J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2019 Aug;45(4):174-179. 10.5125/jkaoms.2019.45.4.174.
Masticatory muscle tendon-aponeurosis hyperplasia accompanied by limited mouth opening
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Maxillofacial Surgery, Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, Tokyo, Japan. yoda.mfs@tmd.ac.jp
- KMID: 2456034
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2019.45.4.174
Abstract
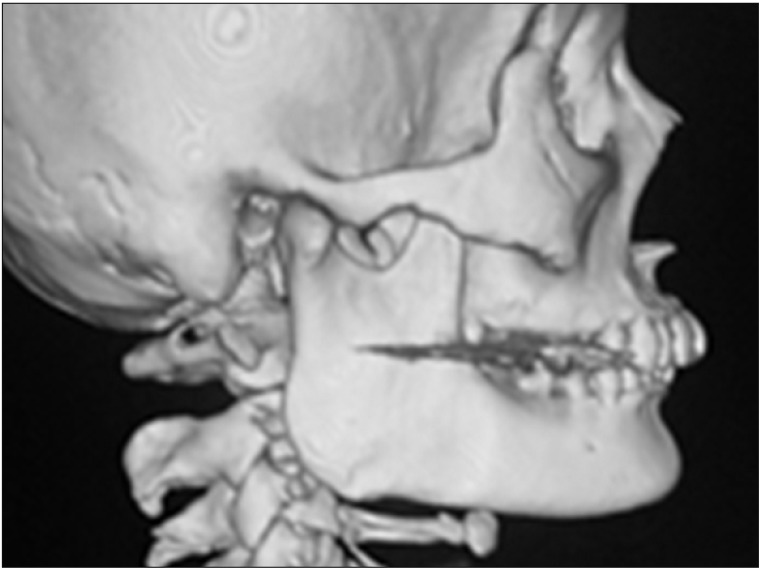
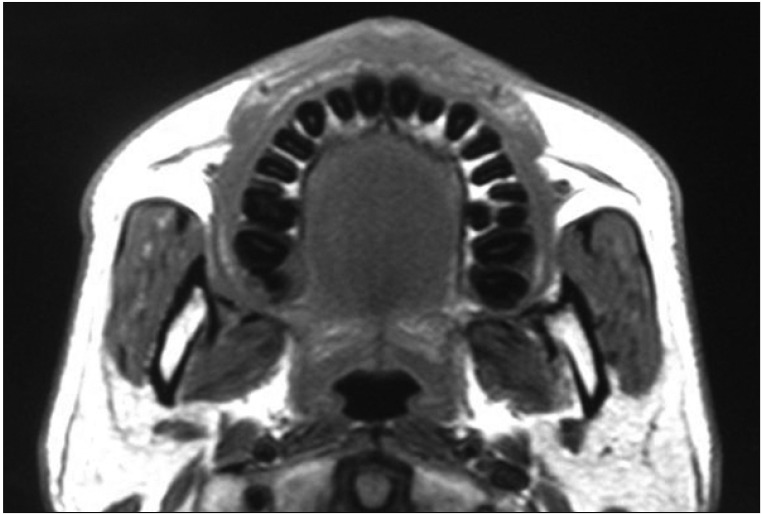
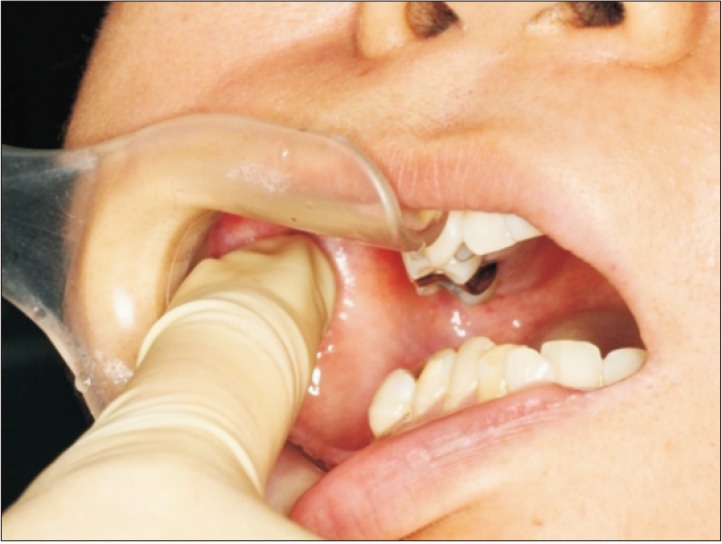
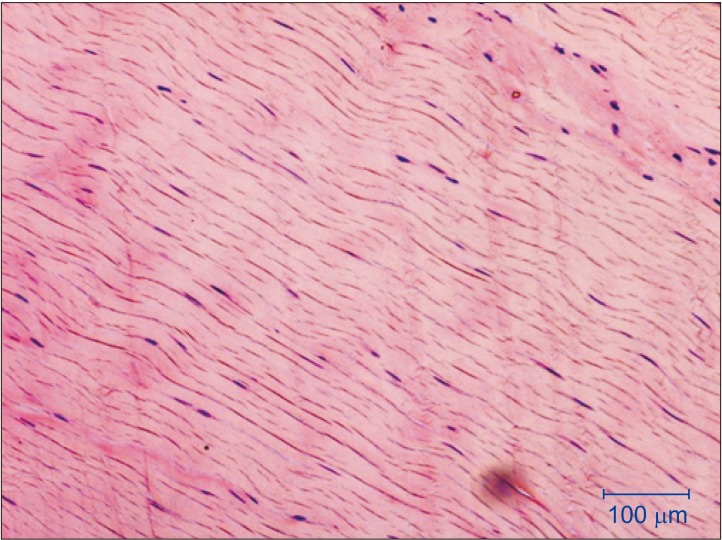
- Patients with masticatory muscle tendon-aponeurosis hyperplasia (MMTAH) experience limited mouth opening due to restricted muscle extension. Hyperplastic aponeurosis and tendons lead to the restriction of muscle extension. The criteria for the diagnosis of MMTAH are limited mouth opening that progresses very slowly from adolescence, intraoral palpation reveals a hard cord-like structure along the overhang of the anterior border of the masseter muscle on maximum mouth opening, and a square mandible. Conservative treatment, including pharmacotherapy, occlusal splint and physical therapy are ineffective. The standard therapy is surgical treatment, such as anterior partial aponeurectomy of the masseter muscle and coronoidectomy. The long-term results are very satisfying.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dhanrajani PJ, Jonaidel O. Trismus: aetiology, differential diagnosis and treatment. Dent Update. 2002; 29:88–92. 94PMID: 11928347.
Article2. Satheeshkumar PS, Mohan MP, Jacob J. Restricted mouth opening and trismus in oral oncology. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2014; 117:709–715. PMID: 24842447.
Article3. Inoue N, Yamaguchi T, Satou J, Satou C, Minowa K, Iizuka T. A case of restricted mandibular movement resulting from hyperplasia of the masseter muscle aponeurosis. Jpn J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000; 46:307–309.
Article4. Murakami K, Yokoe Y, Yasuda S, Tsuboi Y, Iizuka T. Prolonged mandibular hypomobility patient with a “square mandible” configuration with coronoid process and angle hyperplasia. Cranio. 2000; 18:113–119. PMID: 11202821.
Article5. Beckers HL. Masseteric muscle hypertrophy and its intraoral surgical correction. J Maxillofac Surg. 1977; 5:28–35. PMID: 265349.
Article6. Kakudo K, Yoda T. New concept of limited mouth opening associated with square mandible: diagnosis and treatment for masticatory muscle tendon-aponeurosis hyperplasia. J Jpn Soc TMJ. 2009; 21:28–30.7. Yoda T, Sato T, Abe T, Sakamoto I, Tomaru Y, Omura K, et al. Long-term results of surgical therapy for masticatory muscle tendon-aponeurosis hyperplasia accompanied by limited mouth opening. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009; 38:1143–1147. PMID: 19682860.
Article8. Worni A, Mericske-Stern R, Iizuka T, Büttner M. Eingeschärnkte Mundöffnung-was nun? Swiss Dent J. 2014; 124:935–944. PMID: 25253540.9. Lehman H, Fleissig Y, Abid-el-raziq D, Nitzan DW. Limited mouth opening of unknown cause cured by diagnostic coronoidectomy: a new clinical entity? Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015; 53:230–234. PMID: 25596795.
Article10. Yoda T, Sato T. Re: Limited mouth opening of unknown cause cured by diagnostic coronoidectomy: a new clinical entity? Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2015:53(3):230–4. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015; 53:476–477.
Article11. Arika T, Kakudo K. Hyperplasia of tendon and aponeurosis of masticatory muscles (HyTAM)-clinical appearance. J Jpn Soc TMJ. 2009; 21:31–34.12. Nakamoto N, Sato T, Enoki Y, Nakamoto A, Hori N, Fukushima Y, et al. An analysis of maxillofacial morphology of patients with hyperplasia of the tendon and aponeurosis of masticatory muscles using cephalometric radiography. J Jpn Soc TMJ. 2011; 23:149–154.13. Yoda T. [New diagnoses and treatments of temporomandibular disorders aided by chart illustrations]. Tokyo: Ishiyaku Publishers;2012. Japanese.14. Kobayashi K, Shimoda S, Yoda T, Kakudo K. Current status of MR imaging for the masticatory muscle tendon-aponeurosis hyperplasia. J Jpn Soc TMJ. 2009; 21:35–39.15. Minowa K, Inoue N, Ashikaga Y, Yoshida S, Totsuka Y, Nakamura M. Comparison of magnetic resonance imaging and gross findings regarding masseter muscle aponeuroses in cadavers. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1998; 86:275–279. PMID: 9768414.
Article16. Hayashi N, Yoda T, Tomoda T, Yumoto M, Kitamura T, Okubo M, et al. Longitudinal epidemiological survey on suspected masticatory muscle tendon-aponeurosis hyperplasia in adolescents. J Jpn Soc TMJ. 2018; 30:187–194.17. Chiba R. Histopathologic evaluation of aponeurectomy materials in masticatory muscle tendon-aponeurosis hyperplasia. J Jpn Soc TMJ. 2009; 21:51–54.18. Sato T, Hori N, Nakamoto N, Akita M, Yoda T. Masticatory muscle tendon-aponeurosis hyperplasia exhibits heterotopic calcification in tendons. Oral Dis. 2014; 20:404–408. PMID: 23750917.
Article19. Sato T, Nakamoto A, Hori N, Enoki Y, Fukushima Y, Nakamoto N, et al. Proteomic analysis of masticatory muscle tendon-aponeurosis hyperplasia: a preliminary study using a 2D-DIGE system. J Oral Maxillofac Surg Med Pathol. 2012; 24:185–188.
Article20. Nakamoto A, Sato T, Hirosawa N, Nakamoto N, Enoki Y, Chida D, et al. Proteomics-based identification of novel proteins in temporal tendons of patients with masticatory muscle tendon--aponeurosis hyperplasia. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014; 43:113–119. PMID: 23870541.
Article21. Hayashi N, Sato T, Kokabu S, Usui M, Yumoto M, Ikami E, et al. Possible association of oestrogen and Cryba4 with masticatory muscle tendon-aponeurosis hyperplasia. Oral Dis. 2019; 25:274–281. PMID: 29683234.
Article22. Sato T, Yoda T. Masticatory muscle tendon-aponeurosis hyperplasia: a new clinical entity of limited mouth opening. Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2016; 52:41–48. PMID: 28408955.
Article23. Moroi A, Ueki K, Marukawa K, Okabe K, Mukouzawa A, Nakagawa K, et al. A case of masticatory muscle tendon-aponeurosis hyperplasia improved by mandibular anglectomy. Jpn J Oral Diagn. Oral Med. 2011; 24:188–194.24. Yoshida H, Oshiro N, Fukuda A, Gamoh S, Shimizutani K, Morita S. A case of reformed coronoid process and mandibular angle after coronoidectomy and anglectomy for masticatory muscle tendon-aponeurosis hyperplasia. Oral Radiol. 2014; 30:129–133.
Article25. Sato T, Hayashi N, Enoki Y, Okubo M, Nakaoka C, Nakamoto N, et al. Limited mouth opening with a square mandible configuration: a case of masticatory muscle tendon-aponeurosis hyperplasia. J Surg Case Rep. 2015; 2015:rjv020. PMID: 25770956.
Article26. Nakamoto N, Sato T, Enoki T, Nakamoto A, Hori N, Fukushima Y, et al. Regeneration of tendon and aponeurosis after surgery of masticatory muscle tendon-aponeurosis hyperplasia: report of a case. J Jpn Soc TMJ. 2010; 22:158–162.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Masticatory muscle tendon‑aponeurosis hyperplasia that was initially misdiagnosed for polymyositis: a case report and review of the literature
- Myositis Associated with Infratemporal Space Abscess in Patient with Myxofibrosarcoma of Nasal Cavity: Case Report
- Coronoid impingement syndrome: literature review and clinical management
- Effects of Temporal Muscle Exercise on Mastication after Craniotomy
- Masticatory muscle tenderness in burning mouth syndrome: A case control study