Korean J Radiol.
2019 Sep;20(9):1358-1367. 10.3348/kjr.2018.0715.
Application of Vendor-Neutral Iterative Reconstruction Technique to Pediatric Abdominal Computed Tomography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. iater@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Transdisciplinary Studies, Graduate School of Convergence Science and Technology, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Advanced Institute of Convergence Technology, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2455764
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.0715
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To compare image qualities between vendor-neutral and vendor-specific hybrid iterative reconstruction (IR) techniques for abdominopelvic computed tomography (CT) in young patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
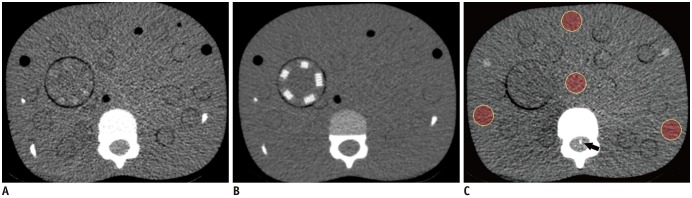
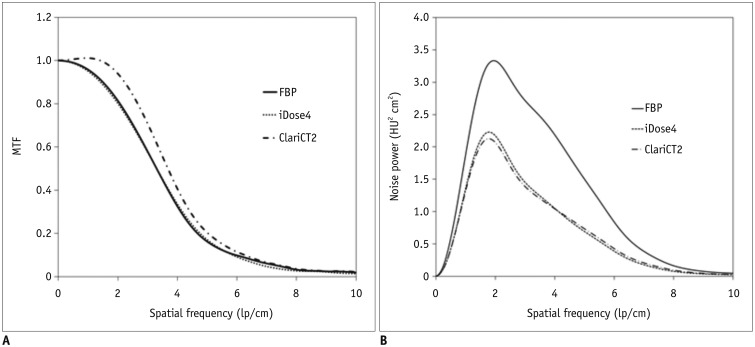
In phantom study, we used an anthropomorphic pediatric phantom, age-equivalent to 5-year-old, and reconstructed CT data using traditional filtered back projection (FBP), vendor-specific and vendor-neutral IR techniques (ClariCT; ClariPI) in various radiation doses. Noise, low-contrast detectability and subjective spatial resolution were compared between FBP, vendor-specific (i.e., iDose1 to 5; Philips Healthcare), and vendor-neutral (i.e., ClariCT1 to 5) IR techniques in phantom. In 43 patients (median, 14 years; age range 1-19 years), noise, contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR), and qualitative image quality scores of abdominopelvic CT were compared between FBP, iDose level 4 (iDose4), and ClariCT level 2 (ClariCT2), which showed most similar image quality to clinically used vendor-specific IR images (i.e., iDose4) in phantom study. Noise, CNR, and qualitative imaging scores were compared using one-way repeated measure analysis of variance.
RESULTS
In phantom study, ClariCT2 showed noise level similar to iDose4 (14.68-7.66 Hounsfield unit [HU] vs. 14.78-6.99 HU at CT dose index volume range of 0.8-3.8 mGy). Subjective low-contrast detectability and spatial resolution were similar between ClariCT2 and iDose4. In clinical study, ClariCT2 was equivalent to iDose4 for noise (14.26-17.33 vs. 16.01-18.90) and CNR (3.55-5.24 vs. 3.20-4.60) (p > 0.05). For qualitative imaging scores, the overall image quality ([reader 1, reader 2]; 2.74 vs. 2.07, 3.02 vs. 2.28) and noise (2.88 vs. 2.23, 2.93 vs. 2.33) of ClariCT2 were superior to those of FBP (p < 0.05), and not different from those of iDose4 (2.74 vs. 2.72, 3.02 vs. 2.98; 2.88 vs. 2.77, 2.93 vs. 2.86) (p > 0.05).
CONCLUSION
Vendor-neutral IR technique shows image quality similar to that of clinically used vendor-specific hybrid IR technique for abdominopelvic CT in young patients.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Coakley FV, Gould R, Yeh BM, Arenson RL. CT radiation dose: what can you do right now in your practice? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011; 196:619–625. PMID: 21343506.
Article2. Costello JE, Cecava ND, Tucker JE, Bau JL. CT radiation dose: current controversies and dose reduction strategies. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013; 201:1283–1290. PMID: 24261368.
Article3. Hara AK, Wellnitz CV, Paden RG, Pavlicek W, Sahani DV. Reducing body CT radiation dose: beyond just changing the numbers. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013; 201:33–40. PMID: 23789656.
Article4. Maldjian PD, Goldman AR. Reducing radiation dose in body CT: a primer on dose metrics and key CT technical parameters. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013; 200:741–747. PMID: 23521441.
Article5. Solomon J, Marin D, Roy Choudhury K, Patel B, Samei E. Effect of radiation dose reduction and reconstruction algorithm on image noise, contrast, resolution, and detectability of subtle hypoattenuating liver lesions at multidetector CT: filtered back projection versus a commercial model-based iterative reconstruction algorithm. Radiology. 2017; 284:777–787. PMID: 28170300.
Article6. Zacharias C, Alessio AM, Otto RK, Iyer RS, Philips GS, Swanson JO, et al. Pediatric CT: strategies to lower radiation dose. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013; 200:950–956. PMID: 23617474.
Article7. Willemink MJ, de Jong PA, Leiner T, de Heer LM, Nievelstein RA, Budde RP, et al. Iterative reconstruction techniques for computed tomography Part 1: technical principles. Eur Radiol. 2013; 23:1623–1631. PMID: 23314600.
Article8. Beister M, Kolditz D, Kalender WA. Iterative reconstruction methods in X-ray CT. Phys Med. 2012; 28:94–108. PMID: 22316498.
Article9. Lee KB, Goo HW. Quantitative image quality and histogram-based evaluations of an iterative reconstruction algorithm at low-to-ultralow radiation dose levels: a phantom study in chest CT. Korean J Radiol. 2018; 19:119–129. PMID: 29354008.
Article10. Infante JC, Liu Y, Rigsby CK. CT image quality in sinogram affirmed iterative reconstruction phantom study - is there a point of diminishing returns? Pediatr Radiol. 2017; 47:333–341. PMID: 27891546.
Article11. Won Kim C, Kim JH. Realistic simulation of reduced-dose CT with noise modeling and sinogram synthesis using DICOM CT images. Med Phys. 2014; 41:011901. PMID: 24387509.
Article12. Ahn CK, Yang Z, Heo C, Jin H, Park B, Kim JH. A deep learning-enabled iterative reconstruction of ultra-low-dose CT: use of synthetic sinogram-based noise simulation technique. SPIE Medical Imaging. 2018; 10573:1057335.
Article13. Moore BM, Brady SL, Mirro AE, Kaufman RA. Size-specific dose estimate (SSDE) provides a simple method to calculate organ dose for pediatric CT examinations. Med Phys. 2014; 41:071917. PMID: 24989395.
Article14. Strauss KJ, Goske MJ. Estimated pediatric radiation dose during CT. Pediatr Radiol. 2011; 41(Suppl 2):472–482. PMID: 21847725.
Article15. Ryu YJ, Choi YH, Cheon JE, Ha S, Kim WS, Kim IO. Knowledge-based iterative model reconstruction: comparative image quality and radiation dose with a pediatric computed tomography phantom. Pediatr Radiol. 2016; 46:303–315. PMID: 26546568.
Article16. CIRS. ATOM® Dosimetry Phantoms. Accessed August 9, 2019. Available at: http://www.cirsinc.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/701-706-ATOM-PB-120418.pdf.17. Nickoloff EL. Measurement of the PSF for a CT scanner: appropriate wire diameter and pixel size. Phys Med Biol. 1988; 33:149–155. PMID: 3353449.
Article18. Baek J, Pelc NJ. The noise power spectrum in CT with direct fan beam reconstruction. Med Phys. 2010; 37:2074–2081. PMID: 20527540.
Article19. Mayo-Smith WW, Gupta H, Ridlen MS, Brody JM, Clements NC, Cronan JJ. Detecting hepatic lesions: the added utility of CT liver window settings. Radiology. 1999; 210:601–604. PMID: 10207455.
Article20. Löve A, Olsson ML, Siemund R, Stålhammar F, Björkman-Burtscher IM, Söderberg M. Six iterative reconstruction algorithms in brain CT: a phantom study on image quality at different radiation dose levels. Br J Radiol. 2013; 86:20130388. PMID: 24049128.
Article21. Karmazyn B, Liang Y, Ai H, Eckert GJ, Cohen MD, Wanner MR, et al. Optimization of hybrid iterative reconstruction level in pediatric body CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014; 202:426–431. PMID: 24450687.
Article22. Siegel MJ, Hildebolt C, Bradley D. Effects of automated kilovoltage selection technology on contrast-enhanced pediatric CT and CT angiography. Radiology. 2013; 268:538–547. PMID: 23564712.
Article23. Ryu YJ, Kim WS, Choi YH, Cheon JE, Lee SM, Cho HH, et al. Pediatric chest CT: wide-volume and helical scan modes in 320-MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015; 205:1315–1321. PMID: 26587939.
Article24. Lee JH, Choi YH, Cheon JE, Lee SM, Cho HH, Shin SM, et al. Improved abdominal MRI in non-breath-holding children using a radial k-space sampling technique. Pediatr Radiol. 2015; 45:840–846. PMID: 25616364.
Article25. Russell MT, Fink JR, Rebeles F, Kanal K, Ramos M, Anzai Y. Balancing radiation dose and image quality: clinical applications of neck volume CT. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:727–731. PMID: 18223095.
Article26. McHugh ML. Interrater reliability: the kappa statistic. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2012; 22:276–228. PMID: 23092060.
Article27. Fletcher JG, Hara AK, Fidler JL, Silva AC, Barlow JM, Carter RE, et al. Observer performance for adaptive, image-based denoising and filtered back projection compared to scanner-based iterative reconstruction for lower dose CT enterography. Abdom Imaging. 2015; 40:1050–1059. PMID: 25725794.
Article28. Khawaja RD, Singh S, Blake M, Harisinghani M, Choy G, Karaosmanoglu A, et al. Ultralow-dose abdominal computed tomography: comparison of 2 iterative reconstruction techniques in a prospective clinical study. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2015; 39:489–498. PMID: 26182223.29. Pourjabbar S, Singh S, Kulkarni N, Muse V, Digumarthy SR, Khawaja RD, et al. Dose reduction for chest CT: comparison of two iterative reconstruction techniques. Acta Radiol. 2015; 56:688–695. PMID: 24948790.
Article30. Padole A, Digumarthy S, Flores E, Madan R, Mishra S, Sharma A, et al. Assessment of chest CT at CTDIvol less than 1 mGy with iterative reconstruction techniques. Br J Radiol. 2017; 90:20160625. PMID: 28055250.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm, Automatic Exposure Control on Image Quality, and Radiation Dose: Phantom Experiments with Coronary CT Angiography Protocols
- Dosimetric Effects of Low Dose 4D CT Using a Commercial Iterative Reconstruction on Dose Calculation in Radiation Treatment Planning: A Phantom Study
- Radiation Dose Reduction via Sinogram Affirmed Iterative Reconstruction and Automatic Tube Voltage Modulation (CARE kV) in Abdominal CT
- Performance of Half-dose Chest Computed Tomography in Lung Malignancy Using an Iterative Reconstruction Technique
- Fast Cardiac CINE MRI by Iterative Truncation of Small Transformed Coefficients