Temporal and Geospatial Trends of Hypertension Management in Korea: a Nationwide Study 2002–2016
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Preventive Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hckim@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Graduate School, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Division of Cardiology, Severance Cardiovascular Hospital and Cardiovascular Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Big Data Steering Department, National Health Insurance Service, Wonju, Korea.
- KMID: 2454047
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2018.0358
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
Geographic distribution of hypertension management in Korea has never been reported. We investigated temporal and regional trends of hypertension management in Korea.
METHODS
For each calendar year from 2002 to 2016, we identified 2,423,245 to 7,549,989 persons aged ≥30 years treated for hypertension (total 80,564,109 cases). We calculated yearly age-sex standardized rates for medication adherence, combination therapy, blood test, and urine test according to geographic regions. We then used multivariate logistic regression to calculate odds ratios for hypertension management adjusted for individual-level sociodemographic factors.
RESULTS
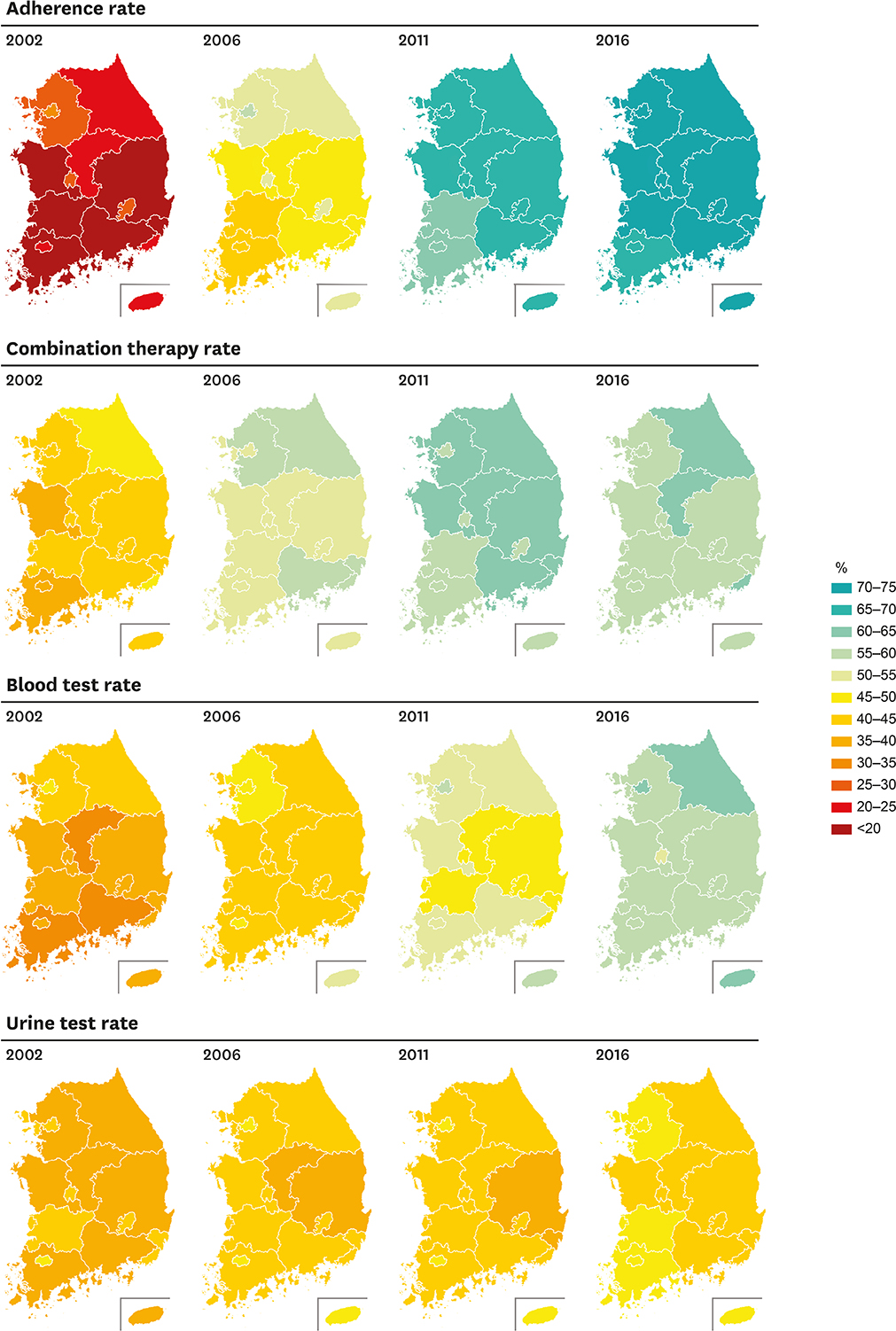
Adherence rates have markedly increased from 24.4% (2002) to 71.6% (2016) nationwide. Regional difference was prominent in 2002 (highest, 31.7% in Seoul; lowest, 14.4% in Jeonbuk), but has become less noticeable over 15 years (highest, 73.1% in Daejeon; lowest, 69.0% in Jeonnam, 2016). Combination therapy rates increased from 42.8% (2002) to 61.0% (2011), but are in decreasing trend after 2011. Blood test rates were 58.8% in 2016, whereas urine test rates have been stagnant below 50% across all regions. Geographic variations of combination therapy and complication screening rates were not profound. Results from multivariable logistic regression, adjusted for age and sex, were in agreement with trends observed by standardized rates. The odds ratios remained unchanged when the models were further adjusted for employment status and household income.
CONCLUSIONS
Regional difference in hypertension management was evident in the past, but has become less apparent over the last 15 years in Korea.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 6 articles
-
Differential Control Rate of Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure among Korean Adults with Hypertension: the Sixth Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2013–2015 (KNHANES VI)
So Mi Jemma Cho, Hokyou Lee, Wook Bum Pyun, Hyeon Chang Kim
Korean Circ J. 2019;49(11):1035-1048. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2019.0049.Improving the Quality of Hypertension Management: Multifaceted Approach
Mi-Hyang Jung, Sang-Hyun Ihm
Korean Circ J. 2019;49(6):528-531. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2019.0055.Big Challenge in Big Data Research: Continual Dispute on Big Data Analysis
Hae-Young Lee
Korean Circ J. 2020;50(1):69-71. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2019.0349.Comparison of First-Line Dual Combination Treatments in Hypertension: Real-World Evidence from Multinational Heterogeneous Cohorts
Seng Chan You, Sungjae Jung, Joel N. Swerdel, Patrick B. Ryan, Martijn J. Schuemie, Marc A. Suchard, Seongwon Lee, Jaehyeong Cho, George Hripcsak, Rae Woong Park, Sungha Park
Korean Circ J. 2020;50(1):52-68. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2019.0173.The Follow-up Study of Changes in Frailty in Elderly Receiving Home Health Care of the Public Health Center
Dong Ok Lee, Young Ran Chin
J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2019;30(4):528-538. doi: 10.12799/jkachn.2019.30.4.528.Trends in Regional Disparity in Cardiovascular Mortality in Korea, 1983–2019
Eunji Kim, Jongmin Baek, Min Kim, Hokyou Lee, Jang-Whan Bae, Hyeon Chang Kim
Korean Circ J. 2022;52(11):829-843. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2022.0156.
Reference
-
1. GBD 2016 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017; 390:1345–1422.2. Grotto I, Huerta M, Sharabi Y. Hypertension and socioeconomic status. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2008; 23:335–339.
Article3. Chow CK, Teo KK, Rangarajan S, et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in rural and urban communities in high-, middle-, and low-income countries. JAMA. 2013; 310:959–968.
Article4. Lloyd-Sherlock P, Beard J, Minicuci N, Ebrahim S, Chatterji S. Hypertension among older adults in low- and middle-income countries: prevalence, awareness and control. Int J Epidemiol. 2014; 43:116–128.
Article5. Reynolds K, Gu D, Muntner P, et al. Geographic variations in the prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in China. J Hypertens. 2003; 21:1273–1281.
Article6. Mindell JS, Shelton NJ, Roth MA, Chaudhury M, Falaschetti E. Persistent regional variation in treatment of hypertension. Public Health. 2012; 126:317–323.
Article7. Marques-Vidal P, Paccaud F. Regional differences in self-reported screening, prevalence and management of cardiovascular risk factors in Switzerland. BMC Public Health. 2012; 12:246.
Article8. Stöckl D, Rückert-Eheberg IM, Heier M, et al. Regional variability of lifestyle factors and hypertension with prediabetes and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus: the population-based KORA-F4 and SHIP-TREND studies in Germany. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0156736.
Article9. Yin M, Augustin B, Fu Z, Yan M, Fu A, Yin P. Geographic distributions in hypertension diagnosis, measurement, prevalence, awareness, treatment and control rates among middle-aged and older adults in China. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:37020.
Article10. Kauhl B, Maier W, Schweikart J, Keste A, Moskwyn M. Exploring the small-scale spatial distribution of hypertension and its association to area deprivation based on health insurance claims in Northeastern Germany. BMC Public Health. 2018; 18:121.
Article11. OECD iLibrary. Doctors' Consultations. place unknown: OECD iLibrary;2018. DOI: 10.1787/1a1ac034-en.12. National Health Insurance Service. 2016 National Health Screening Statistical Yearbook. Wonju: National Health Insurance Service;2017.13. Korean Society Hypertension (KSH). Hypertension Epidemiology Research Working Group. Kim HC, Cho MC. Korea hypertension fact sheet 2018. Clin Hypertens. 2018; 24:13.
Article14. Seong SC, Kim YY, Khang YH, et al. Data resource profile: the national health information database of the national health insurance service in South Korea. Int J Epidemiol. 2017; 46:799–800.15. ACCORD Study Group. Cushman WC, Evans GW, et al. Effects of intensive blood-pressure control in type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:1575–1585.
Article16. Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, et al. 2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2013; 34:2159–2219.17. James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, et al. 2014 evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). JAMA. 2014; 311:507–520.18. SPRINT Research Group. Wright JT Jr, Williamson JD, et al. A randomized trial of intensive versus standard blood-pressure control. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:2103–2116.
Article19. Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension. 2018; 71:e13–115.
Article20. Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, et al. 2018 ESC/ESH guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2018; 39:3021–3104.21. Shin J, Park JB, Kim KI, et al. 2013 Korean Society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of hypertension: part I-epidemiology and diagnosis of hypertension. Clin Hypertens. 2015; 21:1.
Article22. Shin J, Park JB, Kim KI, et al. 2013 Korean Society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of hypertension: part II-treatments of hypertension. Clin Hypertens. 2015; 21:2.
Article23. Halpern MT, Khan ZM, Schmier JK, et al. Recommendations for evaluating compliance and persistence with hypertension therapy using retrospective data. Hypertension. 2006; 47:1039–1048.
Article24. Pedigo A, Aldrich T, Odoi A. Neighborhood disparities in stroke and myocardial infarction mortality: a GIS and spatial scan statistics approach. BMC Public Health. 2011; 11:644.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Temporal Trends of Cardiac Implantable Electronic Device Implantations: a Nationwide Population-based Study
- Korea hypertension fact sheet 2018
- Incidence and Management Trends of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures in South Korea: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
- The Choice of First-line Therapy and Combination Therapy in Disease Management of Hypertension
- Medical management of hypertension