Ann Clin Neurophysiol.
2018 Jul;20(2):105-108. 10.14253/acn.2018.20.2.105.
Acute pontine infarction in a patient with persistent left superior vena cava
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology and Stroke Center, Yeungnam University Medical Center, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Department of Neruology, Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu, Korea. woosubb@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2454715
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14253/acn.2018.20.2.105
Abstract
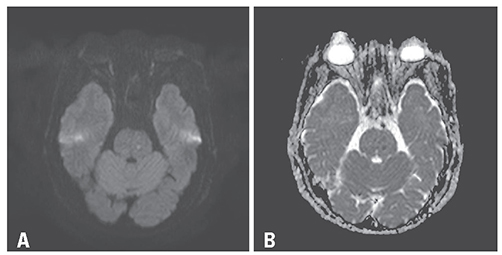
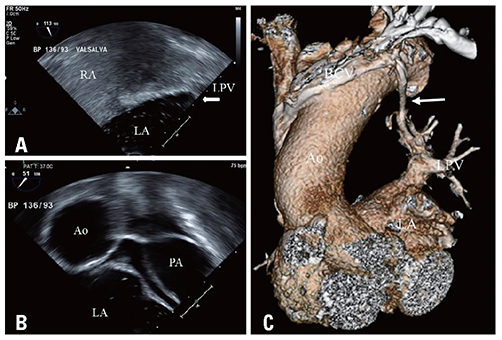
- Persistent left superior vena cava (PLSVC) is a common venous anomaly of the thorax and usually drains into the right atrium. Less often it drains into the left atrium and has previously been related to ischemic stroke. We report a case of PLSCV that founded during ischemic stroke evaluation in a 77-year-old woman which was detected on transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) and transcranial Doppler ultrasonography (TCD) with saline agitated test and computed tomography.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Paval J, Nayak S. A persistent left superior vena cava. Singapore Med J. 2007; 48:e90–e93.2. Yousaf M, Malak SF. Left atrial drainage of a persistent left superior vena cava. Radiol Case Rep. 2015; 3:225.
Article3. Goyal SK, Punnam SR, Verma G, Ruberg FL. Persistent left superior vena cava: a case report and review of literature. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2008; 6:50.
Article4. Rawal G, Kumar R, Yadav S, Verma D. Persistent left superior vena cava: a rare case with clinical significance. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016; 10:Od17–Od18.
Article5. Hutyra M, Skala T, Sanak D, Novotny J, Köcher M, Taborsky M. Persistent left superior vena cava connected through the left upper pulmonary vein to the left atrium: an unusual pathway for paradoxical embolization and a rare cause of recurrent transient ischaemic attack. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2010; 11:E35.
Article6. Tsang W, Boulos M, Moody AR, Sahlas DJ, Morgan CD. An unusual cause of stroke--the importance of saline contrast echocardiography. Echocardiography. 2008; 25:908–910.
Article7. Gupta SK, Shetkar SS, Ramakrishnan S, Kothari SS. Saline contrast echocardiography in the era of multimodality imaging--importance of “bubbling it right”. Echocardiography. 2015; 32:1707–1719.8. Thaiyananthan NN, Jacono FJ 3rd, Patel SR, Kern JA, Stoller JK. Right-to-left anatomic shunt associated with a persistent left superior vena cava: the importance of injection site in demonstrating the shunt. Chest. 2009; 136:617–620.9. Butera G, Salvia J, Carminati M. When side matters: contrast echocardiography with injection from the left antecubital vein to detect a persistent left superior vena cava draining to the left atrium in a patient with cerebral stroke. Circulation. 2012; 125:e1.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Persistent Left Superior Vena Cava with Interruption of Inferior Vena Cava
- Persistent Left Superior Vena Cava with Absent Right Superior Vena Cava and Large Atrial Septal Defect in Visceroatrial Situs solitus
- A Case of Persistent Left SVC Associated with Tricuspid Regurgitation
- Persistent Left Sperior Vena Cava Draining into the Left Atrium with Absent Right Superior Vena Cava in Tetralogy of Fallot
- Congenital Absence of the Azygos Vein with Persistent Left Superior Vena Cava: A Case Report