J Adv Prosthodont.
2019 Jun;11(3):187-192. 10.4047/jap.2019.11.3.187.
A study of fracture loads and fracture characteristics of teeth
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dental Hygiene, College of Health Sciences, Seongnam Campus, Eulji University, Seongnam, Republic of Korea.
- 2Department of Prosthodontics, College of Dentistry, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Republic of Korea.
- 3Division of Restorative Science and Prosthodontics, College of Dentistry, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA. han.10@osu.edu
- KMID: 2450995
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2019.11.3.187
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this in vitro study was to investigate the fracture loads and modes of failure for the full range of natural teeth under simulated occlusal loading.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
One hundred and forty natural teeth were taken from mandibles and maxillas of patients. There were 14 groups of teeth with 10 teeth in each group (5 males and 5 females). Each specimen was embedded in resin and mounted on a positioning jig, with the long axis of the tooth at an inclined angle of 30 degrees. A universal testing machine was used to measure the compression load at which fracture of the tooth specimen occurred; loads were applied on the incisal edge and/or functional cusp.
RESULTS
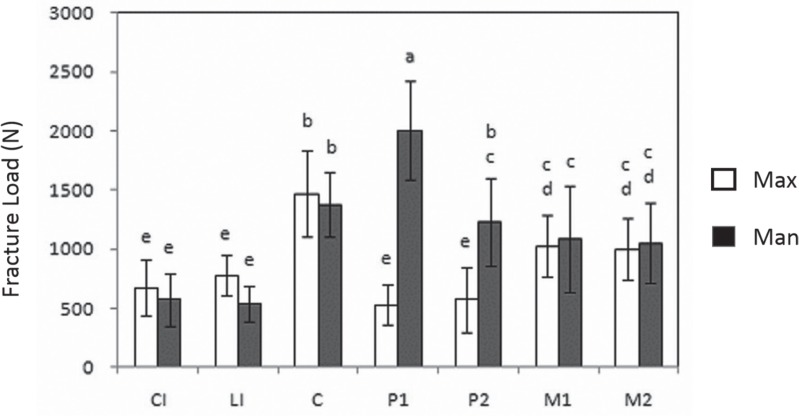
The mean fracture load for the mandibular first premolar was the highest (2002 N) of all the types of teeth, while the mean fracture load for the maxillary first premolar was the lowest (525 N). Mean fracture loads for the mandibular and maxillary incisors, and the first and second maxillary premolars, had significantly lower values compared to the other types of teeth. The mean fracture load for the teeth from males was significantly greater than that for the teeth from females. There was an inverse relationship between age and mean fracture load, in which older teeth had lower fracture loads compared to younger teeth.
CONCLUSION
The mean fracture loads for natural teeth were significantly different, with dependence on tooth position and the sex and age of the individual.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jordan RE, Abrams L, Kraus BS. Dental anatomy and occlusion. Mosby-Year Book: 1992. p. 43–66.2. Habelitz S, Marshall SJ, Marshall GW Jr, Balooch M. Mechanical properties of human dental enamel on the nanometre scale. Arch Oral Biol. 2001; 46:173–183. PMID: 11163325.
Article3. Pegoretti A, Fambri L, Zappini G, Bianchetti M. Finite element analysis of a glass fibre reinforced composite endodontic post. Biomaterials. 2002; 23:2667–2682. PMID: 12059016.
Article4. Strub JR, Beschnidt SM. Fracture strength of 5 different all-ceramic crown systems. Int J Prosthodont. 1998; 11:602–609. PMID: 10023224.5. Potiket N, Chiche G, Finger IM. In vitro fracture strength of teeth restored with different all-ceramic crown systems. J Prosthet Dent. 2004; 92:491–495. PMID: 15523339.
Article6. Attia A, Kern M. Fracture strength of all-ceramic crowns luted using two bonding methods. J Prosthet Dent. 2004; 91:247–252. PMID: 15060494.
Article7. Al-Omiri MK, Mahmoud AA, Rayyan MR, Abu-Hammad O. Fracture resistance of teeth restored with post-retained restorations: an overview. J Endod. 2010; 36:1439–1449. PMID: 20728706.8. Dong JK, Oh SC, Kim SD. Fracture strength of the IPS empress crown: The effect of occlusal depth and axial inclination on upper first premolar crowns. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 1999; 37:127–133.9. Lee IS, Kim JM, Dong JK. Fracture strength of zirconia ceramic crowns according to tooth position. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2010; 48:94–100.
Article10. Lee JH, Dong JK. Enamel thickness of maxillary first premolar. J Korean Acad Stomatognathic Funct Occlusion. 2002; 18:31–38.11. Shin DK, Kang HJ, Park YS, Park KS, Dong JK. Fracture strength of the IPS empress crown: the effects of incisal reduction and axial inclination on upper canine. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2005; 43:30–40.12. Song BK, Lee HH, Dong JK. Fracture strength of the IPS empress crown. The effect of occlusal depth and axial inclination on upper central incisor. J Korean Acad Stomatognathic Funct Occlusion. 2000; 16:237–245.13. Nam YS, Dong JK. Fracture strength of the IPS empress crown. The effect of incisal reduction and axial inclination on lower central incisor. J Korean Acad Stomatognathic Funct Occlusion. 2003; 19:207–217.14. Kim HJ, Lee HH, Nam YS, Dong JK. Fracture strength of the IPS empress crown: The effect of occlusal depth and axial inclination on lower second premolar. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2002; 40:441–450.15. Ottl P, Hahn L, Lauer HCh, Fay M. Fracture characteristics of carbon fibre, ceramic and non-palladium endodontic post systems at monotonously increasing loads. J Oral Rehabil. 2002; 29:175–183. PMID: 11856397.
Article16. Wall JG, Reisbick MH, Johnston WM. Incisal-edge strength of porcelain laminate veneers restoring mandibular incisors. Int J Prosthodont. 1992; 5:441–446. PMID: 1290573.17. Oh SC. A study on morphology and size of clinical crown of permanent mandibular molar in Korean adult. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 1999; 37:242–255.18. Browning JD, Meadors LW, Eick JD. Movement of three removable partial denture clasp assemblies under occlusal loading. J Prosthet Dent. 1986; 55:69–74. PMID: 3511242.
Article19. Jo JH, Vang MS. Stress analysis of various esthetic restorations by finite element method. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 1991; 29:129–146.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of fracture strength and pattern of endodontically treated teeth restored with fiber posts and metal cast post
- THE PROGNOSIS OF THE TEETH IN THE MANDIBULAR FRACTURE LINES
- Surgical Management of a Mandible Subcondylar Fracture
- Effect of ferrule on the fracture resistance of mandibular premolars with prefabricated posts and cores
- Effect of connector configuration on the fracture load in conventional and translucent zirconia three-unit fixed dental prostheses