Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2019 Jul;22(4):387-391. 10.5223/pghn.2019.22.4.387.
Hepatotoxicity in an Adolescent with Black Iced Tea Overconsumption
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Paediatrics, Larnaca General Hospital, Larnaca, Cyprus. adamos@paidiatros.com
- 2European University Medical School, Nicosia, Cyprus.
- 3Third Department of Paediatrics, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, General University Hospital “ATTIKONâ€, Athens, Greece.
- KMID: 2451579
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2019.22.4.387
Abstract
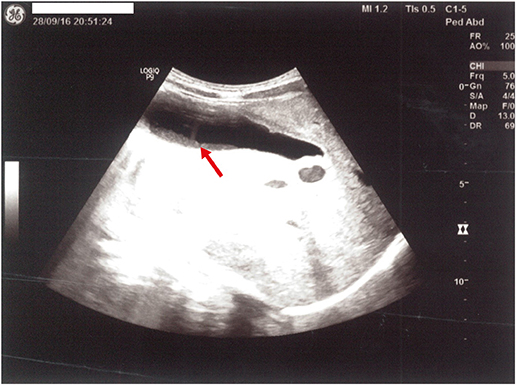
- Tea is the most widely consumed beverage after water in the world. The consumption of iced tea has increased in Western countries and spiked among teenagers for enjoyment, freshening up and alertness. A teenager presented with symptoms of hepatitis. Liver ultrasound revealed sludge in the gallbladder. Laboratory investigations excluded all known causes of hepatotoxicity. Detail nutritional history revealed that the patient had been drinking 1.5-2 liters of black iced tea per day for the last three months. He was immediately advised to stop drinking any tea. Gradually all symptoms disappeared and two months after discontinuation of the tea, all liver enzymes returned to normal and the sludge in the gallbladder disappeared. This case report underlines the importance of a meticulous assessment of a child's dietary behavior when investigating a case of hepatotoxicity and raises awareness about the potential side effects of tea overconsumption.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Del Rio D, Calani L, Scazzina F, Jechiu L, Cordero C, Brighenti F. Bioavailability of catechins from ready-to-drink tea. Nutrition. 2010; 26:528–533.
Article2. Mazzanti G, Menniti-Ippolito F, Moro PA, Cassetti F, Raschetti R, Santuccio C, et al. Hepatotoxicity from green tea: a review of the literature and two unpublished cases. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2009; 65:331–341.
Article3. Brown AC. Liver toxicity related to herbs and dietary supplements: online table of case reports. Part 2 of 5 series. Food Chem Toxicol. 2017; 107:472–501.
Article4. Siddiqui IA, Afaq F, Adhami VM, Ahmad N, Mukhtar H. Antioxidants of the beverage tea in promotion of human health. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2004; 6:571–582.
Article5. Khan N, Mukhtar H. Tea polyphenols for health promotion. Life Sci. 2007; 81:519–533.
Article6. Friedman M. Overview of antibacterial, antitoxin, antiviral, and antifungal activities of tea flavonoids and teas. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2007; 51:116–134.
Article7. Hodgson JM, Croft KD. Tea flavonoids and cardiovascular health. Mol Aspects Med. 2010; 31:495–502.
Article8. Ojo OO, Ladeji O, Nadro MS. Studies of the antioxidative effects of green and black tea (Camellia sinensis) extracts in rats. J Med Food. 2007; 10:345–349.
Article9. Bunchorntavakul C, Reddy KR. Review article: herbal and dietary supplement hepatotoxicity. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013; 37:3–17.
Article10. Navarro VJ, Senior JR. Drug-related hepatotoxicity. N Engl J Med. 2006; 354:731–739.
Article11. LiverTox. Clinical and Research information on drug-induced liver injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institutes of Health;2018. cited 2016 Aug 3. Available from: http://www.livertox.nih.gov/.12. Mazzanti G, Di Sotto A, Vitalone A. Hepatotoxicity of green tea: an update. Arch Toxicol. 2015; 89:1175–1191.
Article13. Larrey D. Hepatotoxicity of herbal remedies. J Hepatol. 1997; 26:Suppl 1. 47–51.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of commercial tea beverages containing citric acid on tooth surfaces
- Transactivation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha by green tea extracts
- Relation between Endogenous Stem Cells and Green Tea Extract in Overconsumption and Amiodarone Induced Thyroid Damage in Rat
- Interrelations Among Beverage Intake, Food Behavior and Personality in Adolescents
- Anti-melanogenic effects of black, green, and white tea extracts on immortalized melanocytes