Arch Hand Microsurg.
2019 Sep;24(3):260-266. 10.12790/ahm.2019.24.3.260.
Sensate Medial Plantar Free Flap Transfer and Adductor Pollicis Myotomy for Treatment of Palmar Burn Scar Contracture
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Plastic Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ecjeong@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2456251
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.2019.24.3.260
Abstract
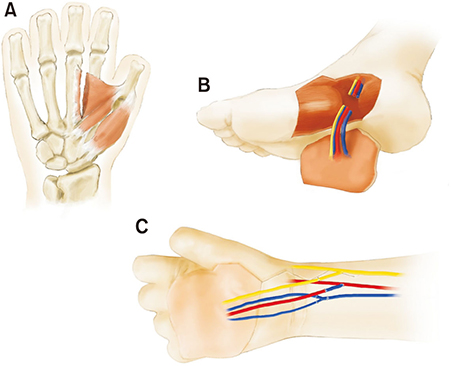
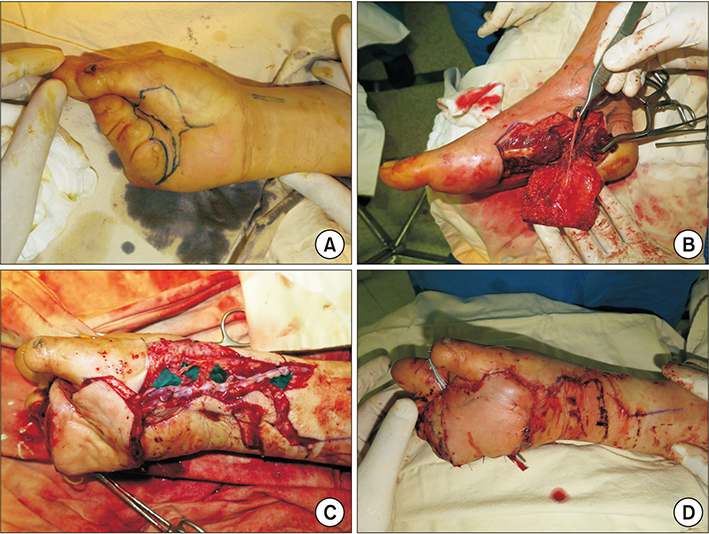
- A postburn contracture involving the palmar skin and subcutaneous tissues results in a severe loss of functionality of the affected hand. The corrective surgical procedures aim for an improvement of the range of motion of the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints and target the reconstruction of a durable and sensitive palmar-specific anatomical structure. We successfully treated a 53-year-old male patient with a long-standing postburn contracture of all the right MCP joints and underlying palmar tissue. We performed contracture release and adductor pollicis myotomy and reconstructed the resultant palmar defect with a sensate medial plantar free flap to restore acute skin sensitivity and resurface the glabrous skin of the palm. The Kirschner-wire fixation utilized for stabilizing the extended MCP joints was maintained for 3 weeks after contracture release. The restored palmar skin and soft tissue improved the MCP joint movements, enabling grasping and pinching motions and thus restoring functionality of the operated hand.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ninkovíc MM, Schwabegger AH, Wechselberger G, Anderl H. Reconstruction of large palmar defects of the hand using free flaps. J Hand Surg Br. 1997; 22:623–630.2. Engelhardt TO, Rieger UM, Schwabegger AH, Pierer G. Functional resurfacing of the palm: flap selection based on defect analysis. Microsurgery. 2012; 32:158–166.
Article3. Ninković M, Wechselberger G, Schwabegger A, Anderl H. The instep free flap to resurface palmar defects of the hand. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1996; 97:1489–1493.
Article4. Kuran I, Turgut G, Bas L, Ozkan T, Bayri O, Gulgonen A. Comparison between sensitive and nonsensitive free flaps in reconstruction of the heel and plantar area. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000; 105:574–580.
Article5. Chai YM, Wang CY, Wen G, Zeng BF, Cai PH, Han P. Combined medialis pedis and medial plantar fasciocutaneous flaps based on the medial plantar pedicle for reconstruction of complex soft tissue defects in the hand. Microsurgery. 2011; 31:45–50.
Article6. Yavari M, Ghazisaidi MR, Hoseini Zahmatkesh S, Jahadi R. Comparison of sole to palm reconstruction using the combined medial plantar and medial pedis free flaps and abdominal pedicle flap for extensive palm injuries. Acta Med Iran. 2010; 48:214–217.7. Van Heest AE. Surgical technique for thumb-in-palm deformity in cerebral palsy. J Hand Surg Am. 2011; 36:1526–1531.
Article8. Azar FM, Beaty JH, Canale ST. Campbell's operative orthopaedics. 13th ed. Elsevier;2016. p. 3650–3652.9. Sungur N, Ulusoy MG, Boyacgil S, et al. Kirschner-wire fixation for postburn flexion contracture deformity and consequences on articular surface. Ann Plast Surg. 2006; 56:128–132.
Article10. Saraiya H. Is 20 years of immobilization, not sufficient to render metacarpophalangeal joints completely useless?--correction of a 20-year old post-burn palmar contracture: a case report. Burns. 2001; 27:192–195.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reconstruction of extreme post-burn scar contracture of the ankle using a thoracodorsal artery perforator flap: a case report
- Clinical Experience of Thumb-in-palm Deformity
- Staged Treatment of an Extensive Post-Burn Scar Contracture with Chronic Ulceration of the Knee Joint: A Case Report
- Reconstruction of Postburn Scar Contracture of the Sole Using the Medialis Pedis Free Flap
- Correction of Burn Scar Contracture: Indication and Choice of Free Flap