Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2019 Sep;11(5):655-663. 10.4168/aair.2019.11.5.655.
Effects of Vacuuming Mattresses on Allergic Rhinitis Symptoms in Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Hallym University, Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Hwaseong, Korea.
- 2Allergy and Clinical Immunology Research Center, Hallym University College of Medicine, Hwaseong, Korea. pedalllee@gmail.com
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Medicine, Graduate School, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Pediatrics, Severance Hospital, Institute of Allergy, Brain Korea 21 PLUS Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Pediatrics, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Anyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2452756
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2019.11.5.655
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the effects of daily vacuuming of mattresses on the concentration of house dust mite (HDM) allergens and on allergic rhinitis (AR) symptoms in children sensitized to HDM.
METHODS
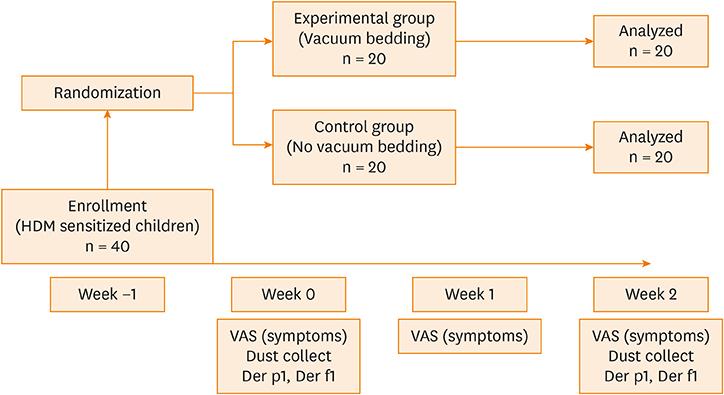
Forty children between the ages of 6 and 12 years with mild persistent AR and sensitized only to HDM were enrolled and randomly allocated to 2 groups. Caregivers of children in the experimental group cleaned the children's rooms and vacuumed their mattresses daily for 2 weeks. Caregivers of children in the control group cleaned the children's rooms without vacuuming mattresses. Symptoms of AR were checked weekly and dust samples were collected from the mattresses before and after the study.
RESULTS
Demographics at the beginning of the study were not significantly different between the 2 groups. In the experimental group, symptoms of AR and dust weight were significantly decreased after 2 weeks (total symptoms of AR, P <0.001; sneezing, P < 0.001; rhinorrhea, P <0.001; nasal obstruction, P < 0.001; itching, P <0.001; and dust weight, P = 0.006). The concentrations of HDM allergens were not changed significantly (Der p1, P = 0.333; Der f1, P = 0.841). In the control group, there were no significant changes in symptoms of AR, dust weight, or the concentration of HDM allergens.
CONCLUSIONS
Our findings showed that daily vacuuming of mattresses reduced dust weight and symptoms of AR. However, the concentration of HDM allergens did not significantly decrease.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brozek JL, Bousquet J, Baena-Cagnani CE, Bonini S, Canonica GW, Casale TB, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) guidelines: 2010 revision. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 126:466–476.2. Asher MI, Montefort S, Björkstén B, Lai CK, Strachan DP, Weiland SK, et al. Worldwide time trends in the prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in childhood: ISAAC Phases One and Three repeat multicountry cross-sectional surveys. Lancet. 2006; 368:733–743.
Article3. Hong SJ, Ahn KM, Lee SY, Kim KE. The prevalences of asthma and allergic diseases in Korean children. Korean J Pediatr. 2008; 51:343–350.
Article4. Kang SY, Song WJ, Cho SH, Chang YS. Time trends of the prevalence of allergic diseases in Korea: a systematic literature review. Asia Pac Allergy. 2018; 8:e8.
Article5. Yoon J, Choi YJ, Lee E, Cho HJ, Yang SI, Kim YH, et al. Allergic rhinitis in preschool children and the clinical utility of FeNO. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017; 9:314–321.
Article6. Sung M, Kim SW, Kim JH, Lim DH. Regional difference of causative pollen in children with allergic rhinitis. J Korean Med Sci. 2017; 32:926–932.
Article7. Kim DH, Park YS, Jang HJ, Kim JH, Lim DH. Prevalence and allergen of allergic rhinitis in Korean children. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2016; 30:72–78.
Article8. Park HJ, Lee JH, Park KH, Ann HW, Jin MN, Choi SY, et al. A nationwide survey of inhalant allergens sensitization and levels of indoor major allergens in Korea. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014; 6:222–227.
Article9. Gøtzsche PC, Johansen HK. House dust mite control measures for asthma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008; CD001187.
Article10. Platts-Mills TA. Allergen avoidance in the treatment of asthma: problems with the meta-analyses. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 122:694–696.
Article11. Nurmatov U, van Schayck CP, Hurwitz B, Sheikh A. House dust mite avoidance measures for perennial allergic rhinitis: an updated Cochrane systematic review. Allergy. 2012; 67:158–165.
Article12. Arroyave WD, Rabito FA, Carlson JC, Friedman EE, Stinebaugh SJ. Impermeable dust mite covers in the primary and tertiary prevention of allergic disease: a meta-analysis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014; 112:237–248.
Article13. Wu FF, Wu MW, Pierse N, Crane J, Siebers R. Daily vacuuming of mattresses significantly reduces house dust mite allergens, bacterial endotoxin, and fungal β-glucan. J Asthma. 2012; 49:139–143.
Article14. Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, Denburg J, Fokkens WJ, Togias A, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) 2008. Allergy. 2008; 63:Suppl 86. 8–160.15. Statulator. Sample size calculator for comparing two paired means [Internet]. place unknown: Statulator;2014. cited 2014 Feb 25. Available from: http://statulator.com/SampleSize/ss2PM.html.16. Urbaniak GC, Plous S. Research Randomizer (Version 4.0) [Internet]. Lancaster (PA): Research Randomizer;cited 2013 Jun 22. Available from: http://www.randomizer.org/.17. Wu FF, Siebers R, Chang CF, Hsieh SW, Wu MW, Chen CY, et al. Indoor allergens and microbial bio-contaminants in homes of asthmatic children in central Taiwan. J Asthma. 2009; 46:745–749.
Article18. Koh GC, Shek LP, Kee J, Tai BC, Wee A, Ng V, et al. An association between floor vacuuming and dust-mite and serum eosinophil cationic protein in young asthmatics. Indoor Air. 2009; 19:468–473.
Article19. Vicendese D, Dharmage SC, Tang ML, Olenko A, Allen KJ, Abramson MJ, et al. Bedroom air quality and vacuuming frequency are associated with repeat child asthma hospital admissions. J Asthma. 2015; 52:727–731.
Article20. Wang Y, Xiong L, Yin X, Wang J, Zhang Q, Yu Z, et al. House dust mite allergen levels in households and correlation with allergic rhinitis symptoms. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2014; 28:193–196.
Article21. Sercombe JK, Liu-Brennan D, Causer SM, Tovey ER. The vertical distribution of house dust mite allergen in carpet and the effect of dry vacuum cleaning. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2007; 210:43–50.
Article22. Baek JH, Cho E, Kim MA, Lee SW, Kang YS, Sheen YH, et al. Response to nonallergenic irritants in children with allergic and nonallergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2016; 8:346–352.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of wheezing in early childhood in the development of allergic rhinitis in later years
- Diagnosis of Allergic Rhinitis
- Prevalence and comorbidity of allergic diseases in preschool children
- Allergic Rhinitis and Sleep-disordered Breathing
- The Role of Aviation Medical Examiners in the Diagnosis, Treatment and Aeromedical Assessment of Patients with Allergic Rhinitis