Cancer Res Treat.
2019 Jul;51(3):1222-1230. 10.4143/crt.2018.595.
Prognostic Value and Staging Classification of Lymph Nodal Necrosis in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma after Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou, China. chenxiaozhong2016@163.com
- KMID: 2454313
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2018.595
Abstract
- PURPOSE
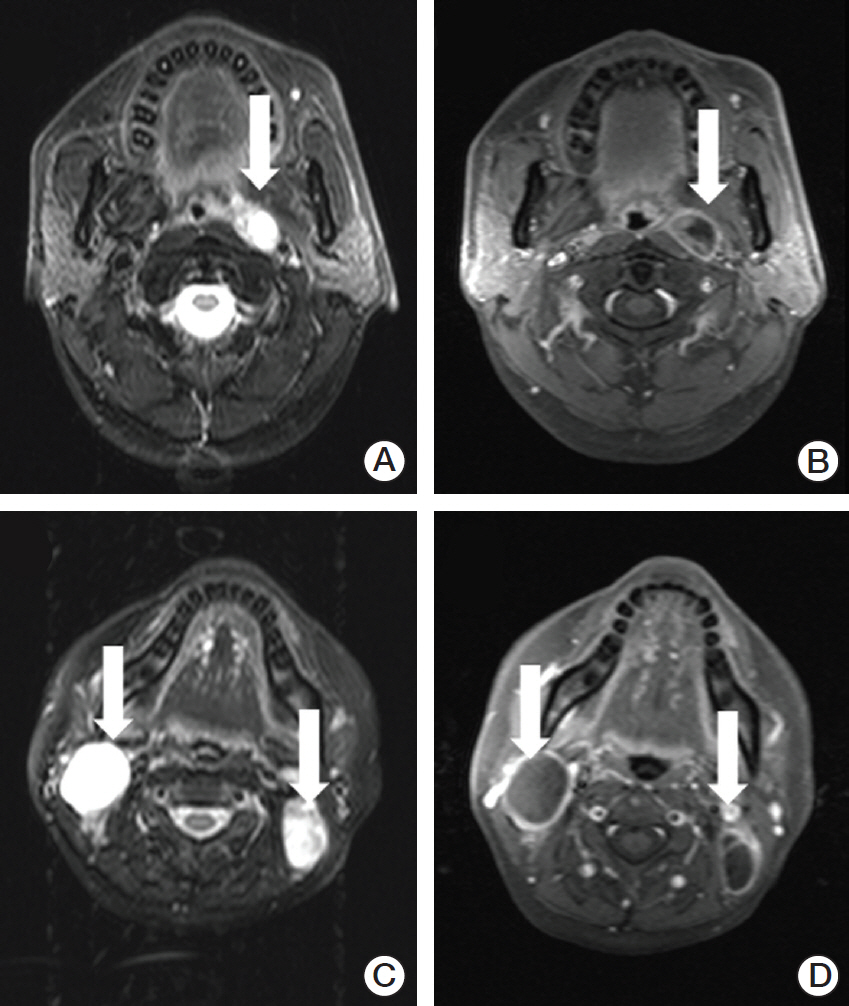
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the prognostic value of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)"’determined lymph nodal necrosis (LNN) in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) and explore the feasibility of an N-classification system based on the 8th edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) system.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The MRI scans of 616 patients with newly diagnosed stage T1-4N1-3M0 NPC who were treated with definitive intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) were reviewed.
RESULTS
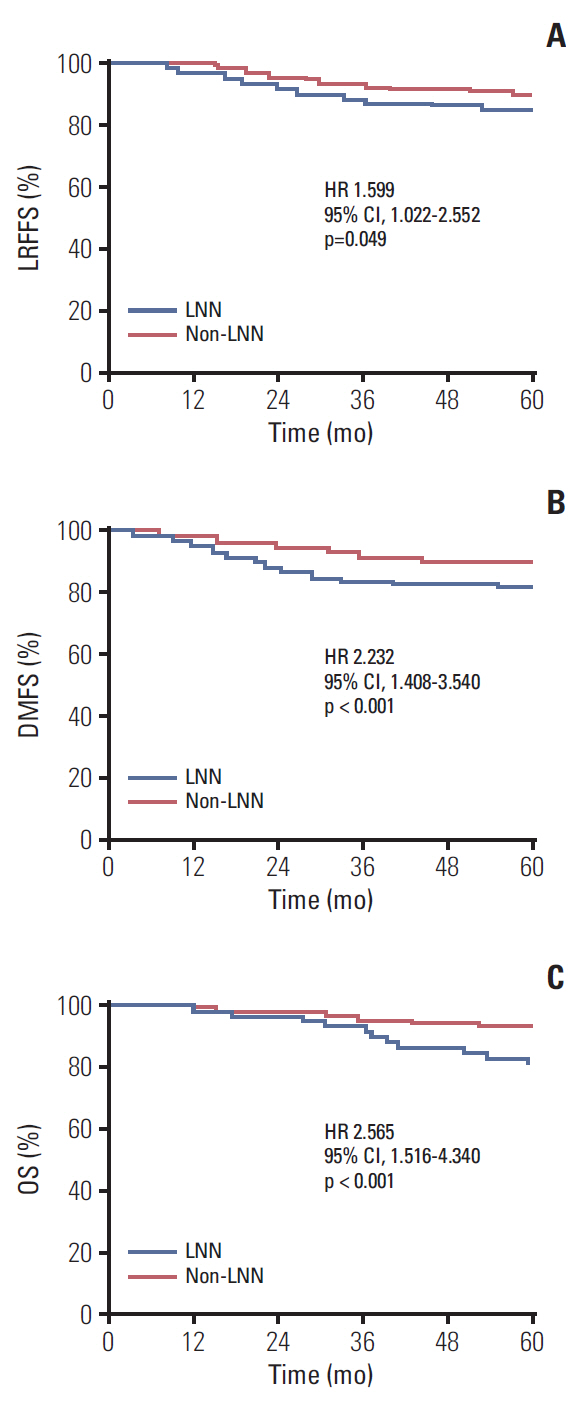
Multivariate analysis showed that LNN was an independent negative prognostic predictor of distant metastasis free survival (hazard ratio, 1.634; 95% confidence interval, 1.023 to 2.609; p=0.040) and overall survival (hazard ratio, 2.154; 95% confidence interval, 1.282 to 3.620; p=0.004). Patients of classification N1 disease with LNN were reclassified as classification N2, and classification N2 disease with LNN as classification N3 in the proposed N-classification system. Correlation with death and distant failure was significant, and the total difference between N1 and N3 was wider with the proposed system.
CONCLUSION
MRI-determined LNN is an independent negative prognostic factor for NPC. The proposed N classification system is powerfully predictive.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Sun X, Su S, Chen C, Han F, Zhao C, Xiao W, et al. Long-term outcomes of intensity-modulated radiotherapy for 868 patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: an analysis of survival and treatment toxicities. Radiother Oncol. 2014; 110:398–403.
Article2. Lin S, Pan J, Han L, Guo Q, Hu C, Zong J, et al. Update report of nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with reduced-volume intensity-modulated radiation therapy and hypothesis of the optimal margin. Radiother Oncol. 2014; 110:385–9.
Article3. Lee AW, Ng WT, Chan LL, Hung WM, Chan CC, Sze HC, et al. Evolution of treatment for nasopharyngeal cancer--success and setback in the intensity-modulated radiotherapy era. Radiother Oncol. 2014; 110:377–84.4. Cao CN, Luo JW, Gao L, Yi JL, Huang XD, Wang K, et al. Update report of T4 classification nasopharyngeal carcinoma after intensity-modulated radiotherapy: an analysis of survival and treatment toxicities. Oral Oncol. 2015; 51:190–4.
Article5. Chua ML, Wee JT, Hui EP, Chan AT. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 2016; 387:1012–24.
Article6. Amin MB, Edge S, Greene F, Byrd DR, Brookland RK, Washington MK, et al. AJCC cancer staging manual. 8th ed. New York: Springer;2017.7. Zhang B, Tian J, Dong D, Gu D, Dong Y, Zhang L, et al. Radiomics features of multiparametric MRI as novel prognostic factors in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2017; 23:4259–69.
Article8. Lan M, Huang Y, Chen CY, Han F, Wu SX, Tian L, et al. Prognostic value of cervical nodal necrosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: analysis of 1800 patients with positive cervical nodal metastasis at MR imaging. Radiology. 2015; 276:619.
Article9. Mao YP, Liang SB, Liu LZ, Chen Y, Sun Y, Tang LL, et al. The N staging system in nasopharyngeal carcinoma with radiation therapy oncology group guidelines for lymph node levels based on magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Cancer Res. 2008; 14:7497–503.
Article10. Chua DT, Sham JS, Kwong DL, Choy DT, Leong L, Chan FL. Evaluation of cervical nodal necrosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by computed tomography: incidence and prognostic significance. Head Neck. 1997; 19:266–75.
Article11. Zhang LL, Li JX, Zhou GQ, Tang LL, Ma J, Lin AH, et al. Influence of cervical node necrosis of different grades on the prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with intensity-modulated radiotherapy. J Cancer. 2017; 8:959–66.
Article12. Cao C, Jiang F, Jin Q, Jin T, Huang S, Hu Q, et al. Paranasal sinus invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma after intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Cancer Res Treat. 2019; 51:73–9.
Article13. van den Brekel MW, Stel HV, Castelijns JA, Nauta JJ, van der Waal I, Valk J, et al. Cervical lymph node metastasis: assessment of radiologic criteria. Radiology. 1990; 177:379–84.
Article14. Jin T, Qin WF, Jiang F, Jin QF, Wei QC, Jia YS, et al. Cisplatin and fluorouracil induction chemotherapy with or without docetaxel in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Transl Oncol. 2019; 12:633–9.
Article15. Wang TJ, Riaz N, Cheng SK, Lu JJ, Lee NY. Intensity-modulated radiation therapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a review. J Radiat Oncol. 2012; 1:129–46.
Article16. Tang LL, Guo R, Zhou G, Sun Y, Liu LZ, Lin AH, et al. Prognostic value and staging classification of retropharyngeal lymph node metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with intensity-modulated radiotherapy. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e108375.
Article17. Groome PA, Schulze K, Boysen M, Hall SF, Mackillop WJ. A comparison of published head and neck stage groupings in carcinomas of the oral cavity. Head Neck. 2001; 23:613–24.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Paranasal Sinus Invasion in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma after Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging–Detected Intracranial Extension in the T4 Classification Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma with Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy
- Prognostic value of nodal SUVmax of 18F-FDG PET/CT in nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with intensity-modulated radiotherapy
- Proposal of the Nodal Stage Based on the Number of Metastatic Lymph Nodes in Patients with Gastric Cancer
- Tumor volume/metabolic information can improve the prognostication of anatomy based staging system for nasopharyngeal cancer? Evaluation of the 8th edition of the AJCC/UICC staging system for nasopharyngeal cancer