack Palsy Presenting as a First Manifestation of Hereditary Neuropathy with Liability to Pressure Palsy
- Identification of de novo BSCL2 Asn88Ser Variant with Atypical Presentation of Distal Hereditary Motor Neuropathy Type 5: Clinical Challenge in Diagnosis of Motor Neuron Diseases
- Ultrastructural Findings of Hereditary Sensory and Autonomic Neuropathies, Type IV and II