Yonsei Med J.
2019 Apr;60(4):346-351. 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.4.346.
Effectiveness of Bi-Parametric MR/US Fusion Biopsy for Detecting Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer in Prostate Biopsy Naïve Men
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, School of Medicine, Jeju National University, Jeju, Korea. urology.park@gmail.com
- KMID: 2450189
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2019.60.4.346
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To explore the effect of bi-parametric MRI-ultrasound (MR/US) fusion prostate biopsy on the detection of overall cancer and significant prostate cancer (sPCa).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We examined 140 patients with suspected prostate cancer lesions on MRI from August 2016 to March 2018. All patients had undergone 3T pre-biopsy bi-parametric (T2 weighted and diffusion-weighted) prostate MRI (bpMRI), and their MRI images were evaluated with Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) version 2.0. MR/US fusion targeted prostate biopsy was performed for lesions with a PI-RADS score ≥3 before systemic biopsy. The results of targeted and systemic biopsy were evaluated in regards to detection rate according to PI-RADS score.
RESULTS
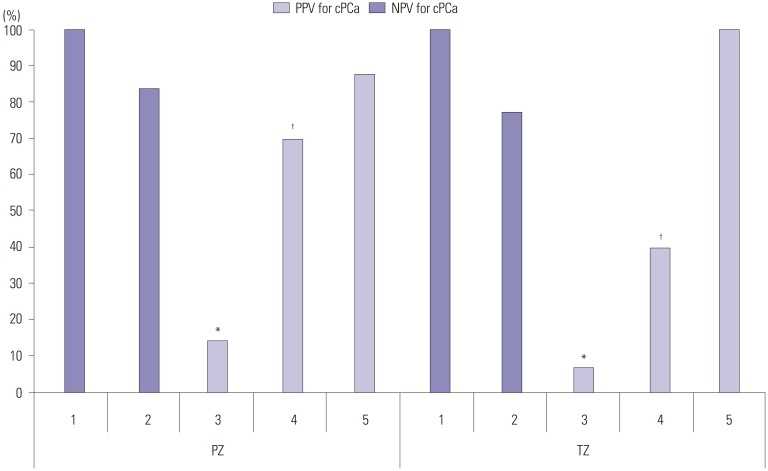
Of the patients (mean age=67.2 years, mean prostate-specific antigen level=8.1 ng/mL), 66 (47.1%) and 37 (26.4%) patients were diagnosed with cancer and significant prostate cancer, respectively. The rate of positive targeted biopsy increased with higher PI-RADS score (3: 40.4%, 4: 56.7%, 5: 90.0%). The proportion of significant prostate cancer among positive target lesions was 65.3% (32/49).
CONCLUSION
bpMRI is a feasible tool with which to identify sPCa. MR/US fusion biopsy, rather than systemic biopsy, can help identify sPCa. We recommend using supplemental tools to increase prostate cancer detection in patients with PI-RADS 3 lesions.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Talicia Tarver. Cancer facts & figures 2012. American Cancer Society (ACS). J Consum Health Internet. 2012; 16:366–367.2. Scheenen TW, Rosenkrantz AB, Haider MA, Fütterer JJ. Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging in prostate cancer management: current status and future perspectives. Invest Radiol. 2015; 50:594–600. PMID: 25974203.3. Rosenkrantz AB, Triolo MJ, Melamed J, Rusinek H, Taneja SS, Deng FM. Whole-lesion apparent diffusion coefficient metrics as a marker of percentage Gleason 4 component within Gleason 7 prostate cancer at radical prostatectomy. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015; 41:708–714. PMID: 24616064.
Article4. Rosenkrantz AB, Shanbhogue AK, Wang A, Kong MX, Babb JS, Taneja SS. Length of capsular contact for diagnosing extraprostatic extension on prostate MRI: assessment at an optimal threshold. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016; 43:990–997. PMID: 26395278.
Article5. Mottet N, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Briers E, Cumberbatch MG, De Santis M, et al. EAU-ESTRO-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer. Part 1: screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent. Eur Urol. 2017; 71:618–629. PMID: 27568654.
Article6. Barentsz JO, Richenberg J, Clements R, Choyke P, Verma S, Villeirs G, et al. ESUR prostate MR guidelines 2012. Eur Radiol. 2012; 22:746–757. PMID: 22322308.
Article7. Weinreb JC, Barentsz JO, Choyke PL, Cornud F, Haider MA, Macura KJ, et al. PI-RADS Prostate Imaging – Reporting and Data System: 2015, version 2. Eur Urol. 2016; 69:16–40. PMID: 26427566.
Article8. Fütterer JJ, Briganti A, De Visschere P, Emberton M, Giannarini G, Kirkham A, et al. Can clinically significant prostate cancer be detected with multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging? A systematic review of the literature. Eur Urol. 2015; 68:1045–1053. PMID: 25656808.
Article9. Stanzione A, Imbriaco M, Cocozza S, Fusco F, Rusconi G, Nappi C, et al. Biparametric 3T magnetic resonance imaging for prostatic cancer detection in a biopsy-naïve patient population: a further improvement of PI-RADS v2? Eur J Radiol. 2016; 85:2269–2274. PMID: 27842676.10. Fascelli M, Rais-Bahrami S, Sankineni S, Brown AM, George AK, Ho R, et al. Combined biparametric prostate magnetic resonance imaging and prostate-specific antigen in the detection of prostate cancer: a validation study in a biopsy-naive patient population. Urology. 2016; 88:125–134. PMID: 26680244.
Article11. De Visschere P, Lumen N, Ost P, Decaestecker K, Pattyn E, Villeirs G. Dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging has limited added value over T2-weighted imaging and diffusion-weighted imaging when using PI-RADSv2 for diagnosis of clinically significant prostate cancer in patients with elevated PSA. Clin Radiol. 2017; 72:23–32. PMID: 27726850.
Article12. Di Campli E, Delli Pizzi A, Seccia B, Cianci R, d'Annibale M, Colasante A, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of biparametric vs multiparametric MRI in clinically significant prostate cancer: comparison between readers with different experience. Eur J Radiol. 2018; 101:17–23. PMID: 29571792.
Article13. Lee DH, Nam JK, Lee SS, Han JY, Lee JW, Chung MK, et al. Comparison of multiparametric and biparametric MRI in first round cognitive targeted prostate biopsy in patients with PSA levels under 10 ng/mL. Yonsei Med J. 2017; 58:994–999. PMID: 28792144.
Article14. Rais-Bahrami S, Siddiqui MM, Vourganti S, Turkbey B, Rastinehad AR, Stamatakis L, et al. Diagnostic value of biparametric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as an adjunct to prostate-specific antigen (PSA)-based detection of prostate cancer in men without prior biopsies. BJU Int. 2015; 115:381–388. PMID: 24447678.
Article15. Sathianathen NJ, Konety BR, Soubra A, Metzger GJ, Spilseth B, Murugan P, et al. Which scores need a core? An evaluation of MR-targeted biopsy yield by PIRADS score across different biopsy indications. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2018; 21:573–578. PMID: 30038389.
Article16. Sheridan AD, Nath SK, Syed JS, Aneja S, Sprenkle PC, Weinreb JC, et al. Risk of clinically significant prostate cancer associated with prostate imaging reporting and data system category 3 (equivocal) lesions identified on multiparametric prostate MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2018; 210:347–357. PMID: 29112469.
Article17. Liddell H, Jyoti R, Haxhimolla HZ. mp-MRI prostate characterised PIRADS 3 lesions are associated with a low risk of clinically significant prostate cancer-a retrospective review of 92 biopsied PIRADS 3 lesions. Curr Urol. 2015; 8:96–100. PMID: 26889125.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Multiparametric MRI in the Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
- Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer
- Chemotherapy With Androgen Deprivation for Hormone-Naïve Prostate Cancer
- Diagnostic Accuracy and Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging–Ultrasound Fusion Transperineal Targeted and Template Systematic Prostate Biopsy Based on Bi-parametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- A Predictive Model Based on Bi-parametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Clinical Parameters for Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer in the Korean Population