Ann Lab Med.
2019 Sep;39(5):496-498. 10.3343/alm.2019.39.5.496.
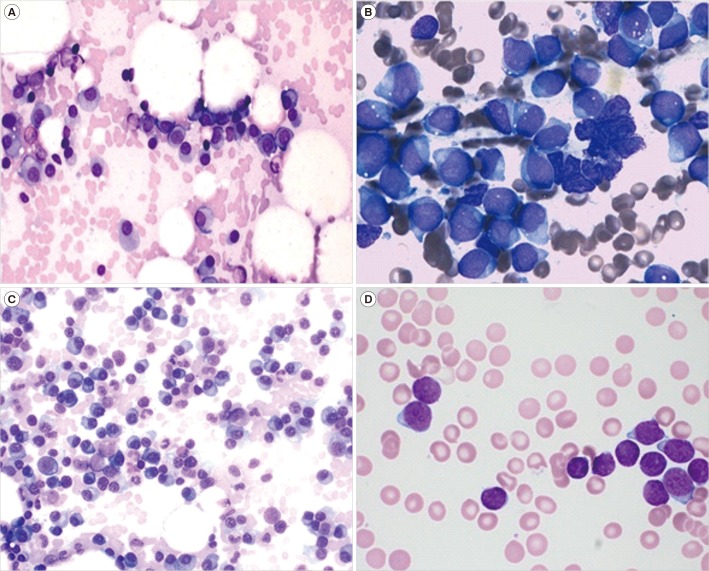
Two Rare Cases of Therapy-Related Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Patients With Plasma Cell Myeloma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. cjpark@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2450974
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2019.39.5.496
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Immune Checkpoint Programmed Cell Death Protein-1 (PD-1) Expression on Bone Marrow T Cell Subsets in Patients With Plasma Cell Myeloma
Min Young Lee, Chan-Jeoung Park, Young-Uk Cho, Eunkyoung You, Seongsoo Jang, Eul Ju Seo, Jung-Hee Lee, Dok Hyun Yoon, Cheolwon Suh
Ann Lab Med. 2021;41(3):259-267. doi: 10.3343/alm.2021.41.3.259.
Reference
-
1. Hong J, Lee JH. Recent advances in multiple myeloma: a Korean perspective. Korean J Intern Med. 2016; 31:820–834. PMID: 27604794.2. Reddi DM, Lu CM, Fedoriw G, Liu YC, Wang FF, Ely S, et al. Myeloid neoplasms secondary to plasma cell myeloma: an intrinsic predisposition or therapy-related phenomenon? A clinicopathologic study of 41 cases and correlation of cytogenetic features with treatment regimens. Am J Clin Pathol. 2012; 138:855–866. PMID: 23161720.3. Tang G, Zuo Z, Thomas DA, Lin P, Liu D, Hu Y, et al. Precursor B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia occurring in patients with a history of prior malignancies: is it therapy-related. Haematologica. 2012; 97:919–925. PMID: 22207681.4. Lau LG, Tan LK, Koay ES, Liu TC. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia after tandem autologous stem cell transplantations for multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 2005; 19:299–301. PMID: 15526017.5. Piszcz J, Bolkun L, Cichocka E, Kloczko J. Secondary acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in a multiple myeloma patient. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2012; 16:593–595. PMID: 23788951.6. Vardiman JW, Arber AD, et al. Therapy-related myeloid neoplasms. In : Swerdlow SH, Campo E, editors. World Health Organization classification of tumours. Pathology and genetics of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC Press;2017. p. 241–243.7. Lee SG, Choi JR, Kim JS, Park TS, Lee KA, Song J. Therapy-related acute lymphoblastic leukemia with t(9;22)(q34;q11.2):a case study and review of the literature. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2009; 191:51–54. PMID: 19389510.8. Chen W, Wang E, Lu Y, Gaal KK, Huang Q. Therapy-related acute lymphoblastic leukemia without 11q23 abnormality: report of six cases and a literature review. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010; 133:75–82. PMID: 20023261.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Precursor B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Two Patients with a History of Cytotoxic Therapy
- Simultaneous presentation of plasma cell myeloma and hairy cell leukemia
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Presented as Multiple Breast Masses
- SOLITARY PLASMA CELL MYELOMA ON ANTERIOR MAXILLA: A CASE REPORT
- A Case of Cutaneous Plasmacytoma Treated with Thalidomide