Investig Clin Urol.
2016 Nov;57(6):401-407. 10.4111/icu.2016.57.6.401.
Advantage of urological experience with both transperitoneal and retroperitoneal laparoscopy in lymph node biopsy for malignant lymphoma diagnosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Tenri Hospital, Tenri, Japan. hkawa02@yahoo.co.jp
- 2Department of Hematology, Tenri Hospital, Tenri, Japan.
- KMID: 2451398
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/icu.2016.57.6.401
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Laparoscopic urologists are familiar with both transperitoneal and retroperitoneal approaches. That experience is an advantage when devising a strategy for intra-abdominal lymph node biopsy. We report the feasibility and effectiveness of laparoscopic biopsy using a urological laparoscopic technique for the treatment of patients with clinically suspected intra-abdominal lymphoma.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
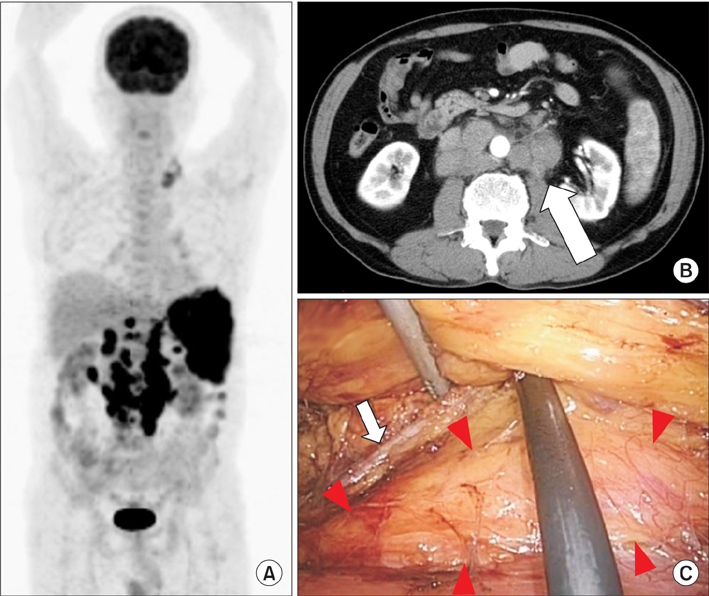
From October 2010 to April 2015, a total of 22 patients underwent laparoscopic biopsy for suspected intra-abdominal lymphoma. We adopted a retroperitoneal approach for paraaortic or paracaval masses, whereas we used a transperitoneal approach for mesenteric, iliac, or obturator masses. Whenever possible, an entire node was removed; otherwise, the biopsy consisted of wedge resection sized at least 1 cm³.
RESULTS
Biopsy specimens were obtained from the following lymph node sites: 10 paraaortic, 5 paracaval, 3 mesenteric, 2 obturator, 1 common iliac, and 1 perinephric fat. Laparoscopic lymph node biopsy was completed in all patients, and there were no conversions to open surgery. The median operating time was 97 minutes (range, 62-167 minutes). The estimated blood loss was <50 mL in all cases. Postoperatively, one patient (4.5%) had symptomatic chylous lymphocele that required surgical intervention. Precise diagnosis was established for all patients: malignant lymphoma in 20 patients and metastatic urothelial carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of unknown origin in 1 patient each. All lymphomas could be fully subclassified.
CONCLUSIONS
Appropriate use of the transperitoneal or retroperitoneal approach is safe and effective for laparoscopic lymph node biopsy in patients with suspected intra-abdominal lymphoma.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Biopsy/methods
*Clinical Competence
Feasibility Studies
Female
Humans
Laparoscopy/*methods
Lymph Node Excision/methods
Lymph Nodes/pathology
Lymphoma/diagnostic imaging/*pathology
Male
Middle Aged
Peritoneum
Positron-Emission Tomography
Retroperitoneal Space
Retrospective Studies
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Urologic Surgical Procedures/standards
Figure
Reference
-
1. Silecchia G, Raparelli L, Perrotta N, Fantini A, Fabiano P, Monarca B, et al. Accuracy of laparoscopy in the diagnosis and staging of lymphoproliferative diseases. World J Surg. 2003; 27:653–658.2. Jaffe ES. The 2008 WHO classification of lymphomas: implications for clinical practice and translational research. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2009; 523–531.3. Bakshi N, Maghfoor I. The current lymphoma classification: new concepts and practical applications triumphs and woes. Ann Saudi Med. 2012; 32:296–305.4. Asoglu O, Porter L, Donohue JH, Cha SS. Laparoscopy for the definitive diagnosis of intra-abdominal lymphoma. Mayo Clin Proc. 2005; 80:625–631.5. Bhandarkar DS, Shah RS, Katara AN, Shankar M, Chandiramani VA, Udwadia TE. Laparoscopic biopsy in patients with abdominal lymphadenopathy. J Minim Access Surg. 2007; 3:14–18.6. Muskat PC, Johnson RA, Bowers GJ. Staging laparotomy in Hodgkin's lymphoma: 1979 to 1988. Am J Surg. 1991; 162:603–606.7. Vandervelde C, Kamani T, Varghese A, Ramesar K, Grace R, Howlett DC. A study to evaluate the efficacy of image-guided core biopsy in the diagnosis and management of lymphoma--results in 103 biopsies. Eur J Radiol. 2008; 66:107–111.8. Balestreri L, Morassut S, Bernardi D, Tavio M, Talamini R, Gloghini A, et al. Efficacy of CT-guided percutaneous needle biopsy in the diagnosis of malignant lymphoma at first presentation. Clin Imaging. 2005; 29:123–127.9. Amador-Ortiz C, Chen L, Hassan A, Frater JL, Burack R, Nguyen TT, et al. Combined core needle biopsy and fine-needle aspiration with ancillary studies correlate highly with traditional techniques in the diagnosis of nodal-based lymphoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 2011; 135:516–524.10. Daly SC, Klairmont M, Arslan B, Vigneswaran Y, Roggin KF, Ujiki MB, et al. Laparoscopy has a superior diagnostic yield than percutaneous image-guided biopsy for suspected intraabdominal lymphoma. Surg Endosc. 2015; 29:2496–2499.11. Casaccia M, Torelli P, Cavaliere D, Panaro F, Nardi I, Rossi E, et al. Laparoscopic lymph node biopsy in intra-abdominal lymphoma: high diagnostic accuracy achieved with a minimally invasive procedure. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2007; 17:175–178.12. Gossot D, de Kerviler E, Brice P, Mariette X, Meignin V, Cazals-Hatem D, et al. Surgical endoscopic techniques in the diagnosis and follow-up of patients with lymphoma. Br J Surg. 1998; 85:1107–1110.13. Mann GB, Conlon KC, LaQuaglia M, Dougherty E, Moskowitz CH, Zelenetz AD. Emerging role of laparoscopy in the diagnosis of lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 1998; 16:1909–1915.14. Diulus L, Chalikonda S, Pitt T, Rosenblatt S. Efficacy of laparoscopic mesenteric/retroperitoneal lymph node biopsy. Surg Endosc. 2009; 23:389–393.15. Hara I, Tanaka K, Yamada Y, Miyake H, Takenaka A, Fujisawa M. Usefulness of laparo- or retroperitoneoscopic biopsy for retroperitoneal lymph node swelling of unknown origin. Int J Urol. 2007; 14:466–469.16. Clayman RV, Kavoussi LR, Soper NJ, Dierks SM, Meretyk S, Darcy MD, et al. Laparoscopic nephrectomy: initial case report. J Urol. 1991; 146:278–282.17. Yuan JB, Zu XB, Miao JG, Wang J, Chen MF, Qi L. Laparoscopic pelvic lymph node dissection system based on preoperative primary tumour stage (T stage) by computed tomography in urothelial bladder cancer: results of a single-institution prospective study. BJU Int. 2013; 112:E87–E91.18. Neyer M, Peschel R, Akkad T, Springer-Stöhr B, Berger A, Bartsch G, et al. Long-term results of laparoscopic retroperitoneal lymph-node dissection for clinical stage I nonseminomatous germ-cell testicular cancer. J Endourol. 2007; 21:180–183.19. Salky BA, Bauer JJ, Gelernt IM, Kreel I. The use of laparoscopy in retroperitoneal pathology. Gastrointest Endosc. 1988; 34:227–230.20. Porte H, Copin MC, Eraldi L, Roumilhac D, Jaillard-Thery S, Puech P, et al. Retroperitoneoscopy for the diagnosis of infiltrating retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy and masses. Br J Surg. 1997; 84:1433–1436.21. Scholz HS, Petru E, Benedicic C, Haas J, Tamussino K, Winter R. Fibrin application for preventing lymphocysts after retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy in patients with gynecologic malignancies. Gynecol Oncol. 2002; 84:43–46.22. Docimo G, Limongelli P, Conzo G, Gili S, Bosco A, Rizzuto A, et al. Axillary lymphadenectomy for breast cancer in elderly patients and fibrin glue. BMC Surg. 2013; 13:Suppl 2. S8.23. Benevento R, Santoriello A, Pellino G, Sciaudone G, Candilio G, De Fatico GS, et al. The effects of low-thrombin fibrin sealant on wound serous drainage, seroma formation and length of postoperative stay in patients undergoing axillary node dissection for breast cancer. A randomized controlled trial. Int J Surg. 2014; 12:1210–1215.24. Navarro-Rodríguez E, Gómez-Luque I, Díaz-Jiménez N, Rioja-Torres P, Bascuñana-Estudillo G, Ruiz-Rabelo JF, et al. Effectiveness of an absorbable fibrin sealant patch to reduce lymphoceles formation after axillary lymphadenectomy for breast cancer: a matched-pair analysis. Am J Surg. 2014; 208:824–830.25. Marchioni M, Ingrosso M, De Francesco P, Primiceri G, Manco R, Tenaglia RL. The use of haemostatic agents and sealants for the prevention of lymphocele after urological surgery: a review of the literature. Surg Technol Int. 2015; 27:45–50.26. D'souza MM, Jaimini A, Bansal A, Tripathi M, Sharma R, Mondal A, et al. FDG-PET/CT in lymphoma. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2013; 23:354–365.27. Glaudemans AW, de Vries EF, Galli F, Dierckx RA, Slart RH, Signore A. The use of (18)F-FDG-PET/CT for diagnosis and treatment monitoring of inflammatory and infectious diseases. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013; 2013:623036.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of malignant lymphoma of testis, adrenal gland and retroperitoneal lymph nodes
- Lymphography as a diagnostic method in malignant lymphoma
- Comparison of Changes in Carbon Dioxide Absorption during Transperitoneal Laparoscopic Surgery and Intraperitoneal Laparoscopic Surgery
- A Case Report of Infiltrative Polyneuropathy Associated with Lymphoma
- Hyaline-vascular Variant of Castleman's Disease in Retroperitoneum