Ann Clin Neurophysiol.
2019 Jul;21(2):105-107. 10.14253/acn.2019.21.2.105.
Acute unilateral isolated abducens nerve palsy associated with anti-GM1 immunoglobulin M antibody
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. koodaelim@gmail.com
- KMID: 2454733
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14253/acn.2019.21.2.105
Abstract
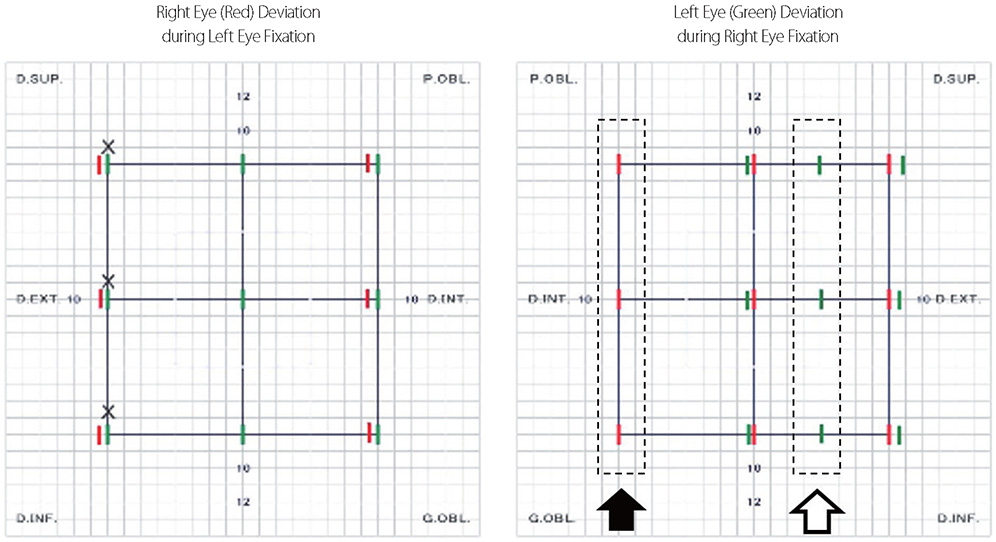
- Acute ophthalmoparesis that includes the oculomotor, trochlear, or abducens nerve may occur as an initial presentation of Miller Fisher syndrome (MFS). The symptoms of MFS or variant forms of Guillain-Barre syndrome are pathogenically related to anti-GQ1b antibodies. We report a case of a 36-year-old man with unilateral isolated abducens nerve palsy associated with anti-GM1 antibody. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of unilateral isolated abducens nerve palsy with positivity for anti-GM1 immunoglobulin M antibody.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Isolated facial diplegia variant of Guillain–Barré syndrome with anti-GM1 IgG antibody
Jin Ho Jung, Sukyoon Lee, Jung Hwa Seo, Jong Seok Bae, Kyong Jin Shin, Jong Kuk Kim, Byeol-A Yoon, Seong-il Oh
Ann Clin Neurophysiol. 2022;24(1):17-20. doi: 10.14253/acn.2022.24.1.17.
Reference
-
1. Chou KL, Galetta SL, Liu GT, Volpe NJ, Bennett JL, Asbury AK, et al. Acute ocular motor mononeuropathies: prospective study of the roles of neuroimaging and clinical assessment. J Neurol Sci. 2004; 219:35–39.
Article2. Odaka M, Yuki N, Hirata K. Anti-GQ1b IgG antibody syndrome: clinical and immunological range. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2001; 70:50–55.
Article3. Kaida K, Ariga T, Yu RK. Antiganglioside antibodies and their pathophysiological effects on Guillain-Barre syndrome and related disorders--a review. Glycobiology. 2009; 19:676–692.
Article4. Willison HJ, Yuki N. Peripheral neuropathies and anti-glycolipid antibodies. Brain. 2002; 125(Pt 12):2591–2625.
Article5. Lavallée P, Vidailhet M, Dussaule JC, Derkinderen P. Post-infectious ophtalmoparesis associated with anti-GM1 but not with anti-GQ1b antibodies. Eur J Neurol. 2001; 8:475–476.
Article6. Go T. Partial oculomotor nerve palsy associated with elevated anti-galactocerebroside and anti-GM1 antibodies. J Pediatr. 2000; 137:425–426.
Article7. Han TH, Kim DY, Park DW, Moon JH. Transient isolated lower bulbar palsy with elevated serum anti-GM1 and anti-GD1b antibodies during aripiprazole treatment. Pediatr Neurol. 2017; 66:96–99.
Article8. Fusco C, Bertani G, Scarano A, Giustina ED. Acute ophthalmoparesis associated with anti-GM1, anti-GD1a, and anti-GD1b antibodies after enterovirus infection in a 6-year-old girl. J Child Neurol. 2007; 22:432–434.
Article9. Katchanov J, Lünemann JD, Masuhr F, Meisel A, Möller H, Zschenderlein R. Isolated abducens nerve paresis associated with high titer of anti-asialo-GM1 following Campylobacter jejuni enteritis. J Neurol. 2004; 251:1404–1405.
Article10. Caudie C, Quittard PA, Bouhour F, Vial C, Garnier L, Fabien N. Comparison of commercial tests for detecting multiple anti-ganglioside autoantibodies in patients with well-characterized immune-mediated peripheral neuropathies. Clin Lab. 2013; 59:1277–1287.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Isolated Unilateral Abducens Nerve Palsy Caused by Clival Metastasis from Rectal Cancer
- Unilateral Abducens Nerve Palsy Associated with Ruptured Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm
- A Patient Presented With Unilateral Abducens Nerve Palsy: A Variant Form of Guillain-Barre Syndrome With Anti-GT1a Antibody
- Acute Rhinosinusitis in Prominently Pneumatized Sphenoid Sinus Presenting with Unilateral Abducens Nerve Palsy
- A Case of Abducens Nerve Palsy Caused by Isolated Sphenoid Fungal Sinusitis