Imaging Sci Dent.
2019 Jun;49(2):79-86. 10.5624/isd.2019.49.2.79.
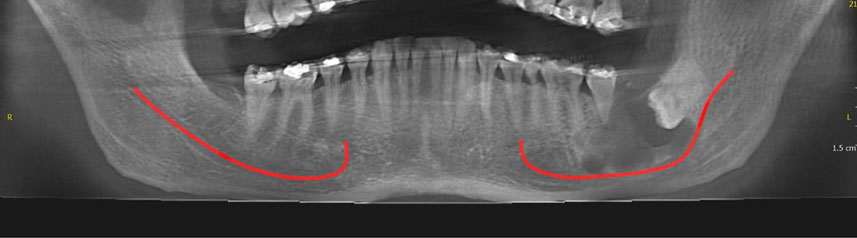
Common conditions associated with displacement of the inferior alveolar nerve canal: A radiographic diagnostic aid
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral Medicine, School of Dentistry, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, School of Dentistry, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
- 3Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. m.behnaz@sbmu.ac.ir
- KMID: 2450173
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2019.49.2.79
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study reviewed the common conditions associated with displacement of inferior alveolar nerve canal.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
General search engines and specialized databases including Google Scholar, Pub Med, Pub Med Central, Science Direct, and Scopus were used to find relevant studies by using keywords such as "mandibular canal", "alveolar canal", "inferior alveolar nerve canal", "inferior dental canal", "inferior mandibular canal" and "displacement".
RESULTS
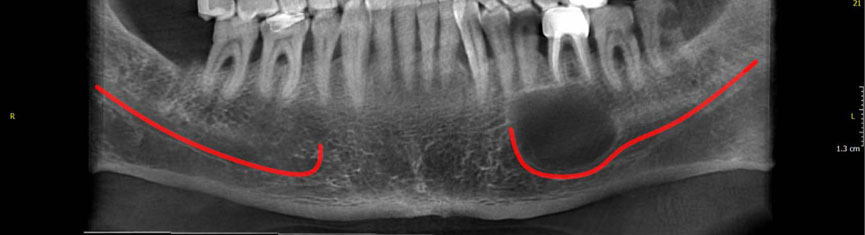
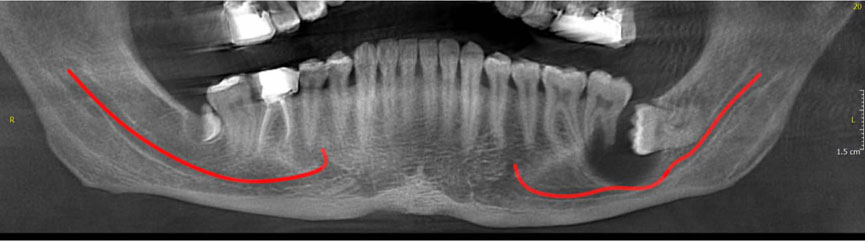
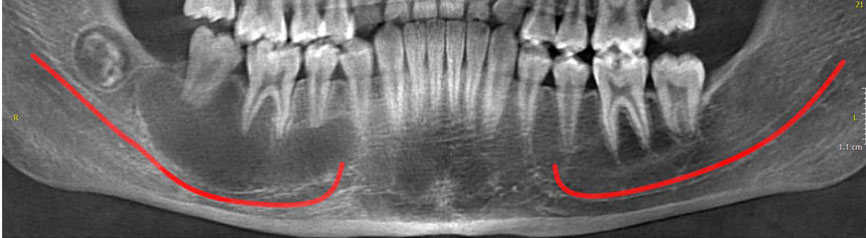
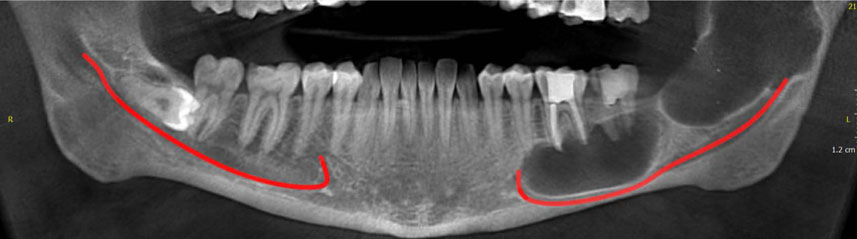
About 120 articles were found, of which approximately 70 were broadly relevant to the topic. We ultimately included 37 articles that were closely related to the topic of interest. When the data were compiled, the following 8 lesions were found to have a relationship with displacement of mandibular canal: radicular/residual cysts, dentigerous cyst, odontogenic keratocyst, aneurysmal bone cyst, ameloblastoma, central giant cell granuloma, fibrous dysplasis, and cementossifying fibroma.
CONCLUSION
When clinicians encounter a lesion associated with displaced mandibular canal, they should first consider these entities in the differential diagnosis. This review would help dentists make more accurate diagnoses and develop better treatment plans according to patients' radiographs.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Srinivasan K, Seith A, Gadodia A, Sharma R, Kumar A, Roychoudhury A, et al. Evaluation of the inferior alveolar canal for cysts and tumors of the mandible-comparison of multidetector computed tomography and 3-dimensional volume interpolated breath-hold examination magnetic resonance sequence with curved multiplanar reformatted reconstructions. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012; 70:2327–2332.
Article2. de Oliveira-Santos C, Souza PH, de Azambuja Berti-Couto S, Stinkens L, Moyaert K, Rubira-Bullen IR, et al. Assessment of variations of the mandibular canal through cone beam computed tomography. Clin Oral Investig. 2012; 16:387–393.
Article3. Boeddinghaus R, Whyte A. Current concepts in maxillofacial imaging. Eur J Radiol. 2008; 66:396–418.
Article4. Abdi I, Taheri Talesh K, Yazdani J, Keshavarz Meshkin Fam S, Ghavimi MA, Arta SA. The effect of ameloblastoma and keratocystic odontogenic tumor on the displacement pattern of inferior alveolar canal in CBCT examinations. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2016; 10:155–161.
Article5. Mortazavi H, Baharvand M. Review of common conditions associated with periodontal ligament widening. Imaging Sci Dent. 2016; 46:229–237.
Article6. Jamdade A, Nair GR, Kapoor M, Sharma N, Kundendu A. Localization of a peripheral residual cyst: diagnostic role of CT scan. Case Rep Dent. 2012; 2012:760571.
Article7. Karam N, Karam F, Nasseh I, Noujeim M. Residual cyst with a misleading clinical and radiological appearance. J Oral Maxillofac Radiol. 2013; 1:17–20.
Article8. Shivhare P, Singh A, Haidry N, Yadav M, Shankarnarayan L. Multilocular radicular cyst - a common pathology with uncommon radiological appearance. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016; 10:ZD13–ZD15.
Article9. Farman AG, Nortjé CJ, Grotepass FW. Pathological conditions of the mandible: their effect on the radiographic appearance of the inferior dental (mandibular) canal. Br J Oral Surg. 1977; 15:64–74.
Article10. Mortazavi H, Baharvand M. Jaw lesions associated with impacted tooth: a radiographic diagnostic guide. Imaging Sci Dent. 2016; 46:147–157.
Article11. Zerrin E, Husniye DK, Peruze C. Dentigerous cysts of the jaws: clinical and radiological findings of 18 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Radiol. 2014; 2:77–81.
Article12. Yonetsu K, Bianchi JG, Troulis MJ, Curtin HD. Unusual CT appearance in an odontogenic keratocyst of the mandible: case report. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; 22:1887–1889.13. Simsek HO, Yildirim D, Gormez O, Yuce E, Kapucuoglu FN. Aneurysmal bone cyst of the mandible: report of a case with a review of the literature. J Oral Maxillofac Radiol. 2014; 2:64–67.
Article14. Pai D, Kamath AT, Kudva A, Solomon MM, Kumar S, Sasikumar P. Concomitant central giant cell granuloma and aneurysmal bone cyst in a young child. Case Rep Dent. 2017; 2017:6545848.
Article15. Sharma GH, Dabir AV, Das DA, Talreja-Kanchan PP. Bilateral aneurysmal bone cyst of the mandible: a case report. J Indian Acad Oral Med Radiol. 2015; 27:479–483.
Article16. Flores IL, Hamilton ME, Zanchin-Baldissera E, Uchoa-Vasconcelos AC, Chaves-Tarquinio SB, Neutzling-Gomes AP. Simple and aneurysmal bone cyst: aspects of jaw pseudocysts based on an experience of Brazilian pathology service during 53 years. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2017; 22:e64–e69.
Article17. Kolokythas A, Al-Ghamian H, Miloro M. Does a difference exist in inferior alveolar canal displacement caused by commonly encountered pathologic entities? An observational study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011; 69:1944–1951.
Article18. Gümgüm S, Hoşgören B. Clinical and radiographic behaviour of ameloblastoma in 4 cases. J Can Dent Assoc. 2005; 71:481–484.19. Avril L, Lombardi T, Ailianou A, Burkhardt K, Varoquaux A, Scolozzi P, et al. Radiolucent lesions of the mandible: a pattern-based approach to diagnosis. Insights Imaging. 2014; 5:85–101.
Article20. Chawla C, Rao PK, Kini R, Bhandarkar GP, Kashyap R, Holla V. Central giant cell granuloma - a case report. Am J Diagn Imaging. 2017; 2:17–20.21. Kamble KA, Guddad SS, Guddad SS, Lingappa A. Central giant cell granuloma: a case report with review of literature. J Indian Acad Oral Med Radiol. 2016; 28:98–101.
Article22. Gupta M, Gupta M, Singh S, Kaur R. Central giant cell granuloma of the maxilla. BMJ Case Rep. 2013; 2013:pii: bcr2013009102.
Article23. Baskaran P, Gopal M, Rastogi V, Misra SR. Aggressive central giant cell granuloma of the mandible, a diagnostic dilemma. J Oral Maxillofac Radiol. 2015; 3:88–91.
Article24. de Noronha Santos Netto J, Machado Cerri J, Miranda AM, Pires FR. Benign fibro-osseous lesions: clinicopathologic features from 143 cases diagnosed in an oral diagnosis setting. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2013; 115:e56–e65.25. Nityasri V, Haris PS, Bose T, Balan A. Fibrous dysplasia - a 13-year retrospective radiographic analysis in a south Indian population. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2011; 40:282–289.26. Macdonald-Jankowski DS, Li TK. Fibrous dysplasia in a Hong Kong community: the clinical and radiological features and outcomes of treatment. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2009; 38:63–72.
Article27. Petrikowski CG, Pharoah MJ, Lee L, Grace MG. Radiographic differentiation of osteogenic sarcoma, osteomyelitis and fibrous dysplasia of the jaws. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1995; 80:744–750.
Article28. Singer SR, Mupparapu M, Rinaggio J. Clinical and radiographic features of chronic monosotic fibrous dysplasia of the mandible. J Can Dent Assoc. 2004; 70:548–552.29. Harmon M, Arrigan M, Toner M, O'Keeffe SA. A radiological approach to benign and malignant lesions of the mandible. Clin Radiol. 2015; 70:335–350.
Article30. Giunta JL, Heffez L, Doku HC. Superior and buccal displacement of the mandibular canal in fibrous dysplasia. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1985; 43:460–462.
Article31. Goldberg MH, Sperling A. Gross displacement of the mandibular canal: a radiographic sign of benign fibro-osseous bone disease. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1981; 51:225–228.
Article32. Mortazavi H, Baharvand M, Rahmani S, Jafari S, Parvaei P. Radiolucent rim as a possible diagnostic aid for differentiating jaw lesions. Imaging Sci Dent. 2015; 45:253–261.
Article33. MacDonald-Jankowski DS. Cemento-ossifying fibromas in the jaws of Hong Kong Chinese. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 1998; 27:298–304.
Article34. MacDonald-Jankowski DS, Li TK. Ossifying fibroma in a Hong Kong community: the clinical and radiological features and outcomes of treatment. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2009; 38:514–523.
Article35. MacDonald-Jankowski DS. Ossifying fibroma: a systematic review. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2009; 38:495–513.
Article36. Fanibunda K, Reed MF. Cemento-ossifying fibroma of the mandible. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 1997; 26:246–248.
Article37. Saikrishna D, Shetty S, Ramya S. Massive ossifying fibroma of mandible. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2014; 4:81–84.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The study of evaluation to relationship between the inferior alveolar nerve and the mandibular third molar by using radiographic image
- Surgical Removal of Dental Implants Dislocated Into the Mandibular Body
- Preliminary study on histologic changes in the nerve and surrounding tissues after inferior alveolar nerve transposition in rabbits
- Avoidance of Injury to the Inferior Alveolar Nerve in Mandibular Angle Contouring; Maneuver of One Inch
- Diplopia after Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block Anesthesia: A Case Report