Ann Dermatol.
2019 Aug;31(Suppl):S22-S23. 10.5021/ad.2019.31.S.S22.
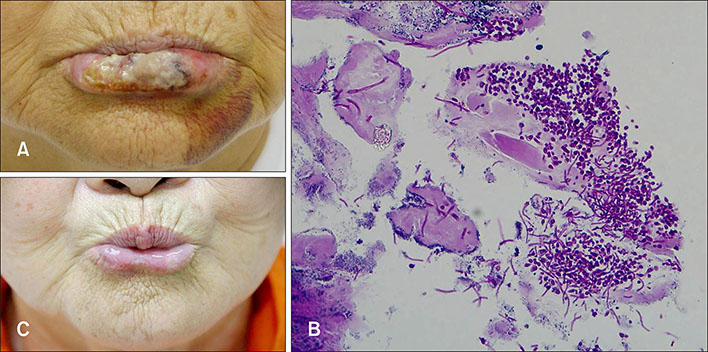
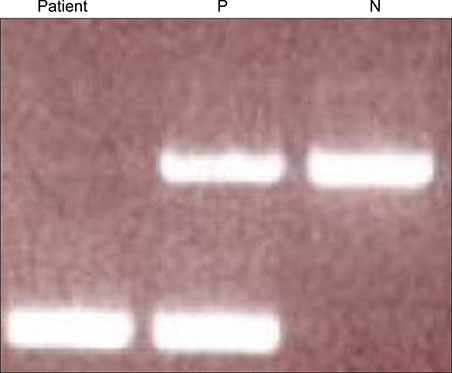
A Case of Cheilocandidiasis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. lyb80@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2456666
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2019.31.S.S22
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Millsop JW, Fazel N. Oral candidiasis. Clin Dermatol. 2016; 34:487–494.
Article2. Sharon V, Fazel N. Oral candidiasis and angular cheilitis. Dermatol Ther. 2010; 23:230–242.
Article3. Terai H, Shimahara M. Cheilitis as a variation of Candidaassociated lesions. Oral Dis. 2006; 12:349–352.
Article