Ann Clin Neurophysiol.
2018 Jul;20(2):93-96. 10.14253/acn.2018.20.2.93.
Sonographic evaluation of the diaphragm in patients with unilateral diaphragmatic paralysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. ji-helpgod@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2454712
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14253/acn.2018.20.2.93
Abstract
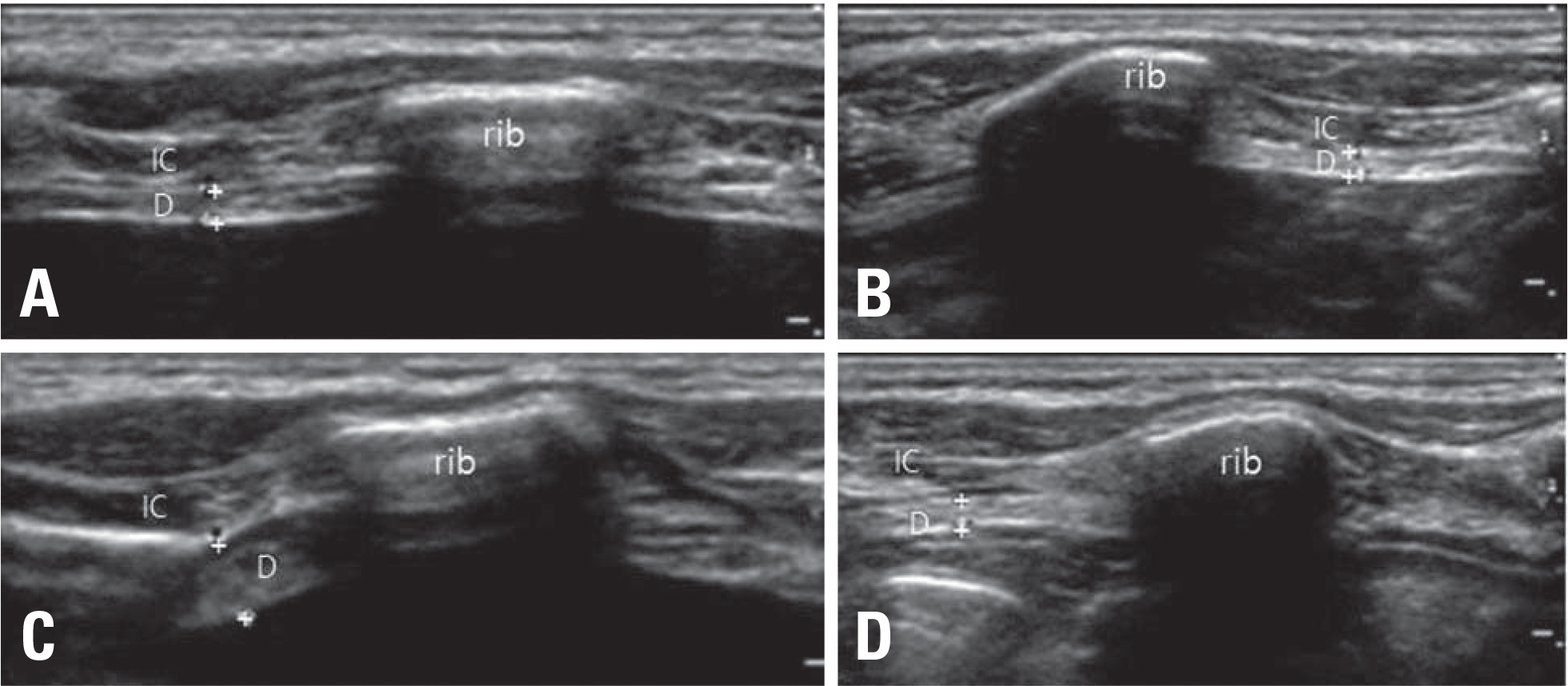
- Evaluation of diaphragm function is challenging because no single test has a high diagnostic yield. We describe ultrasound findings in three cases with acquired unilateral diaphragmatic elevation. These cases confirm that sonographic evaluation is a valid tool for identifying diaphragm dysfunction. In addition, ultrasound measurements of diaphragm thickness and the contractility can be used to determine if a diaphragm is paralyzed and suggest the duration of paralysis (i.e., acute or chronic).
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Sarwal A, Walker FO, Cartwright MS. Neuromuscular ultrasound for evaluation of the diaphragm. Muscle Nerve. 2013; 47:319–329.
Article2. Markand ON, Kincaid JC, Pourmand RA, Moorthy SS, King RD, Mahomed Y, et al. Electrophysiologic evaluation of diaphragm by transcutaneous phrenic nerve stimulation. Neurology. 1984; 34:604–614.
Article3. Seok JI, Kim SY, Walker FO, Kwak SG, Kwon DH. Ultrasonographic findings of the normal diaphragm: thickness and contractility. Ann Clin Neurophysiol. 2017; 19:131–135.
Article4. Baldwin CE, Paratz JD, Bersten AD. Diaphragm and peripheral muscle thickness on ultrasound: intra-rater reliability and variability of a methodology using non-standard recumbent positions. Respirology. 2011; 16:1136–1143.
Article5. Boon AJ, Harper CJ, Ghahfarokhi LS, Strommen JA, Watson JC, Sorenson EJ. Two-dimensional ultrasound imaging of the diaphragm: quantitative values in normal subjects. Muscle Nerve. 2013; 47:884–889.
Article6. Gottesman E, McCool FD. Ultrasound evaluation of the paralyzed diaphragm. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997; 155:15701574.7. Summerhill EM, El-Sameed YA, Glidden TJ, McCool FD. Monitoring recovery from diaphragm paralysis with ultrasound. Chest. 2008; 133:737743.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diagnosis of diaphragmatic paralysis using ultrasound in a cervical herpes zoster patient: A case report
- A Case of Diaphragmatic Eventration Complicated with Contralateral Traumatic Diaphragmatic Paralysis
- Paper-thinned diaphragm: CT sign of diaphragmatic eventration
- A Case of Unilateral Diaphragmatic Paralysis with Brachial Plexus Palsy in the Neonate
- Delayed Onset Transient Diaphragmatic Paralysis after Pacemaker Implantation