Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2019 Jul;22(4):392-399. 10.5223/pghn.2019.22.4.392.
Wilson Disease Comorbid with Hereditary Sensory Autonomic Neuropathy Type IV and Gitelman Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. hryang@snubh.org
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2451580
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2019.22.4.392
Abstract
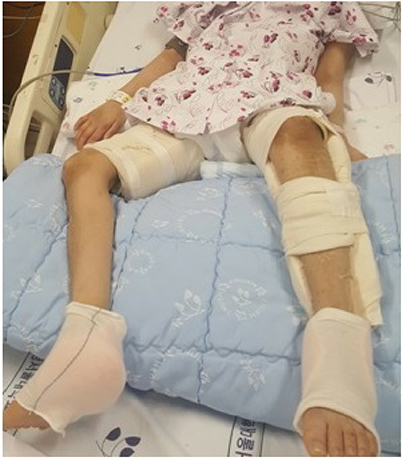
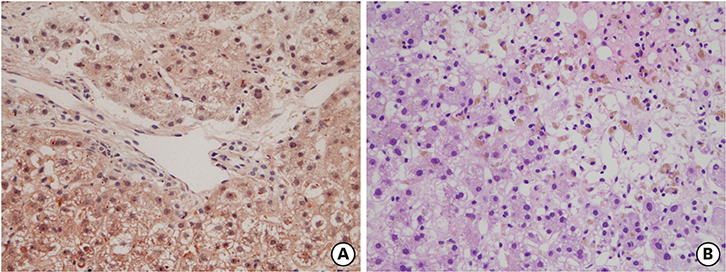
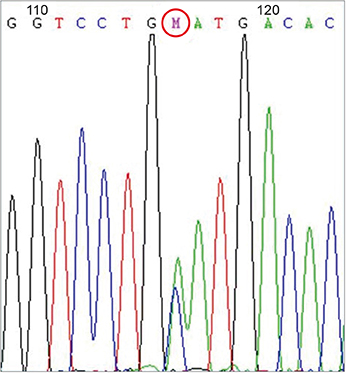
- Wilson disease a rare autosomal recessive inherited disorder of copper metabolism, is characterized by excessive deposition of copper in the liver, brain, and other tissues. Wilson disease is often fatal if it is not recognized early and treated when it is symptomatic. Gitelman syndrome is also an autosomal recessive kidney disorder characterized by low blood levels of potassium and magnesium, decreased excretion of calcium in the urine, and elevated blood pH. Hereditary sensory autonomic neuropathy type IV (HSAN-IV), a very rare condition that presents in infancy, is characterized by anhidrosis, absence of pain sensation, and self-mutilation. It is usually accompanied by developmental delay and mental retardation. We report a case of Wilson disease manifested as fulminant hepatitis, acute pancreatitis, and acute kidney injury in a 15-year-old boy comorbid with HSAN-IV and Gitelman syndrome. Such concurrence of three genetic diseases is an extremely rare case.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Swanson AG. Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhydrosis. A unique syndrome in two male siblings. Arch Neurol. 1963; 8:299–306.2. Sarasola E, Rodríguez JA, Garrote E, Arístegui J, García-Barcina MJ. A short in-frame deletion in NTRK1 tyrosine kinase domain caused by a novel splice site mutation in a patient with congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis. BMC Med Genet. 2011; 12:86.
Article3. Azadvari M, Emami Razavi SZ, Kazemi S. Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type IV in 9 year old boy: a case report. Iran J Child Neurol. 2016; 10:83–85.4. Seo JK. Diagnosis of Wilson disease in young children: molecular genetic testing and a paradigm shift from the laboratory diagnosis. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2012; 15:197–209.
Article5. Socha P, Janczyk W, Dhawan A, Baumann U, D'Antiga L, Tanner S, et al. Wilson's disease in children: a position paper by the Hepatology Committee of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018; 66:334–344.
Article6. Nuttall KL, Palaty J, Lockitch G. Reference limits for copper and iron in liver biopsies. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2003; 33:443–450.7. Patil M, Sheth KA, Krishnamurthy AC, Devarbhavi H. A review and current perspective on Wilson disease. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2013; 3:321–336.
Article8. Gitelman HJ, Graham JB, Welt LG. A new familial disorder characterized by hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1966; 79:221–235.9. Lee JW, Lee J, Heo NJ, Cheong HI, Han JS. Mutations in SLC12A3 and CLCNKB and their correlation with clinical phenotype in patients with Gitelman and Gitelman-like syndrome. J Korean Med Sci. 2016; 31:47–54.
Article10. Simon DB, Nelson-Williams C, Bia MJ, Ellison D, Karet FE, Molina AM, et al. Gitelman's variant of Bartter's syndrome, inherited hypokalaemic alkalosis, is caused by mutations in the thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter. Nat Genet. 1996; 12:24–30.
Article11. Matsuo M, Kurokawa T, Goya N, Ohta M. Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis in a 2-month-old boy. Neurology. 1981; 31:1190–1192.12. Kim JS, Woo YJ, Kim GM, Kim CJ, Ma JS, Hwang TJ, et al. Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis: a case report. J Korean Med Sci. 1999; 14:460–464.
Article13. Levy Erez D, Levy J, Friger M, Aharoni-Mayer Y, Cohen-Iluz M, Goldstein E. Assessment of cognitive and adaptive behaviour among individuals with congenital insensitivity to pain and anhidrosis. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2010; 52:559–562.
Article14. Schulman H, Tsodikow V, Einhorn M, Levy Y, Shorer Z, Hertzanu Y. Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis (CIPA): the spectrum of radiological findings. Pediatr Radiol. 2001; 31:701–705.
Article15. Rosemberg S, Marie SK, Kliemann S. Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis (hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type IV). Pediatr Neurol. 1994; 11:50–56.
Article16. Theodorou SD, Klimentopoulou AE, Papalouka E. Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis. Report of a case and review of the literature. Acta Orthop Belg. 2000; 66:137–145.17. Indo Y. Genetics of congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis (CIPA) or hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type IV. Clinical, biological and molecular aspects of mutations in TRKA(NTRK1) gene encoding the receptor tyrosine kinase for nerve growth factor. Clin Auton Res. 2002; 12:Suppl 1. I20–I32.18. Ferenci P, Caca K, Loudianos G, Mieli-Vergani G, Tanner S, Sternlieb I, et al. Diagnosis and phenotypic classification of Wilson disease. Liver Int. 2003; 23:139–142.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hereditary Sensory Neuropathy Type 2 (Congenital sensory neuropathy): A case report
- A Case of Hereditary Sensory Neuropathy Type II with Acroosteolysis
- Ultrastructural Findings of Hereditary Sensory and Autonomic Neuropathies, Type IV and II
- Hereditary Motor and Sensory Neuropathy Type I: A case report
- Two Novel Mutations in the HSN2 Gene Identified in a Korean Patients with Hereditary Sensory Autonomic Neuropathy Type II