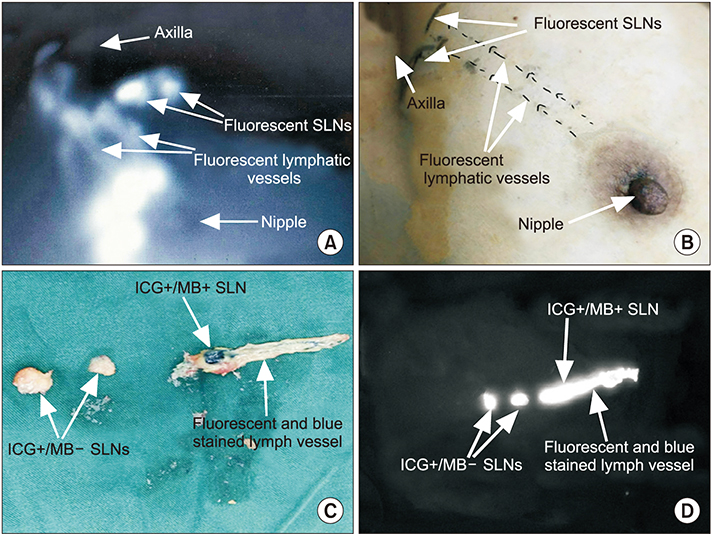
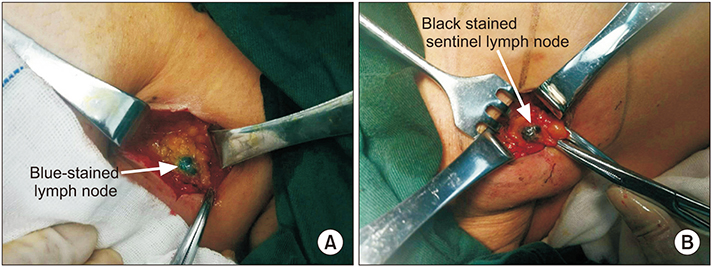
Ann Surg Treat Res.
2019 Jul;97(1):1-6. 10.4174/astr.2019.97.1.1.
Comparative study of indocyanine green combined with blue dye with methylene blue only and carbon nanoparticles only for sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Breast Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital, China Medical University, Shenyang, China. xyzheng@cmu.edu.cn
- KMID: 2450983
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2019.97.1.1
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The combination of indocyanine green and methylene blue (ICG + MB) was reported to be an efficient tracer method in sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB). However, whether this method is superior to MB only or carbon nanoparticles (CN) is controversial. This study was to evaluate the efficacy of the three methods in SLNB for breast cancer, and to analyze its influencing factors.
METHODS
One hundred eighty patients with early breast cancer were recruited and randomly divided into 3 groups. Each group comprising of 60 patients with SLNB using ICG + MB, MB, and CN, respectively. Then the 3 groups were compared in detection rate, mean number of SLNs, and the detection rates and number of metastatic sentinel lymph nodes (SLNs).
RESULTS
The detection rate of SLNs was 100% (60 of 60) in ICG + MB group, 96.7% (58 of 60), and 98.3% (59 of 60) in MB and CN group, respectively, with no significant difference (P = 0.362). Totally, 204 SLNs (mean ± standard deviation [SD] [range], 3.4 ± 1.4 [2-8]) were detected in ICG + MB group, 102 (1.7 ± 0.7 [0-3]) and 145 (2.4 ± 0.7 [0-6]) in MB and CN group, indicating significant difference (P < 0.001). The detection rate of metastatic SLN was 23.3% (14 of 60) in ICG + MB group, which was higher than 18.3% (11 of 60) and 20% (11 of 60) in MB and CN group, respectively, but showed no statistical significance (P = 0.788).
CONCLUSION
ICG + MB method was superior to MB only and CN only methods in the mean number of SLNs, thus predicting axillary lymph node metastasis more accurately. Therefore, in areas where the standard method is not available, ICG + MB may be more suitable as an alternative tracer for SLNB.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Gelber RD, Coates AS, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ, et al. Progress and promise: highlights of the international expert consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2007. Ann Oncol. 2007; 18:1133–1144.
Article2. Paek SH, Yi KH, Kim SJ, Choi JY, Lee KE, Park YJ, et al. Feasibility of sentinel lymph node dissection using Tc-99m phytate in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2017; 93:240–245.
Article3. Oh SY, Kim DY, Kim YB, Suh KW. Clinical application of sentinel lymph node mapping in colon cancer: in vivo vs. ex vivo techniques. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2014; 87:118–122.4. Lyman GH, Somerfield MR, Giuliano AE. Sentinel lymph node biopsy for patients with early-stage breast cancer: 2016 American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Update Summary. J Oncol Pract. 2017; 13:196–198.
Article5. van der Vorst JR, Schaafsma BE, Verbeek FP, Hutteman M, Mieog JS, Lowik CW, et al. Randomized comparison of near-infrared fluorescence imaging using indocyanine green and 99(m) technetium with or without patent blue for the sentinel lymph node procedure in breast cancer patients. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012; 19:4104–4111.
Article6. Lyman GH, Giuliano AE, Somerfield MR, Benson AB 3rd, Bodurka DC, Burstein HJ, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology guideline recommendations for sentinel lymph node biopsy in early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:7703–7720.7. Stratmann SL, McCarty TM, Kuhn JA. Radiation safety with breast sentinel node biopsy. Am J Surg. 1999; 178:454–457.
Article8. Wang X, Liu J, Hou Y, Wang N, Wang M. Logistic regression analysis for factors affecting the successful rate of nano-carbon in sentinel lymph node biopsy. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016; 41:411–416.9. Varghese P, Abdel-Rahman AT, Akberali S, Mostafa A, Gattuso JM, Carpenter R. Methylene blue dye--a safe and effective alternative for sentinel lymph node localization. Breast J. 2008; 14:61–67.
Article10. Wu X, Lin Q, Chen G, Lu J, Zeng Y, Chen X, et al. Sentinel lymph node detection using carbon nanoparticles in patients with early breast cancer. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0135714.
Article11. Simmons R, Thevarajah S, Brennan MB, Christos P, Osborne M. Methylene blue dye as an alternative to isosulfan blue dye for sentinel lymph node localization. Ann Surg Oncol. 2003; 10:242–247.
Article12. Sugie T, Sawada T, Tagaya N, Kinoshita T, Yamagami K, Suwa H, et al. Comparison of the indocyanine green fluorescence and blue dye methods in detection of sentinel lymph nodes in early-stage breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013; 20:2213–2218.
Article13. Ahmed M, Purushotham AD, Douek M. Novel techniques for sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer: a systematic review. Lancet Oncol. 2014; 15:e351–e362.
Article14. Ang CH, Tan MY, Teo C, Seah DW, Chen JC, Chan MY, et al. Blue dye is sufficient for sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2014; 101:383–389.
Article15. Ji Y, Luo N, Jiang Y, Li Q, Wei W, Yang H, et al. Clinical utility of the additional use of blue dye for indocyanine green for sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer. J Surg Res. 2017; 215:88–92.
Article16. Guo J, Yang H, Wang S, Cao Y, Liu M, Xie F, et al. Comparison of sentinel lymph node biopsy guided by indocyanine green, blue dye, and their combination in breast cancer patients: a prospective cohort study. World J Surg Oncol. 2017; 15:196.
Article17. Samorani D, Fogacci T, Dellachiesa L. Use of indocyanine green alone for sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 2015; 22:442–443.
Article18. Yang B, Zheng G, Zuo WS, Yang L, Wang YS, Zheng MZ, et al. Analysis of clinicopathological factors associated with false-negative rate of sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer patients: experience of a single center. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2013; 35:389–393.19. Ban EJ, Lee JS, Koo JS, Park S, Kim SI, Park BW. How many sentinel lymph nodes are enough for accurate axillary staging in t1-2 breast cancer? J Breast Cancer. 2011; 14:296–300.
Article20. Koo BY, Jeong SG, Eom TI, Kang HJ, Kim LS. The number of removed lymph nodes for an acceptable false negative rate in sentinel lymph node biopsy for breast cancer. J Breast Cancer. 2009; 12:100–105.
Article21. Sugie T, Kassim KA, Takeuchi M, Hashimoto T, Yamagami K, Masai Y, et al. A novel method for sentinel lymph node biopsy by indocyanine green fluorescence technique in breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2010; 2:713–720.
Article22. Takeuchi M, Sugie T, Abdelazeem K, Kato H, Shinkura N, Takada M, et al. Lymphatic mapping with fluorescence navigation using indocyanine green and axillary surgery in patients with primary breast cancer. Breast J. 2012; 18:535–541.
Article23. Hutteman M, Mieog JS, van der Vorst JR, Liefers GJ, Putter H, Lowik CW, et al. Randomized, double-blind comparison of indocyanine green with or without albumin premixing for near-infrared fluorescence imaging of sentinel lymph nodes in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011; 127:163–170.
Article24. Yi M, Meric-Bernstam F, Ross MI, Akins JS, Hwang RF, Lucci A, et al. How many sentinel lymph nodes are enough during sentinel lymph node dissection for breast cancer. Cancer. 2008; 113:30–37.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Thyroid Cancer
- Use of Fluorescence Imaging in Combination with Patent Blue Dye versus Patent Blue Dye Alone in Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Breast Cancer
- Methylene Blue for Localization of Sentinel Lymph Nodes in Breast Cancer: A Comparison with Isosulfan Blue
- A Case of Anaphylactic Reactions to Isosulfan Blue Dye in A Cervical Cancer Patient
- Intraparenchymal Methylene Blue Injection for Sentinel Lymph Node in Breast Cancer Patients does not Interfere with the Pulse Oximetry Readings