J Neurocrit Care.
2019 Jun;12(1):64-65. 10.18700/jnc.190085.
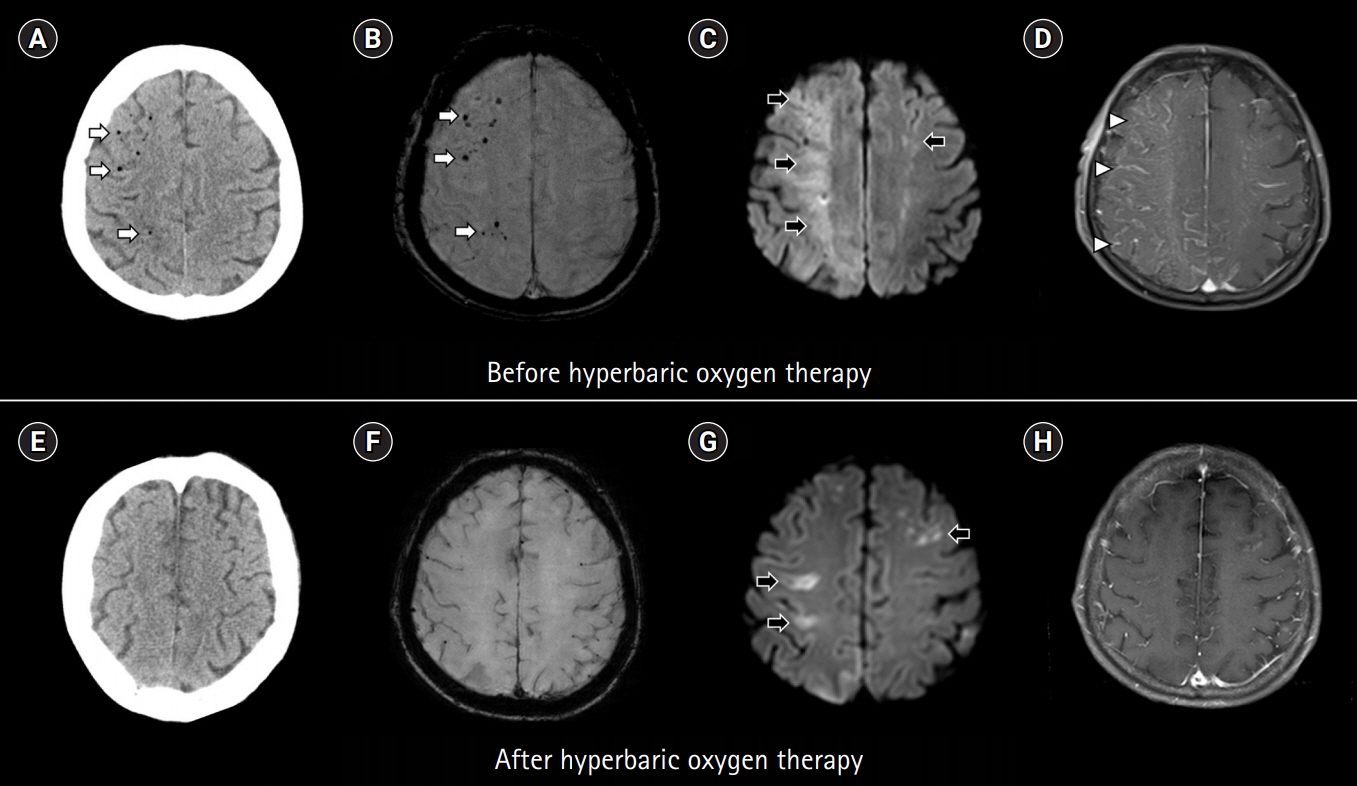
Cerebral air embolism treated using hyperbaric oxygen therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea. sbjeonmd@gmail.com
- KMID: 2452829
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18700/jnc.190085
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Delayed cerebral infarction due to cerebral venous air emboli after cardiac arrest
Yoon-Kyung Lee, Jin-Heon Jeong
J Neurocrit Care. 2021;14(1):61-62. doi: 10.18700/jnc.210012.
Reference
-
1. Jeon SB, Kim JS, Lee DK, Kang DW, Kwon SU. Clinicoradiological characteristics of cerebral air embolism. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2007; 23:459–62.
Article2. Jeon SB, Kang DW. Cerebral air emboli on T2-weighted gradient-echo magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007; 78:871.
Article3. Hjouj M, Last D, Guez D, Daniels D, Sharabi S, Lavee J, et al. MRI study on reversible and irreversible electroporation induced blood brain barrier disruption. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e42817.
Article4. Gill AL, Bell CN. Hyperbaric oxygen: its uses, mechanisms of action and outcomes. QJM. 2004; 97:385–95.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cerebral Air Embolism Following a Gastroscopy
- Spontaneous Absorption of Cerebral Air Embolus Developed Accidentally during an Intra-arterial Procedure
- Stroke Caused by Cerebral Air Embolism after Central Venous Catheter Removal: A Case Report
- A Cerebral Air Embolism after CT-Guided Percutaneous Transthoracic Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy of the Lung
- Four Cases of a Cerebral Air Embolism Complicating a Percutaneous Transthoracic Needle Biopsy