Anesth Pain Med.
2019 Jul;14(3):356-363. 10.17085/apm.2019.14.3.356.
The relationship between the surgical Apgar score and postoperative complications in patients admitted to an intensive care unit after surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Ulsan University Hospital, Ulsan, Korea. inyoung_huh@uuh.ulsan.kr
- KMID: 2454823
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2019.14.3.356
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Surgical Apgar score (SAS) is a 10-point system that measures estimated blood loss, lowest heart rate and lowest mean blood pressure during surgery, and is known to be associated with postoperative complications. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the relationship between SAS and postoperative major complications in patient admitted to intensive care unit (ICU) after surgery.
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed 543 patients who were admitted to the ICU for 8 months. SAS, patient's demographics and postoperative outcomes were collected and analyzed based on anesthetic record and several medical records in an electronic chart system built in hospital. The patients were divided into three groups based on their SAS. The postoperative major complications, duration of ICU stay and duration of hospital stay were compared among the three groups.
RESULTS
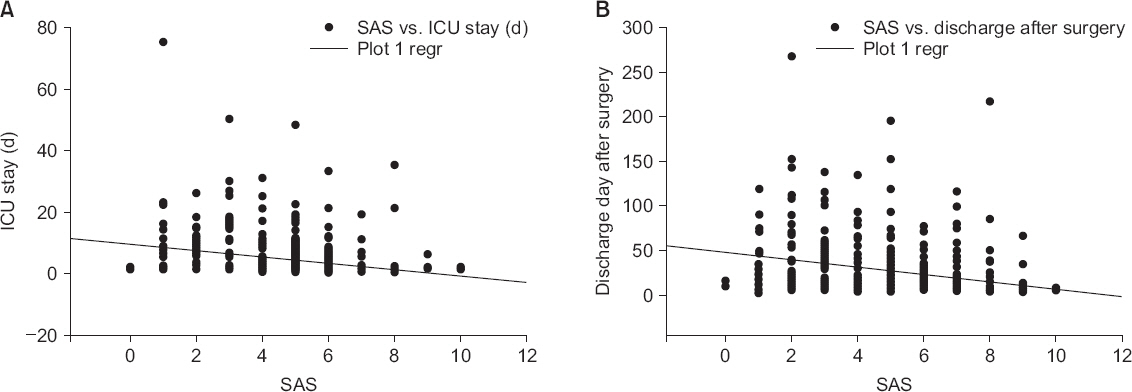
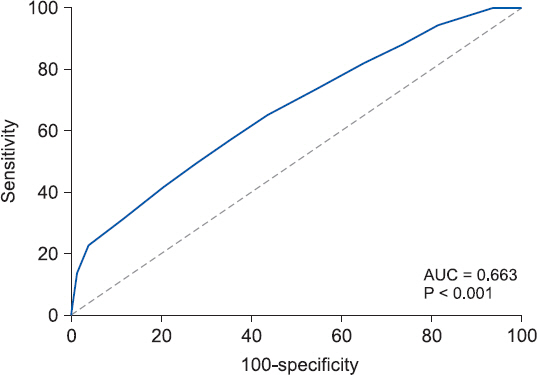
In the low score group, the rate emergency, trauma and hepatobiliary operation were high. In this group, the duration of ICU and hospital stay, use of mechanical ventilation and inotropic in ICU, and postoperative complication were also increased. SAS also had a weak negative correlation with ICU stay and hospital stay. Postoperative complication and mortality rate doubled when compared to reference group (SAS 7-10) according to univariate logistic regression.
CONCLUSIONS
In patients admitted to ICU after surgery, SAS, which can be measured during surgery, is closely related to postoperative parameters including major complications, mortality, and ICU stay. In other words, it is thought that the postoperative outcomes can be improved through appropriate monitoring and intervention for patients with low SAS score.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cavaliere F, Conti G, Costa R, Masieri S, Antonelli M, Proietti R. Intensive care after elective surgery:a survey on 30-day postoperative mortality and morbidity. Minerva Anestesiol. 2008; 74:459–68. PMID: 18762753.2. Gawande AA, Kwaan MR, Regenbogen SE, Lipsitz SA, Zinner MJ. An Apgar score for surgery. J Am Coll Surg. 2007; 204:201–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2006.11.011. PMID: 17254923.3. Assifi MM, Lindenmeyer J, Leiby BE, Grunwald Z, Rosato EL, Kennedy EP, et al. Surgical Apgar score predicts perioperative morbidity in patients undergoing pancreaticoduodenectomy at a high-volume center. J Gastrointest Surg. 2012; 16:275–81. DOI: 10.1007/s11605-011-1733-1. PMID: 22033701.4. Eto K, Yoshida N, Iwatsuki M, Kurashige J, Ida S, Ishimoto T, et al. Surgical Apgar score predicted postoperative morbidity after esophagectomy for esophageal cancer. World J Surg. 2016; 40:1145–51. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-016-3425-1. PMID: 26801506.5. Regenbogen SE, Lancaster RT, Lipsitz SR, Greenberg CC, Hutter MM, Gawande AA. Does the Surgical Apgar Score measure intraoperative performance? Ann Surg. 2008; 248:320–8. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e318181c6b1. PMID: 18650644. PMCID: PMC2562699.6. Ko CY, Hall BL, Hart AJ, Cohen ME, Hoyt DB. The American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program:achieving better and safer surgery. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2015; 41:199–204. DOI: 10.1016/S1553-7250(15)41026-8. PMID: 25977246.7. Owens WD, Felts JA, Spitznagel EL Jr. ASA physical status classifications:a study of consistency of ratings. Anesthesiology. 1978; 49:239–43. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-197810000-00003. PMID: 697077.8. Whiteley MS, Prytherch DR, Higgins B, Weaver PC, Prout WG. An evaluation of the POSSUM surgical scoring system. Br J Surg. 1996; 83:812–5. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.1800830628. PMID: 8696749.9. Lee TH, Marcantonio ER, Mangione CM, Thomas EJ, Polanczyk CA, Cook EF, et al. Derivation and prospective validation of a simple index for prediction of cardiac risk of major noncardiac surgery. Circulation. 1999; 100:1043–9. DOI: 10.1161/01.CIR.100.10.1043. PMID: 10477528.10. Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE. APACHE II:a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med. 1985; 13:818–29. DOI: 10.1097/00003246-198510000-00009. PMID: 3928249.11. Sankar A, Johnson SR, Beattie WS, Tait G, Wijeysundera DN. Reliability of the American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status scale in clinical practice. Br J Anaesth. 2014; 113:424–32. DOI: 10.1093/bja/aeu100. PMID: 24727705. PMCID: PMC4136425.12. Koo CY, Hyder JA, Wanderer JP, Eikermann M, Ramachandran SK. A meta-analysis of the predictive accuracy of postoperative mortality using the American Society of Anesthesiologists' physical status classification system. World J Surg. 2015; 39:88–103. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-014-2783-9. PMID: 25234196.13. Crea N, Di Fabio F, Pata G, Nascimbeni R. APACHE II, POSSUM, and ASA scores and the risk of perioperative complications in patients with colorectal disease. Ann Ital Chir. 2009; 80:177–81. PMID: 20131533.14. Moonesinghe SR, Mythen MG, Das P, Rowan KM, Grocott MP. Risk stratification tools for predicting morbidity and mortality in adult patients undergoing major surgery:qualitative systematic review. Anesthesiology. 2013; 119:959–81. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3182a4e94d. PMID: 24195875.15. Ford MK, Beattie WS, Wijeysundera DN. Systematic review:prediction of perioperative cardiac complications and mortality by the revised cardiac risk index. Ann Intern Med. 2010; 152:26–35. DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-152-1-201001050-00007. PMID: 20048269.16. Davis C, Tait G, Carroll J, Wijeysundera DN, Beattie WS. The Revised Cardiac Risk Index in the new millennium:a single-centre prospective cohort re-evaluation of the original variables in 9,519 consecutive elective surgical patients. Can J Anaesth. 2013; 60:855–63. DOI: 10.1007/s12630-013-9988-5. PMID: 23813289.17. VISION Pilot Study Investigators. Devereaux PJ, Bradley D, Chan MT, Walsh M, Villar JC, et al. An international prospective cohort study evaluating major vascular complications among patients undergoing noncardiac surgery:the VISION Pilot Study. Open Med. 2011; 5:e193–200. PMID: 22567075. PMCID: PMC3345376.18. Jones DR, Copeland GP, de Cossart L. Comparison of POSSUM with APACHE II for prediction of outcome from a surgical highdependency unit. Br J Surg. 1992; 79:1293–6. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.1800791216. PMID: 1486421.19. Ziewacz JE, Davis MC, Lau D, El-Sayed AM, Regenbogen SE, Sullivan SE, et al. Validation of the surgical Apgar score in a neurosurgical patient population. J Neurosurg. 2013; 118:270–9. DOI: 10.3171/2012.10.JNS12436. PMID: 23121434.20. Kinoshita M, Morioka N, Yabuuchi M, Ozaki M. New surgical scoring system to predict postoperative mortality. J Anesth. 2017; 31:198–205. DOI: 10.1007/s00540-016-2290-2. PMID: 27995328. PMCID: PMC5378752.21. Urrutia J, Valdes M, Zamora T, Canessa V, Briceno J. Can the Surgical Apgar Score predict morbidity and mortality in general orthopaedic surgery? Int Orthop. 2012; 36:2571–6. DOI: 10.1007/s00264-012-1696-1. PMID: 23129225. PMCID: PMC3508032.22. Melis M, Pinna A, Okochi S, Masi A, Rosman AS, Neihaus D, et al. Validation of the Surgical Apgar Score in a veteran population undergoing general surgery. J Am Coll Surg. 2014; 218:218–25. DOI: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2013.10.021. PMID: 24315891.23. Sobol JB, Gershengorn HB, Wunsch H, Li G. The surgical Apgar score is strongly associated with intensive care unit admission after high-risk intraabdominal surgery. Anesth Analg. 2013; 117:438–46. DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31829180b7. PMID: 23744956. PMCID: PMC4020414.24. Stoll WD, Taber DJ, Palesch SJ, Hebbar L. Utility of the Surgical Apgar Score in kidney transplantation:is it feasible to predict ICU admission, hospital readmission, length of stay, and cost in this patient population? Prog Transplant. 2016; 26:122–8. DOI: 10.1177/1526924816640948. PMID: 27207400.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- APACHE II Score and Evaluation of Intensive Care Unit Patients
- Cardiac Complications in Patients Admitted to the Neuro-Intensive Care Unit
- Retrospective Analysis of the Postoperative Patients Admitted to General Surgical-Medical Intensive Care Unit
- A Clinical Analysis of Intensive Care Unit Admissions Using APACHE II Scoring System
- Lung Injury Score in Predicting the Outcome of the Patients in the Intensive Care Unit